Definition of Meiosis – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Definition of Meiosis
Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in the parent cell by half and produces four gamete cells. This process is required to produce egg and sperm cells for sexual reproduction
or
Meiosis is a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the cobM original amount of genetic information. These cells are our sex cells – sperm in males, eggs in om) females.
Phages/Stages of Meiosis:
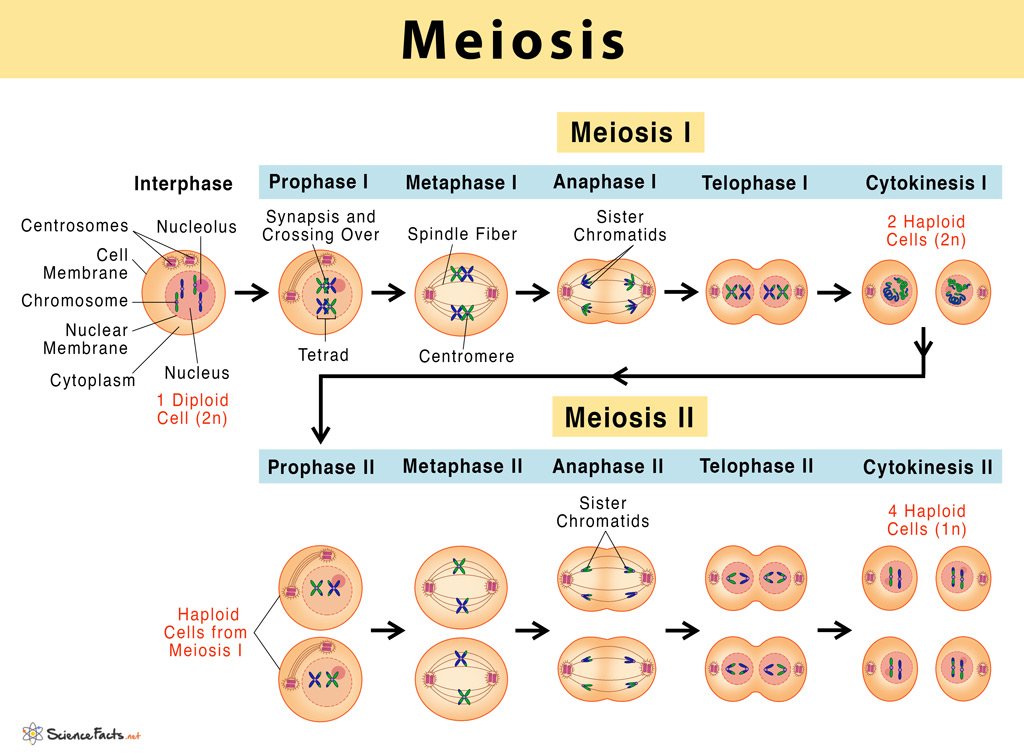
Figure 1.41: Phages/Stages of Meiosis
Meiosis can be divided into nine stages. These are divided between the first time the cell divides (meiosis I) and the second time it divides (meiosis II):
Meiosis I:
1. Interphase
2. Prophase I
3. Metaphase I
4. Anaphase I
5. Telophase I and cytokinesis
Meiosis II:
6. Prophase II
7. Metaphase II
8. Anaphase II
9. Telophase II and cytokinesis

Difference between Mitosis & Meiosis:
| S.N | Differences | Mitosis | Meiosis |
| 1 | Type of Reproduction | Asexual | Sexual |
| 2 | Genetically | Similar | Different |
| 3 | Crossing Over | No, crossing over cannot occur | Yes, mixing of chromosomes can occur, |
| 4 | Number of Divisions | One | TWO |
| 5 | Pairing of Homologs | No | Yes |
| 6 | Mother Cells | Can be either haploid or diploid | Always diploid |
| 7 | Number of Daughter Cells produced | 2 diploid cells | 4 haploid cells |
| 8 | Chromosome Number | Remains the same. | Reduced by half. |
| 9 | Chromosomes Pairing | Does Not Occur | Takes place during zygotene of prophase I and continue upto metaphase I. |
| 10 | Creates | Makes everything other than sex cells. | Sex cells only: female egg cells or male sperm cells. |
| 11 | Takes Place in | Somatic Cells | Germ Cells |

Read More….