Definition of Chikungunya – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Definition of Chikungunya
Chikungunya
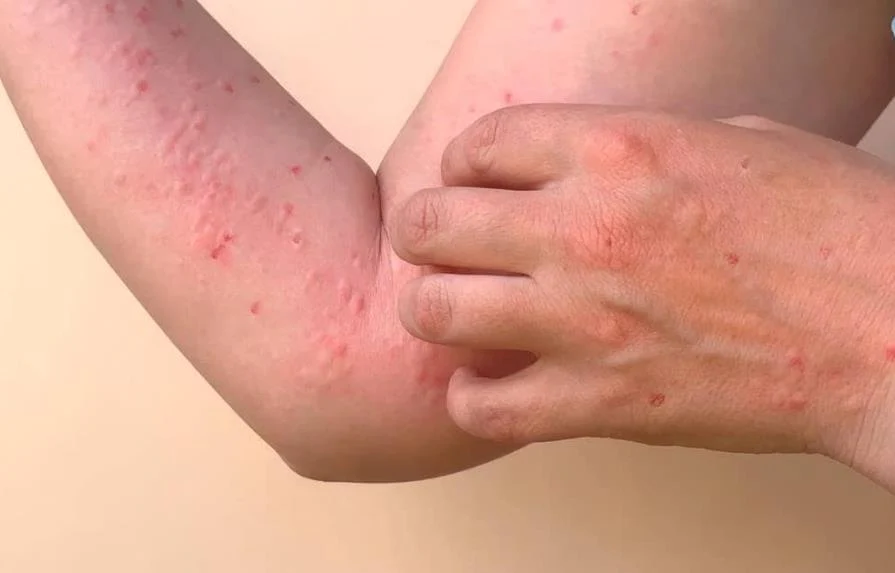
Chikungunya virus is transmitted to people by mosquitoes. The most common symptoms of chikungunya virus infection are fever and joint pain. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, or rash. Outbreaks have occurred in countries in Africa, Asia, Europe, and the Indian and Pacific Oceans. In late 2013, chikungunya virus was found for the first time in the Americas on islands in the Caribbean.
There is a risk that the virus will be imported to new areas by infected travelers. There is no vaccine to prevent or medicine to treat chikungunya virus infection. Travelers can protect themselves by preventing mosquito bites. When traveling to countries with chikungunya virus, use insect repellent, wear long sleeves and pants, and stay in places with air conditioning or that use window and door screens
Chikungunya:
Chikungunya is a viral disease (genus Alphavirus) which is transmitted to humans by infected mosquitoes including Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. The name chikungunya originates from a verb in the Kimakonde language, meaning ‘to become contorted. This refers to the ‘stooped appearance of those suffering with joint pain.
Or
Chikungunya is an infection caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV). Symptoms include fever and joint pain. These typically occur two to twelve days after exposure. Other symptoms may include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, and a rash.
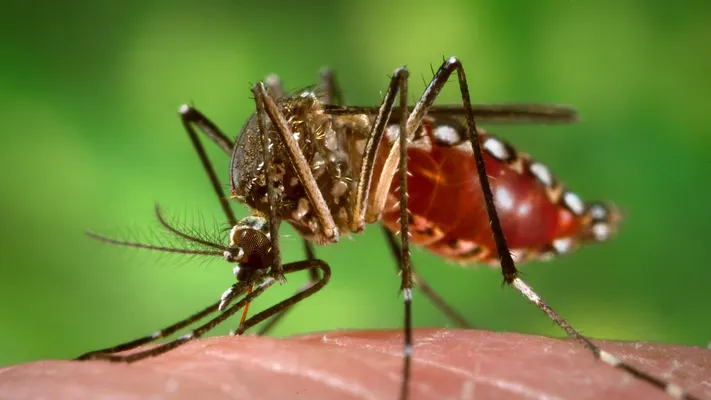

Symptoms
Symptoms appear between 4 and 7 days after the patient has been bitten by the infected mosquito and these include:
- High fever (40°C/ 104°F)
- Joint pain (lower back, ankle, knees, wrists or phalanges)
- Joint swelling
- Rash
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Nausea
- Fatigue
Diagnosis
➤ Only a blood test can definitively diagnose chikungunya as symptoms are not always easy to tell apart from other conditions.
➤ It is important to rule out dengue fever as quickly as possible because of its higher rate of mortality – up to 50 percent if untreated, compared with 0.1 percent Trusted Source for chikungunya.
➤If an individual with the symptoms outlined above has recently visited an area where either of these diseases are common, they should visit a doctor as soon as possible
Complications of Chikungunya:
➤ Uveitis-inflammation of the layer in the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer
composed of the sclera and cornea.
➤ Retinitis-inflammation of the retina.
➤ Myocarditis-inflammation of the heart muscle.
➤ Hepatitis-inflammation of the liver.
➤ Nephritis – inflammation of the kidneys.
➤ Hemorrhage – bleeding.
➤ Meningoencephalitis-inflammation of the membranes of the brain and adjoining cerebral tissue.
➤ Myelitis – inflammation of the spinal cord.
➤ Guillain-Barré syndrome – rare peripheral nervous system disease characterized by muscle weakness.
➤ Cranial nerve palsies – loss of function in the cranial nerves.
Prevention of Chikungunya:
➤ Mosquito control: the vectors of chikungunya breed in and around the house.
- Anti-larval measures:
✔ Environment control (source reduction): The environment should be cleaned up and got rid of water holding containers such as discarded tins, empty pots, and broken bottles and similar other artificial collection of water.
✔ Chemical control: Larviciding-termophos (abate) can be freely used in water collection
- Anti-adult measures: Residual sprays
- Protection against mosquito bites:
✔Use of Mosquito net
✔Use of Mosquito repellents (Diethyltolenamide)
➤ Notification: Occurrence of epidemics needs to be reported
➤ Appropriate treatment of chikungunya.

Another Answer:
Seeing as the major mode of chikungunya transmission is by mosquito bite, the best methods of prevention involve minimizing contact with mosquitos. Steps that can be taken to prevent chikungunya
include:
- Using insect repellent containing DEET (N, N-Diethyl-meta-toluamide) or picaridin on skin and clothing.
- Wearing clothing that covers the whole body.
- Staying indoors as much as possible, especially during early morning and late afternoon.
- Avoiding traveling to areas experiencing outbreaks.
- Using products containing oil of lemon eucalyptus or PMD (p-Menthane-3,8-diol) can be effective.
- Using air-conditioning – this deters mosquitos from entering rooms.
- Sleeping under a mosquito net.
- Using mosquito coils and insecticide vaporizers.
Although chikungunya is very rarely fatal, the symptoms are distressing and can be long-lived. Avoiding mosquitos is key.

Treatment of Chikungunya:
➤ There is no vaccine to prevent or medicine to treat chikungunya virus.
➤ Treat the symptoms:
- Get plenty of rest.
- Drink fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Take medicine such as acetaminophen or paracetamol to reduce fever and pain.
- Do not take aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS until dengue
- can be ruled out to reduce the risk of bleeding). If you are taking medicine for another medical condition, talk to your healthcare provider before taking additional medication.
➤ If patient have chikungunya, prevent mosquito bites for the first week of his/her illness.
- During the first week of infection, chikungunya virus can be found in the blood and passed from an infected person to a mosquito through mosquito bites.
- An infected mosquito can then spread the virus to other people.
Read more:
