Changes of State – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Changes of State
All matter can move from one state to another. It may require extreme temperatures or extreme pressures.
Melting
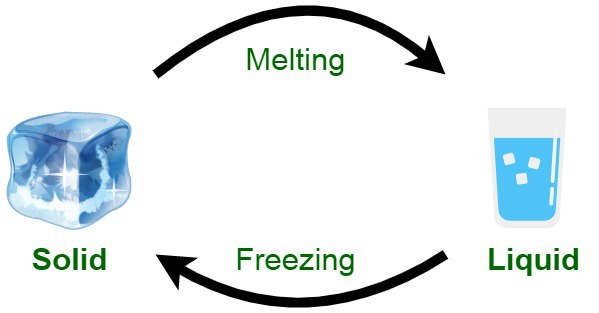
When a solid is heated, the particles are given more energy and start to vibrate faster. At a certain temperature, the particles vibrate so much that their ordered structure breaks down. At this point the solid melts into liquid. The temperature at which this change from solid to liquid happens is called the melting point. Each solid has a set melting point at normal air pressure. At lower air pressure, such as up a mountain, the melting point lowers
Freezing
Lava is liquid rock, which erupts through a volcano at temperatures as high as 1,500°C (2,732°F) through a volcano. However, the red-hot lava cools as it meets the Earth’s surface, and turns back into solid rock again. This change from liquid to solid is called freezing or solidifying. It is the opposite process to melting.
Boiling
When a liquid is heated, the particles are given more energy. They start to move faster and further apart. At a certain temperature, the particles break free of one another and the liquid turns to gas. This is the boiling point. The boiling point of a substance is always the same; it does not vary.

Invisible Steam
Water boils when it reaches its boiling point of 100°C (212°F). This is the temperature at which water turns to steam. Steam is an invisible gas. When it reaches the lid it cools back to a liquid.
Evaporation
Even without boiling water in a kettle, some of the liquid water changes to gas. This is evaporation. It occurs when a liquid turns into a gas far below its boiling point. There are always some particles in a liquid that have enough energy to break free from the rest to become a gas.
Condensation
Dewdrops are often found on a spider’s web early in the morning after a cold night. Water that is present as a gas in the air cools down and changes into tiny drops of liquid water on leaves and windows. This change from gas to liquid is called condensation.

Read More….