Lung Abscess – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Lung Abscess
Definition of Suppurative Pneumonia:
It is the term used to describe a form of pneumonic consolidation in which there is destruction of the lung parenchyma by the inflammatory process.
Definition of Lung abscess:
A large localized collection of pus, or a cavity lined by chronic inflammatory tissue, from which pus has escaped by rupture into a bronchus.
Organisms responsible for Lung abscess:
Streptococcus pneumonae
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pyogens
- Haemophyllus influenzae
- Klebsiella pneumoniae.
- Aspiration pneumonia:
Suppurative pneumonia and pulmonary abscess develop after the inhalation of septic material during operations on the nose, mouth or throat under general anaesthesia, or of vomitus during anaesthesia or
coma.
(Ref by- Kumar & Clark clinical Medicine/819/8+ Short case Abdullah Sir 5th +Davidson’s Medicine 579/23)
Management of Lung Abscess:
C/F of Lung Abscess:
Symptoms:
- Cough productive of large amounts of sputum which is sometimes fetid and blood-stained
- Pleural pain common
- Sudden expectoration of copious amounts of foul sputum occurs if abscess
- ruptures into a bronchus
Clinical signs:
- High remittent pyrexia
- Profound systemic upset: malaise, weakness, loss of wt. et c
- Digital clubbing may develop quickly (10-14 days)
- Chest examination usually reveals signs of consolidation:
✓ Inspection: Chest movement is restricted on the affected side.
✓ Palpation:
o Trachea is central.
o Vocal fremitus: increased.
✓ Percussion: Percussion note: Dull.
✓ Auscultation:
o Breath sound: may be bronchial.
o Increased vocal resonance.
- Pleural rub common
- Rapid deterioration in general health with marked weight loss
Investigations of Lung Abscess:
- Blood count:
✔ Polymorphonuclear leukocytosis
✔ ESR: Raised
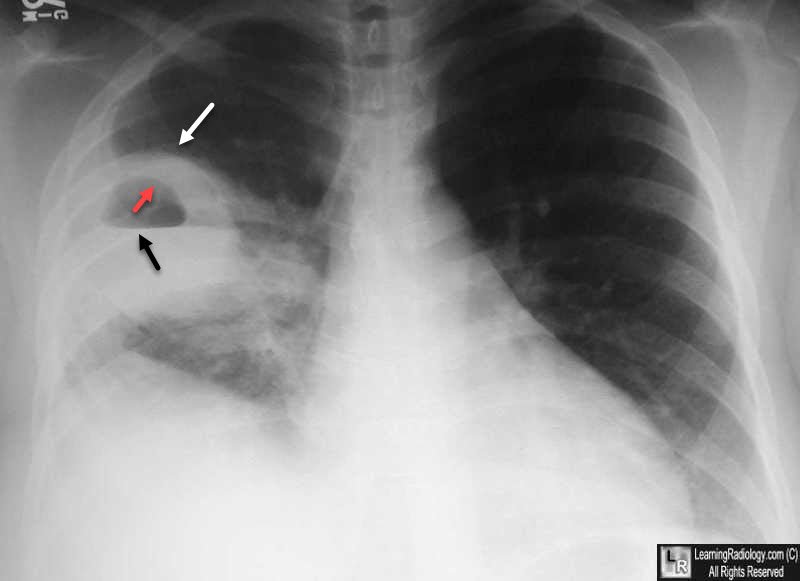
- X-ray chest (P/A view): Showing a well circumscribed area of dense opacity with cavitation & air fluid level.
- Sputum: Gram staining & C/S
- Bronchoscopy.
- CT or MRI.
Treatment Lung Abscess:
1. Ideally antibiotic treatment should start according to C/S.
- Amoxycillin (500 mg)-8 hourly for 4-6 wks.
- Tab. Metronidazole (400 mg) – 8 hourly for 4-6 wks.
If Pt. respond-continue the treatment. If there is no response antibiotic according to C/S.
2. Physiotherapy: Postural drainage.
Nursing Management of Lung Abscess:
- Monitor patient’s temperature (degree and pattern) as there may be increased body temperature; note shivering/diaphoresis
- Monitor the temperature of the environment. Give a warm compress and teach and encourage family
- Review/monitor respiratory frequency, record the ratio of inspiration and expiration
- Auscultate breath sounds and note the existence of bronchial breath sounds
- Assist the patient to a comfortable position
- Perform adequate drainage thru postural drainage aided by percussion, effective coughing and breathing exercises.
- Observe the characteristic of cough
- Provide fluid intake of 3000 ml/day according to tolerance and provide a warm heart and fluid intake between meals instead of
- Give the drugs as ordered (antipyretics, bronchodilators, antibiotics)
- Teach and encourage chest physiotherapy, postural drainage
- Drainage bronchoscopy may be ordered to aid in drainage of abscess.
- Ensure proper nutritional intake. Provide high calorie, high protein diet since chronic infection is associated with a catabolic state