Definition of Emphysema – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
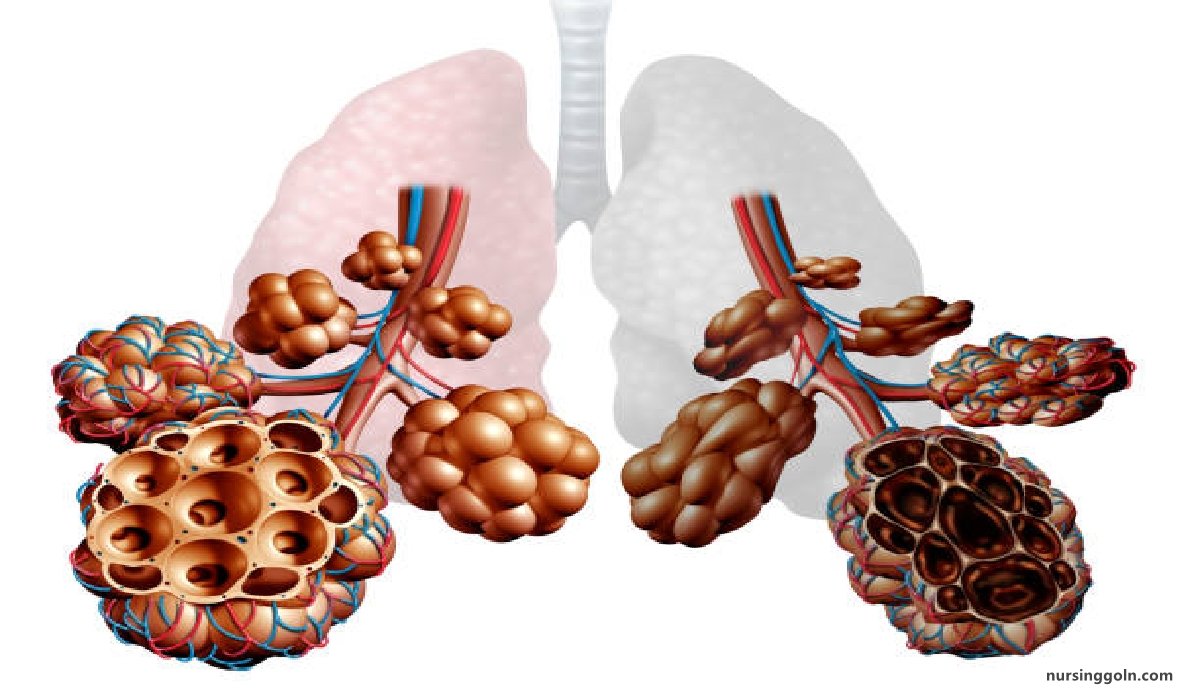
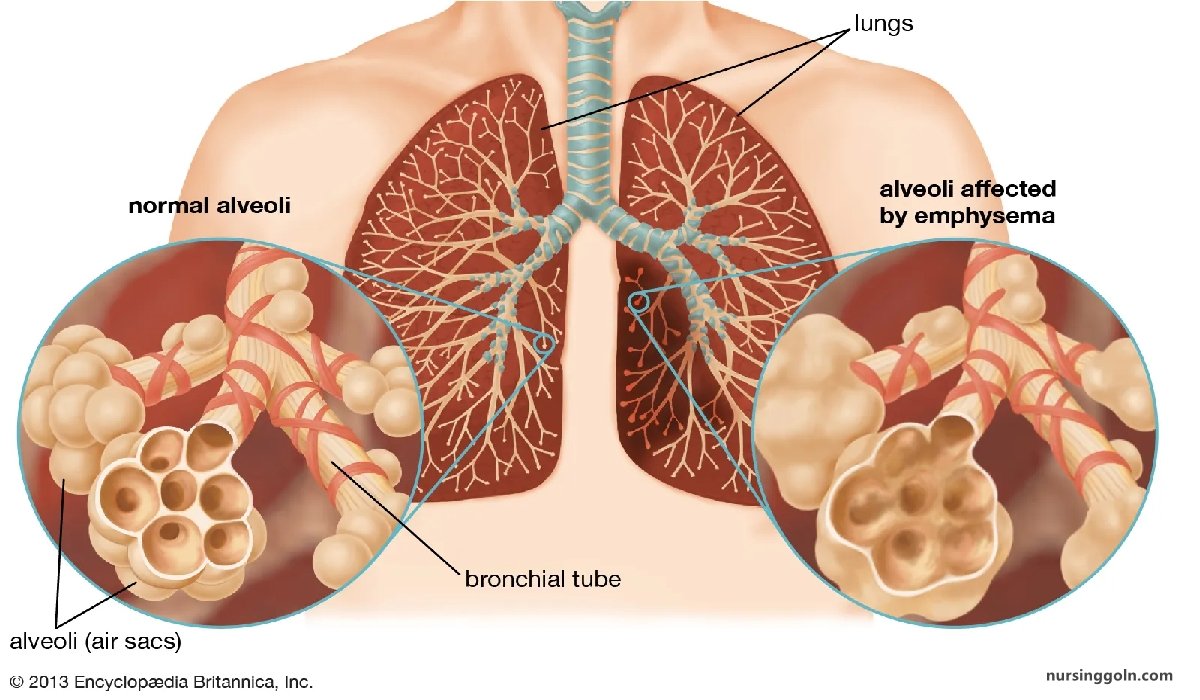
Definition of Emphysema
Emphysema
It is the “permanent distension of alveoli with destruction of their walls distal to terminal bronchioles.
Or,
Emphysema is defined as abnormal distension of the air spaces beyond the terminal bronchioles with destruction of walls of the alveoli.
Types of Emphysema
1. Centriacinar– involves proximal part of acini, limited to respiratory bronchiole with relatively less change in acinus.
2. Panacinar– all the alveoli and alveolar ducts in acinus are involved, both central and peripheral portion. It occurs mostly in (antitrypsin deficiency).
3. Paraseptal-along the septa, blood vessels and pleura.
4. Scar or irregular emphysema– Scaring and damage affecting lung parenchyma without involving acinus structure.
(Ref by- Kumar & Clark clinical Medicine /7 +Harrison’s internal medicine/17)
Diagnosis
Clinical feature
Patient profile
- Elderly (over 40 yrs.)- Smoker.
- Younger-nonsmoker (1 antitrypsin deficiency).
Symptoms
- Exertional dyspnoea( main feature)
- Minimum cough & sputum production
- Intermittent fever
- Weight loss
- Symptoms of associated chronic bronchitis may be present – wheeze, cough.
Sign
General exam:
Appearance-ill looking, pursed lip breathing
Decubitus – patient adopts propped up position fixing the shoulder girdles to assist to accessory muscles of respiratio
Respiratory system
Inspection
- Patient is dyspnoeic, pursed lip breathing
- Respiratory rate is increased
- Barrel shaped chest
- Accessory muscles of respiration in action
- Supra-sternal and supra-clavicular excavation
Palpation
- Trachea is central
- Tracheal tug present
- Crico-sternal distance deceased
- Total lung expansibility – reduced
- Apex beat-may not be palpable
- Vocal fremitus reduced on both sides
Percussion
- Percussion note – may be hyper resonant on both lung fields
- Upper border of liver dullness – obliterated.
- Cardiac dullness obliterated.
Auscultation
- Breath sound-vesicular with prolonged expiration.
- Added sound-few rhonchi (if associated with chronic bronchitis)
Investigation
- X-ray chest
•Bullae is pathognomic
•Hyper-translucency of both lung fields and loss of peripheral vascular markings.
•Prominent pulmonary arterial shadow in both hilum.
•Low flat diaphragm
•Tubular heart
•Widening of intercostal space and ribs appear horizontal.
- Lung function test
•PEFR: Reduced.
•Lung volume: Increased.
- Arterial blood gas analysis
•Raised PaCO2
•Fall Pa02
- Blood count-To exclude anaemia or document polycythaemia.
- Blood culture – To exclude pneumonia.
- High resolution CT
- Low voltage ECG with poor progression of R-wave from VI to V6
- ECG:
- Tall P wave & feature of RVH if corpulmonale develops.
Treatment
- Smoking cessation
- Bronchodilators inhaled route is preferable
•Salbutamol
•Ipratropium bromide
•Theophylline
- Corticosteroids: Reduce frequency and severity of exacerbation’s (2 or more exaerbations
- Pulmonary rehabilitation-Exercise
- 02 therapy: Long term domiciliary O: therapy
- Surgery-Surgical ablation of bullae
- Other measures:
•Antibiotic for Rx of RTI
•Vaccination of influenza & pneumococcus.
•Proper nutrition.
•Obesity, social isolation should be identify and if possible, improved,
•Mucolytic therapy (acetylcysteine 200 mg orally 8 hrly for 8 weeks.
(Ref by- Kumar & Clark clinical Medicine / +Harrison’s internal medicine/17″)
Nice to Know:
Difference between Emphysema and Chronic Bronchitis
| Topics | Emphysema/Pink puffer | Chronic bronchitis Blue bloater |
| History/General examinati | on | |
| Age | >50 years | 30-40 years |
| Chief complaints | Infrequent dyspnoea | Productive cough- |
| Body built | Thin Pink puffer Pursed lip respiration | Overweight Blue bloater |
| Cyanosis | Absent | Present |
| Oedema | Absent | Present |
| Tender hepatomegaly | Absent | Present |
| On examination of respiratory | system | |
| Inspection | Barrel shaped chest Cricosternal distance reduced Tracheal tag is present | Normal shape |
| Palpation | Chest expansion reduced Apex beat cannot be felt | Chest expansion reduced Apex beat cannot be felt |
| Percussion | Hyperresonant | Resonant |
| Diminished breath sound Vesicular with prolonged expiration. No added sound | Vesicular with prolonged expiration Creps & rhonchi present | |
| Arterial blood gas analysis | Arterial PO, & PCO₂ are relatively normal | Arterial blood raised PaCO, & fall Pao |
