Types of Chemical Reactions – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Types of Chemical Reactions
There are four major types of chemical reactions
1. Combination or synthesis reactions
2. Decomposition reactions
3. Substitution or single replacement reactions
4. Metathesis or double displacement reactions
The entire process can be graphically represented by this diagram.
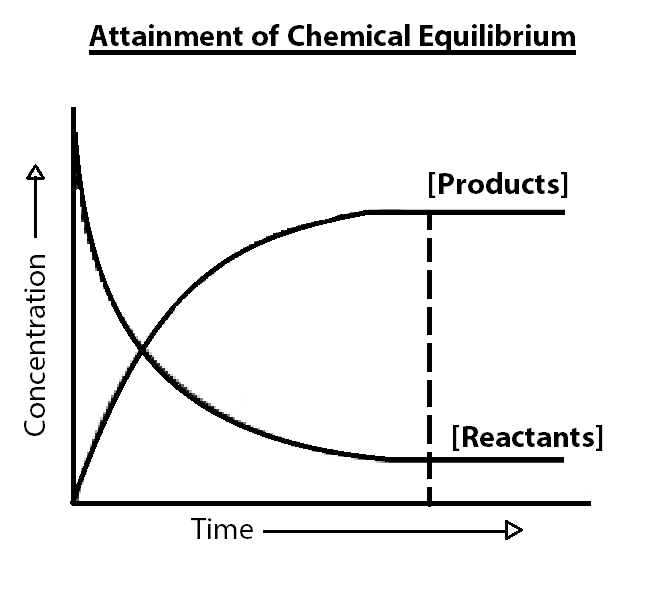
Types of Chemical Equilibrium
There are two types of chemical equilibrium:
1. Homogeneous equilibrium
2. Heterogeneous equilibrium
Homogeneous Equilibrium:
The equilibrium reactions in which all the reactants and the products are in the same phase are known as homogeneous equilibrium reactions. These are divided into two categories:
The number of product molecules is equal to the number of reactant molecules. For example:
- N2 (g) + O2 (g) 2NO (g)
- H2 (g) 12 2HI (g)

Heterogeneous Equilibrium
The equilibrium reactions in which the reactants and the products are present in different phases are known as Heterogeneous equilibrium reactions. For Example:
The dissociation of solid calcium carbonate to give solid calcium oxide and gaseous carbon dioxide:
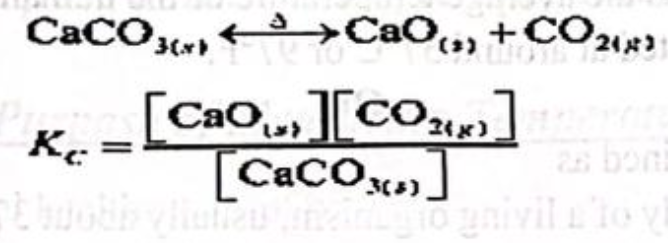
Here as CaO and CaCO3 are pure solids, [CaO] and [CaCO3] are constants.
Important Features of the Equilibrium Constant
- Applicable only in equilibrium state
- Independent of initial concentration of reactants and products
- Depends on temperature; has a unique value for a reaction at a given temperature
- The equilibrium constant for the forward direction is the inverse of the Equilibrium constant for the reverse direction.
- The equilibrium constant for a reaction is related to the equilibrium constant of the corresponding reaction whose equation is obtained by multiplying or dividing the equation for the original reaction by a small integer.
Read More….
