Changes in Body Temperature – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Changes in Body Temperature
Definition of Temperature:
A temperature is an objective comparative measurement of hot or cold. It is measured by a thermometer. Several units exist for measuring temperature, the most common being Celsius (denoted °C; formerly called centigrade), Fahrenheit (denoted °F)
(Ref by- en.wikipedia.org)
Definition of Body Temperature:
The degree of hotness and coldness of the body is called temperature
Normal body temperature:
Range : 97°F-99°F
: 36.0°C-37.5°C
Average: 98.6°F or 37°C
(Ref by-Dr. Ranzu/A guide to physiology and biochemistry, Reflex/15th/15.1)
Or,
Body temperature is defined as the average temperature of the human body. In humans, this average temperature is estimated at around 37°C or 97°F.
Or,
Body temperature may be defined as “The degree of heat in the body of a living organism, usually about 37.0°C (98.6°F) in humans”.
Or,
Body temperature refers to the warmth of the human body. Body heat is produced primarily by exercise and metabolism of food.

Types of Body Temperature:
1. Core temperature.
2. Shell (Skin) temperature.
Skin Temperature:
The temperature that rises and falls with the temperature of the surroundings is called skin temperature. The skin temperature increases during exercise and varies with the temperature of the surroundings. When excessive heat is produced in the body by vigorous exercise, the temperature can rise to as high as 101° to 104° F. Conversely, when the body is exposed to extreme cold, the temperature can fall below 96° F.
Core Temperature:
The temperature of the deep tissues of the body is called core temperature. It remains very constant, within ±1°F (±0.6°C) except when a person develops a febrile illness.
Normal core temperature:
- Oral temperature:
✓ Average: 37 °C or 98.6°F
✓ Range: 36.3-37.1°C or, 97.3-98.8°F - Rectal temperature is 0.5 °C higher than oral temperature.
- Scrotal temperature: 32 °C
- Axillary temperature is 0.5 °C less than oral temp.
Normal Range of Temperature:
| Range | Average |
| 97°-99°F/36°C-37°C | 98.6°F or 37°C |
Purpose of Measuring Temperature:
1. To assess the general health status of patient
2. To assess for any alteration in health status
3. To aid in determining patient’s condition
4. To recognize any variation from the normal and its significance
5. To assist in diagnosis
6. To help doctor to prescribe correct treatment and to note the effect of the treatment
Indications of Measuring Body Temperature:
1. Routine part of assessment on admission for establishing a base-line data.
2. As per agency policy to monitor any change in patients condition.
3. Before, during and after administration of any drug that affects temperature control function.
4. When general condition of patients change.
5. Before and after any nursing intervention that affects temperature of the patient.
Contraindication of Measuring Body Temperature:
A. Oral method:
a) Patient who are not able to hold thermometer in their mouth.
b) Patient who may bite the thermometer like psychiatric patient
c) Infants and small children
d) Surgery or infection in oral cavity
e) Trauma to face or mouth
f) Mouth breathers
g) Patients with history of convulsion
h) Unconsciousness/semi-conscious/ disoriented patients.
i) Patients having chills
j) Un co-operative patient
k) Patients who cannot follow instruction
B. Rectal method
a) Patients after rectal surgery
b) Any rectal pathology
c) Patients having difficulty in assuming position.
d) Acute cardiac position
e) Patients having diarrhea
f) Reduced platelet count
C. Axillary method
a) Any surgery or lesion in axilla.
Common Site of Recording Body Temperature:
1. Mouth or oral cavity under the tongue (98.6°F or 37°C)
2. The axillary (97.6°F or 36.4°C)
3. The rectum (99.5°F or 37.5°C)
4. The groin and Ear/Tympanic membrane (98.6°F or 37.0°C)
5. Skin/ Forehead. (94. 0°F or 34.4°C)
Normal Body Temperature:
A thermometer is placed in the patient’s mouth to obtain an oral temperature, in the anal canal to obtain a rectal temperature, and in an axilla (armpit) to obtain an axillary temperature. Table – 1 shows the average normal temperature for well adults at these various body sites.
| ORAL | RECTAL | AXILLARY |
| 98.6° F | 99.5° F | 97.7° F |
| 37.0° C | 37.5° C | 36.5° C |
Table: Average, normal temperatures for well adults.
Temperature is measured on the Fahrenheit (F) or the Celsius (C) scale. The average, normal, oral temperature for an adult is 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit or 37.0 degrees Celsius (old term: centigrade)
Conversion Formula from Celsius to Fahrenheit:
The temperature T in degrees Fahrenheit (°F) is equal to the temperature T’ in degrees Celsius (°C) times 9/5 plus 32:
T(°F) = (T(°C) × 9/5) + 32
or
T(°F) = T(°C) × 1.8 +32
Example
Convert 20 degrees Celsius to degrees Fahrenheit:
T(°F) = (20°C × 9/5) +32
T(°F) = 68°F
Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion table
| Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) |
| 10°C | 50.0 °F |
| 20°C | 68.0°F |
| 30°C | 86.0 F |
| 40 °C | 104.0 °F |
| 50 °C | 122.0 °F |
| 60 °C | 140.0 °F |
| 70 °C | 158.0 °F |
| 80 °C | 176.0 °F |
| 90 °C | 194.0 °F |
| 100 °C | 212.0°F |
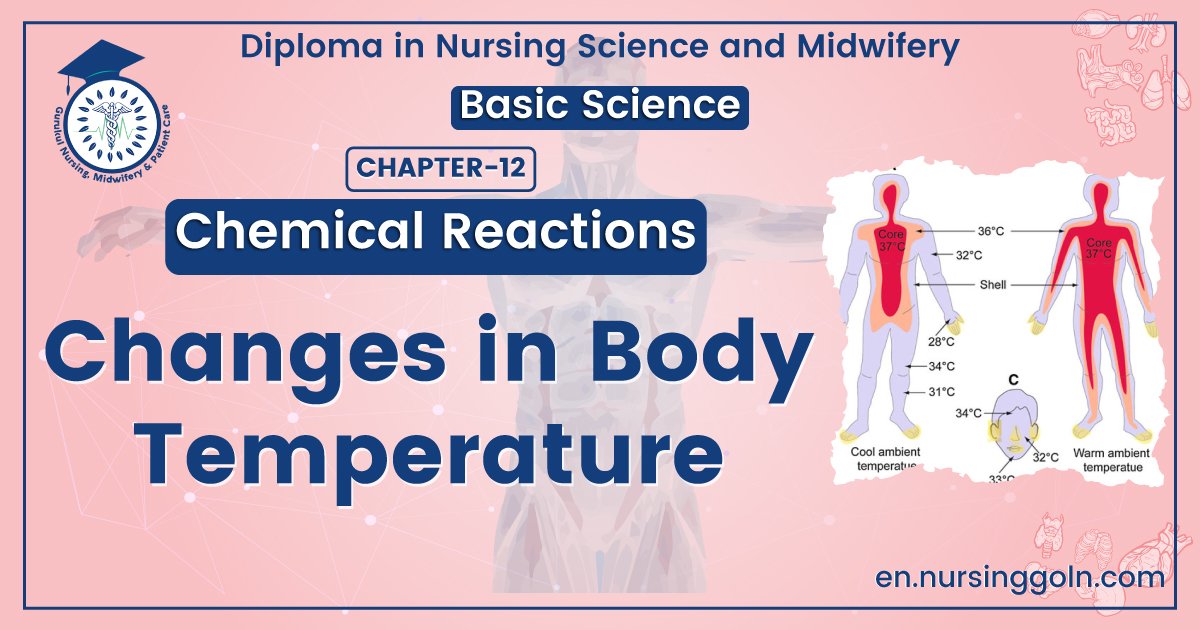
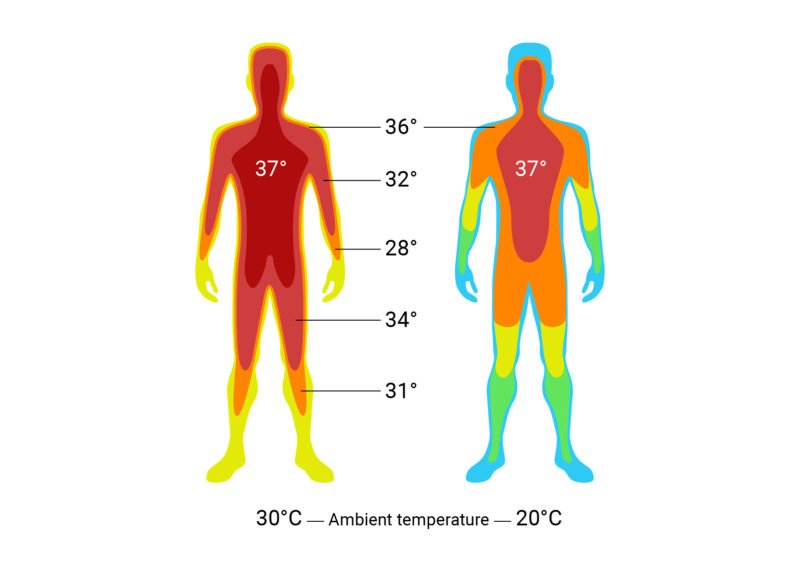
Core temperature
The temperature of the deep tissues of the body is called core temperature.
Normal value: About 37°C or 98.6°F.

Shell temperature:
The temperature that rises and falls with the temperature of the surroundings is called shell70 temperature.
[NOTE: Skin and subcutaneous tissues constitutes the ‘shell’, whereas all other internal structures (covered by the shell) are called ‘core’. When one speaks of the body temperature, he means the core temperature (not the shell temperature). Strictly speaking, ‘core temperature’ is the temperature of blood coming from the heart.]
Difference between core and shell temperature:
| Core temperature | Shell temperature |
| 1. Remains almost constant. | 1. Rises and falls with the temperature of the surroundings. |
| 2. Measured at the Mouth and Rectum. | 2. Measured in the axilla and groin. |
| 3. It is more than shell temperature. | 3. It is less than core temperature. |
| 4. More accurate | 4. Less accurate. |

Read More….