Compositions of Matter – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Compositions of Matter
Substances and Their Compositions
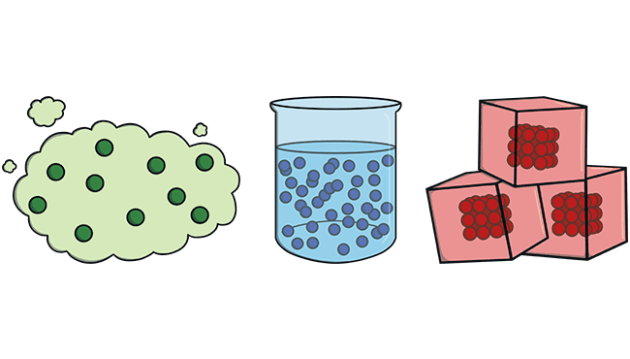
A property is any characteristic of something that can be identified and recognized by a person when it is seen again.
➤ Chemical property:-It is a property that, when observed, causes a substance to change into new substance, e.g., rusting of iron.
➤ Physical property:-A property that can be observed without changing the substance into something different is called physical property, e.g., colour, height, or mass of an object

Compositions of Matter:
The three kinds of matter are
1. Element,
2. Compound, and
3. Mixture.
A sample of matter is either a mixture or a pure substance.
- A. An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. Among the familiar elements are gold, silver, iron, aluminum, copper, sodium, and lead, as well as the oxygen and nitrogen in air. 99% of human body is made up of four elements oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, and carbon, The remainder 1% is made from 24 other elements including trace elements such as calcium and phosphorus are vitally important.
- B. A compound is a pure substance of two or more elements combined in a proportion by mass that is both definite and unique for the compound. A compound is represented by a chemical formula, which contains the symbols of the elements that form the compound, e.g., the elements carbon and oxygen react to form the compound carbon monoxide, CO. The properties of a compound are different from the properties of the elements that combine to form the compound. By certain techniques, a compound can be decomposed to its component elements, e.g., passing an electric current through water, H₂O liberates the elements hydrogen and oxygen.
- C. A mixture consists of two or more pure substances that are present in variable amounts. Air is a mixture whose composition varies, depending on location; Orange juice that consists of water, Vitamin C, fruit sugar, and citric acid.

Read More….