Concept about Body Mechanics – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Concept about Body Mechanics
Definition of Body Mechanics
Body mechanics is defined as “the study of proper body movement to prevent and correct posture problems, reduce stress and enhance physical capabilities,”
or
Body mechanics involves the coordinated effort of muscles, bones, and the nervous system to maintain balance, posture, and alignment during moving, transferring, and positioning patients. Proper body mechanics allows individuals to carry out activities without excessive use of energy, and helps prevent injuries for patients and health care providers

Elements of Body Mechanics
Body movement requires coordinated muscle activity and neurological integration. It involves the basic elements of body alignment (posture), balance, and coordinated movement. Body alignment and posture bring body parts into position to promote optimal balance and body function. When the body is well aligned, whether standing, sitting, or lying, the strain on the joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments is minimized.
Body alignment is achieved by placing one body part in line with another body part in a vertical or horizontal line. Correct alignment contributes to body balance and decreases strain on muscle- skeletal structures. Without this balance, the risk of falls and injuries increase. In the language of body mechanics, the centre of gravity is the centre of the weight of an object or person. A lower centre of gravity increases stability.
This can be achieved by bending the knees and bringing the centre of gravity closer to the base of support, keeping the back straight. A wide base of support is the foundation for stability. A wide base of support is achieved by placing feet a comfortable, shoulder width distance apart. When a vertical line falls from the centre of gravity through the wide base of support, body balance is achieved. If the vertical line moves outside the base of support, the body will lose balance.
The diagram in Figure demonstrates
A. A well-aligned person whose balance is maintained and whose line of gravity falls within the base of support.
B. Demonstrates how balance is not maintained when the line of gravity falls outside the base of support, and diagram
C. Shows how balance is regained when the line of gravity falls within the base of support.
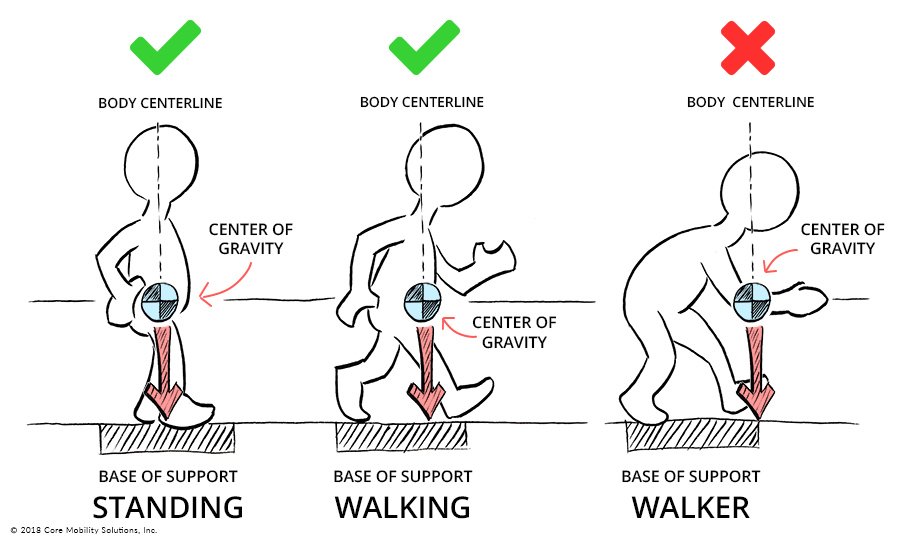
Figure: Centre of gravity
Principles of Body Mechanics
Principles of body mechanics that should be applied during all patient-handling activities.
| Principles of Body Mechanics | |
| Action | Principle |
| Assess the environment. |
|
| Plan the move |
|
| Avoid stretching and twisting |
|
| Ensure proper body stance. |
|
| Stand close to the object being moved. |
|
| Face direction of the movement. |
|
| Avoid lifting. |
|
| Work at waist level. |
|
| Reduce friction between surfaces. |
|
| Bend the knees. |
|
| Push the object rather than pull it, and maintain continuous movement. |
|
| Use assistive devices. |
|
| Work with others. |
|

Read More….
