Definition of Bronchiectasis – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
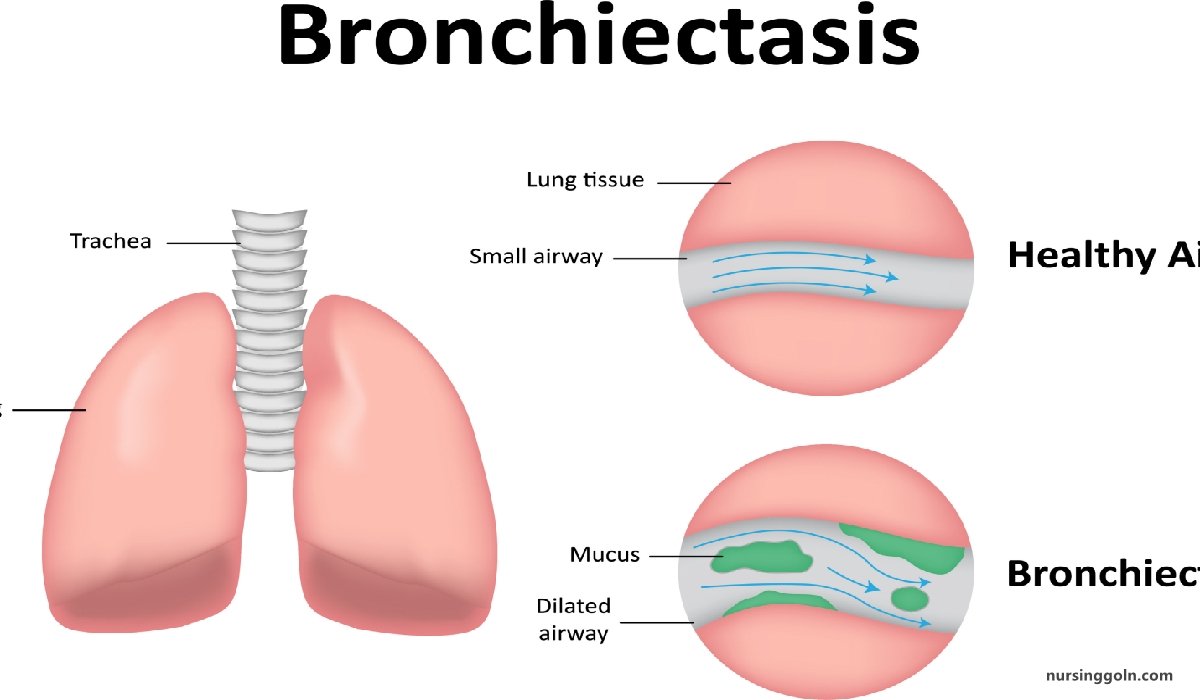
Definition of Bronchiectasis
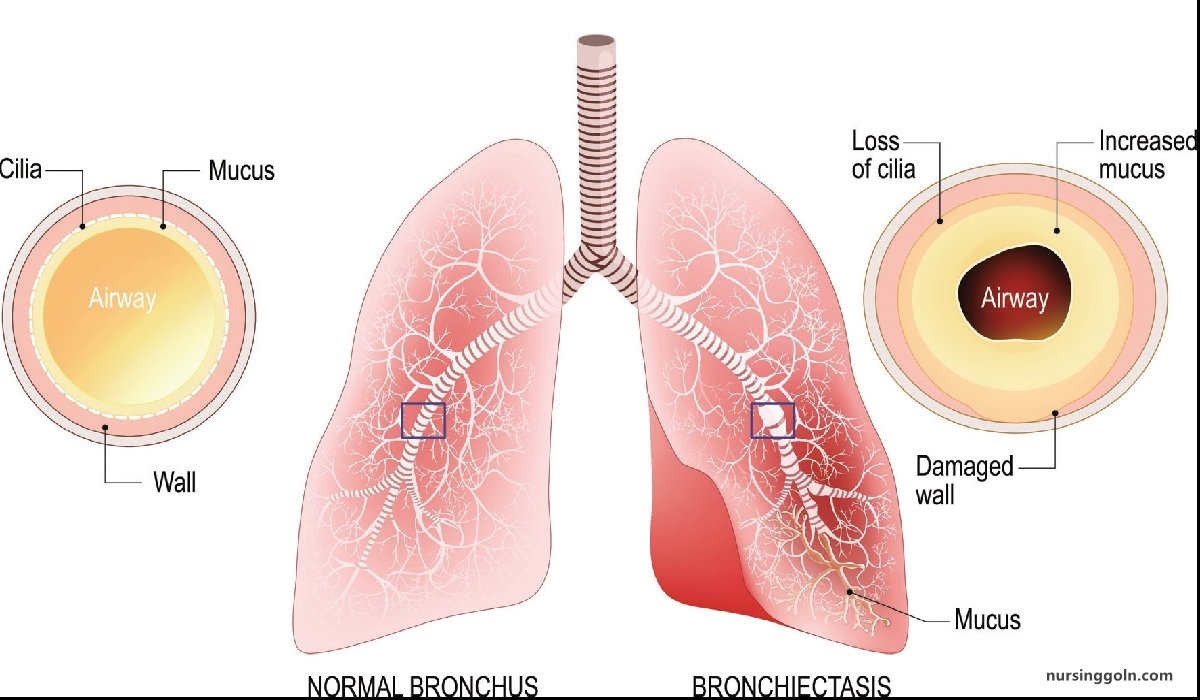
It is the abnormal, permanent dilatation of one or more bronchi with destruction of bronchial wall proximal to the terminal bronchiole.
Types of Bronchiectasis:
1. Saccular or cystic.
2. Cylindrical
3. Fusiform
Pathology:
- Inflammation of bronchus & surrounding tissue.
- Destruction
- Dilatation
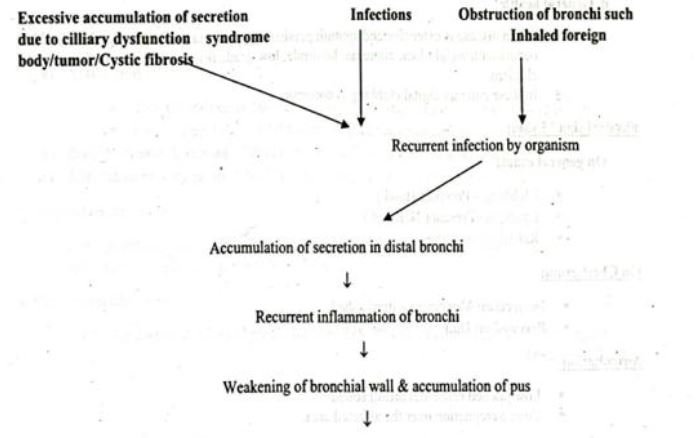
Pathogenesis of Bronchiectasis:
 Dilatation of bronchi
Dilatation of bronchi
↓
Bronchiectasis
Management of Bronchiectasis:
Clinical feature of Bronchiectasis
a. Due to accumulation of pus in dilated bronchi:
- Chronic productive cough usually worse in mornings and often brought on by changes of posture.
- Sputum often copious and persistently purulent in advanced disease.
- Halitosis is a common accompanying feature
b. Due to inflammatory changes in lung and pleura surrounding dilated bronchi
- Fever, malaise and increased cough and sputum volume when spread of infection causes pneumonia, which may be associated with pleurisy.
- Recurrent pleurisy in the same site often occurs in bronchiectasis
c. Haemoptysis
- Can be slight or massive and is often recurrent. Usually associated with purulent sputum or an increase in sputum purulence.
- Can, however, be the only symptom in so-called ‘dry bronchiectasis’ (Cough with Haemoptysis)
d. General health
- When disease is extensive and sputum persistently purulent a decline in general health occurs with weight loss, anorexia, lassitude, low-grade fever, and failure to thrive in children.
- In these patients digital clubbing is common
Physical sign/Exam:
On general exam:
- Clubbing-Present (Hand)
- Cyanosis-Present (Nail bed)
- Raised temperature
On Chest exam:
- Inspection: Movement – diminished
- Auscultation:
Percussion: Dull
- Low pitched bronchial breath sound
- Coarse crepitation over the affected area.
Investigation of Bronchiectasis:
i. Chest X-ray: Multiple ring shadow (honey comb appearance) usually occupy lower zone of lung field. Some of the spaces may contain gas & fluid level
ii. Blood count:
- Neutrophilic leucocytosis
- ESR: Increased
- Anemia: rare
iii. Sputum for Gram staining and C/S and AFB
iv. HRCT scan (Confirmatory)
v. Assessment of ciliary function
vi. Serum immunoglobulin & sweat electrolyte for cystic fibrosis.
vii. Others:
- X-ray PNS
- Lung function test
Treatment of Bronchiectasis:
1. Postural drainage:
a) Percussion over chest wall with cupped hands aids dislodgment of sputum
b) Deep breathing followed by forced expiratory manoeuvers are helpful in augmenting the expectoration of sputum
c) It is done for 5-10 minutes once or twice daily is minimum for most patients.
2. Medical treatment:
a) Antibiotics:
- Tab. Ciprofloxacin 500 mg twice daily for staphylococcus or Gram – ve bacilli.
- Ceftazidime 1-2 gm IV 8 hourly for pseudomonas aeruginosa.
b) Bronchodilator & steroid: Useful in patient with demonstrable airflow limitation.
c) Anti-inflammatory agent: NSAIDs can decrease the rate of progression.
3. Surgical treatment:
a) Partial pneumonectomy: if it is localized to a single lobe/segment (without COPD)
b) Heart-lung transplantation: if it is bilateral & severe.
4. Chest physiotherapy
(Ref by- Kumar & Clark clinical Medicine/819/8+ Short case Abdullah Sir 5th +Davidson’s Medicine 579/23)
Causes/Etiology of Bronchiectasis:
Congenital
- Cystic fibrosis
- Ciliary dysfunction syndromes
✔ Primary ciliary dyskinesia (immotile cilia syndrome)
✔Kartagener’s syndrome (sinusitis and transposition of the viscera)
- Primary hypogammaglobulinaemia
Acquired-children
- Pneumonia (complicating whooping cough or measles)
- Primary TB
- Inhaled foreign body
Acquired-adults
- Suppurative pneumonia
- Pulmonary TB
- Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis complicating asthma.
- Bronchial tumours
(Ref by- Kumar & Clark clinical Medicine/819/8+ Short case Abdullah Sir 5 +Davidson’s Medicine 579/23)
Difference between Bronchiectasis & Lung Abscess.
| Traits | Bronchiectasis | Lung abscess |
| Definition | It is the abnormal, permanent dilatation of one or more bronchi with destruction of bronchial wall proximal to the terminal bronchiole | A large localized collection of pus, or a cavity lined by chronic inflammatory tissue, from which pus has escaped by rupture into a bronchus. |
| Site | Usually bilateral & extensive area is involved | Usually unilateral & localized |
| Disease course | Chronic process | Usually acute process, may be chronic |
| Examination | Coarse crepitation over the affected | Feature of consolidation, & coarse crepitation when bursts & in resolution phase |
| Radiological findings | Ring shaped honey comb appearance (Cystic bronchiectatic) | Cavitary lesion with an air fluid level. |
| Lung function impairment | More | Less |
| Associated diseases | Cystic fibrosis, Pneumonia & tuberculosis | Upper or lower respiratory tract infections |
| Pleural rub | Absent | Present |
Difference pulmonary TB & bronchiectasis
| Traits | Bronchiectasis | Pulmonary TB |
| Definition | It is the abnormal, permanent dilatation of one or more bronchi with destruction of bronchial wall proximal to the terminal bronchiole | Infection of lung parenchyma by M. Tuberculosis formation of classical tubercuous granuloma with central necrosis |
| Night sweating & evening rise of temperature | It is the abnormal, permanent dilatation of one or more bronchi with destruction of bronchial wall proximal to the terminal bronchiole | Usually present |
| Site | Usually not present | Usually unilateral & localized & may be bilateral |
| Disease course | Usually bilateral & extensive area is involved | Acute process, may be chronic |
| Examination | Chronic process & it may results of long standing Pulmonary TB. | Feature of consolidation, cavitation & collapse & pleural effusion |
| Radiological findings | Digital clubbing Coarse crepitation over the affected | Patchy opacity & Radiological feature of consolidation, cavitation & collapse & pleural effusion. |
| Lung function impairment | Ring shaped honey comb appearance (Cystic bronchiectasis) | Less |
| Associated diseases | Cystic fibrosis, Pneumonia & tuberculosis | Immunosuppression, malignancy,DM malnutrition & CKD |
| Spontaneous cure | Absent | Present |
| Diagnosis confirmed by- | HRCT | Identification of tubercle bacilli by microscopy or culture or PCR |
| Anti-TB therapy | Not response | Response |