Otitis Media – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Otitis Media
Otitis Media:
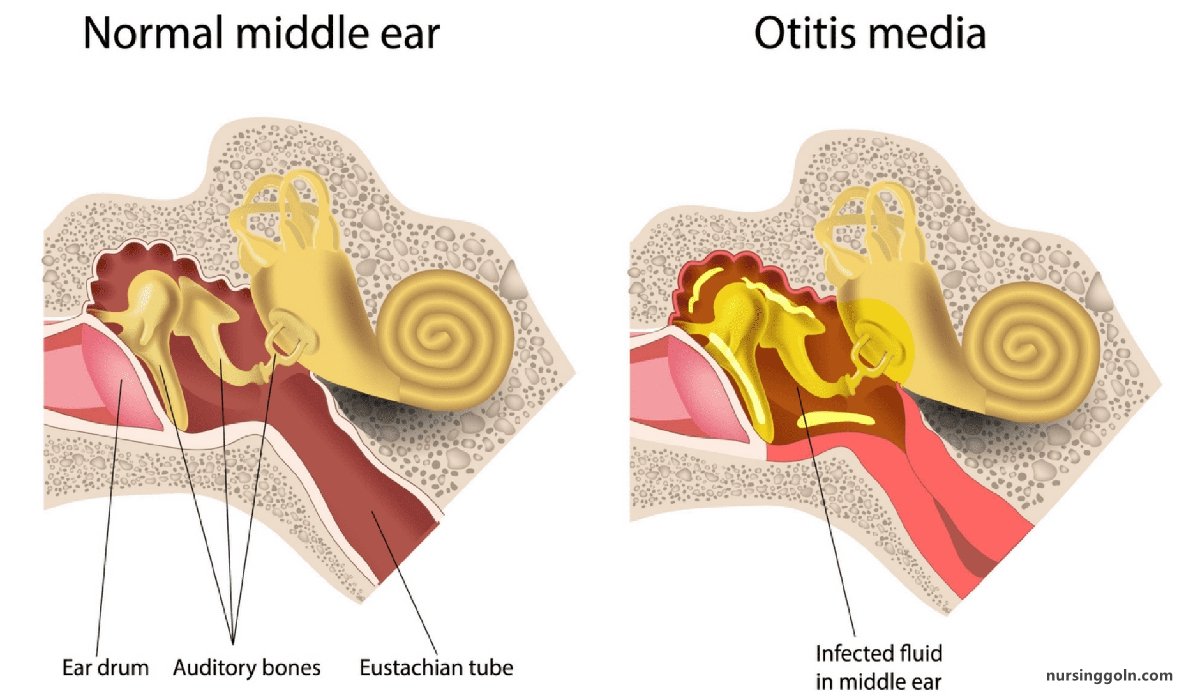
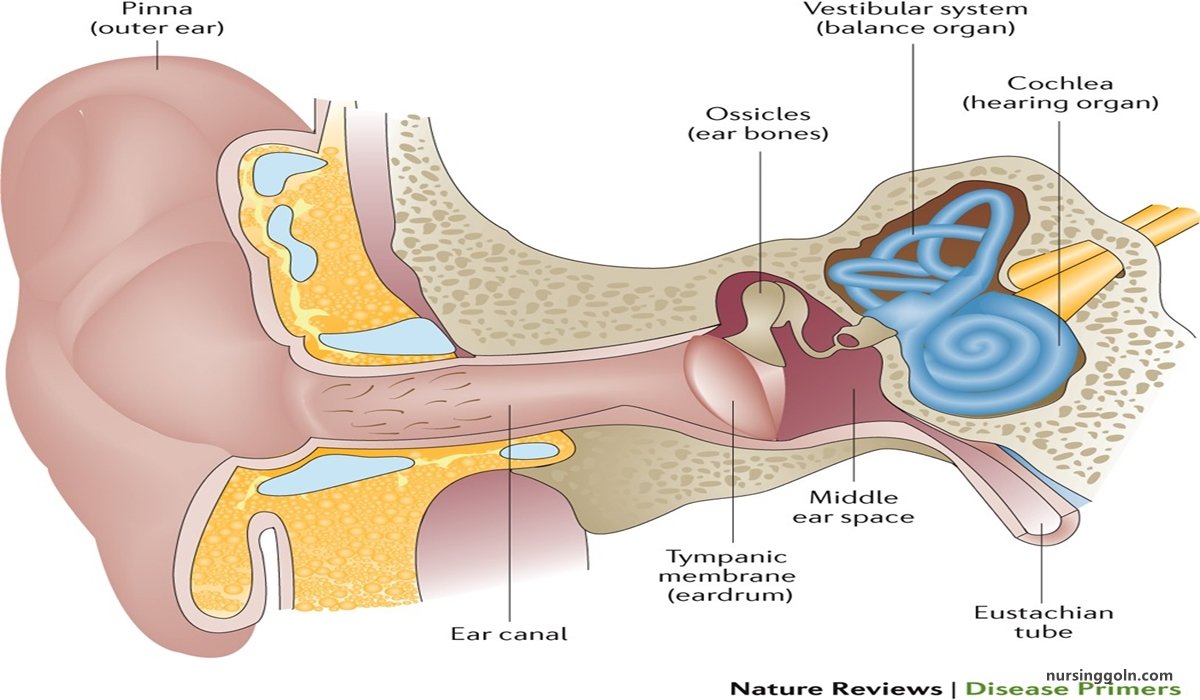
Inflammation of the mucoperiosteal lining of the middle ear cleft is called otitis media (i.e. from eustachian tube up to mastoid air cells)
Classification of Otitis Media:
Acute Suppurative Otitis Media (ASOM)
Definition:
It is an acute inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the middle ear cleft, produced by pus forming organism.
Routes of infection:
- Via eustachian tube.
- Via tympanic membrane
- Blood.
Aetiology:
Predisposing factors:
- Age: Infants & children (due to short and horizontally placed eustachian tube).
- Poor socio-economic condition.
- Climate: Cold.
- Race: Black.
Some associated diseases:
- Recurrent upper respiratory tract infection.
- Common cold.
- Adenoid.
- Acute tonsillitis.
- Exanthemas.
- Nasopharynx – If it blocked by polyp or trauma.
- Chronic sinusitis.
Bacteriology:
- Streptococcus beta haemolyticus.
- Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Staphylococcus aureus.
- Haemophilus influenzae.
Differential diagnosis:
- Furunculosis of the external ear.
- Referred otalgia.
- Herpetic lesion of the ear.
- Post-auricular adenitis.
Management of Acute Suppurative Otitis Media:
Clinical Features:
➤ Crying
➤ Irritability
➤ Sleeplessness
➤ Pulling on the ears
➤ Ear pain
➤ A headache
➤ Neck pain
➤ A feeling of fullness in the ear
➤ Fluid drainage from the ear
➤ A fever
➤ Vomiting
➤ Diarrhea
➤ Irritability
➤ A lack of balance
➤ Hearing loss
Investigations:
➤ Blood for routine microscopic examination.
➤ Pus for culture & sensitivity.
➤ X-ray mastoid Town’s view.
➤ Audiogram in early stage.
Treatment:
➤ Aim of treatment:
- To control infection in the middle ear cleft.
- To give symptomatic relief.
- To ensure patency of eustachian tube for drainage and ventilation.
- To ensure complete resolution and full return of auditory function.
➤ Medical treatment:
- Rest in bed.
- Analgesics paracetamol 500 mg thrice daily after meal till pain subsides. Systemic antibiotics: Amoxicillin 250 mg 8 hourly for 7 days.
- Nasal decongestant: Oxymetazoline 3-4 drops thrice daily for 14 days.
- Sedation.
- Local heat
Local treatment:
➤ Before perforation:
- Myringotomy when yellow spots visualized and intense pain.
- Wet draping.
- Suction.
➤ After perforation:
- Aural toileting.
- Topical antibiotic- Gentamicin/Chloramphenicol.
- Antihistamine.
- Advised for myringoplasty if perforation persists.
➤ Surgical treatment: Cortical mastoidectomy for acute mastoiditis if present.
➤ Treatment of the associated disease.
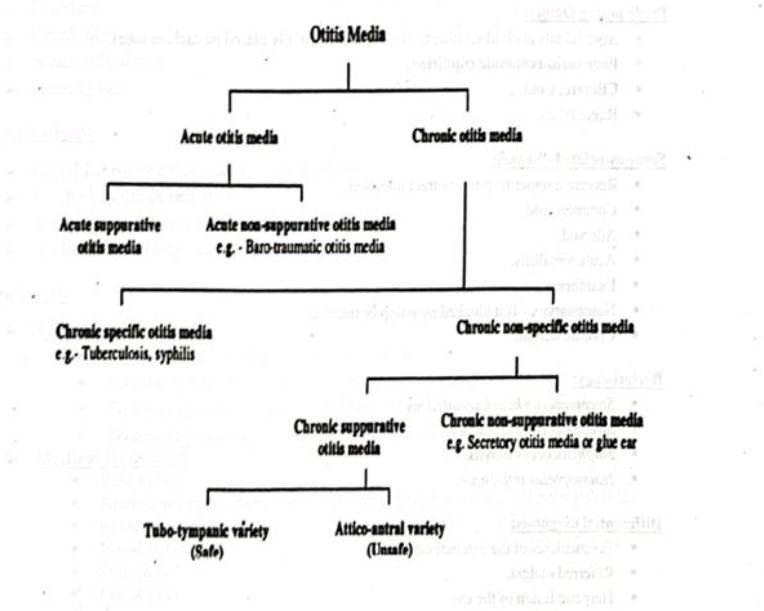
CSOM (Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media)
Definition of CSOM:
It is defined a long-standing chronic suppuration of the middle ear cleft & its mucoperiosteal lining resulting in discharge in ear & deafness.
Types/classification:
- Tubotympanic type (Safe variety).
- Attico-antral type (Unsafe variety).
Causes of CSOM:
- Residue of the acute suppurative otitis media.
- Associated with exanthemas.
- Long-standing secretory otitis media adenoid, upper respiratory tract infection- if eustachian tube is closed for prolonged period.
- Recurrent upper respiratory tract infection inflammation of the eustachian tube.
- Through perforation – traumatic after infection.
- Bacteriology:
✔ Staphylococcus aureus.
✔ Bacillus proteus.
✔ Escherichia coil,
✔ Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
✔ Bacteroids.
Management of CSOM:
Clinical Features:
Symptoms:
➤ Discharge: Profuse, initially mucoid then purulent, usually odourless, intermittent.
➤ Hearing impairment: Conductive type.
➤ Pain: Usually absent. May be present due to secondary infection.
Signs:
➤ Otoscopy:
- Discharge: Profuse, thin, initially mucoid then purulent, odourless.
- Perforation: Central.
➤ Tuning fork test:
- Rinne test: Negative.
- Weber test: Lateralized to the diseased ear.
Investigation:
➤ Ear swabs for culture & sensitivity.
➤ X-ray mastoid town’s view.
➤ Audiogram-Quantitative measurement of hearing loss.
➤ Cochlear functions test.

Treatment:
➤ Conservative treatment:
- Aural toileting: Dry mopping & suction clearance.
- Topical antibiotics: Gentamicin – 3 to 4 drops per ear thrice daily for 10 – 12 days.
- Systemic antibiotics: Amoxycillin 250 mg 8 hourly for 7 days.
- Nasal decongestant: Xylometazoline – 3 to 4 drops per nostrils for 10 to 12 days.
- Antihistamine: Chlorpheniramine meleate 4 mg thrice daily for 10 to 12 days.
- Analgesics: Paracetamol 500 mg thrice daily after meal till pain subsides.
➤ Advice/Precautions:
- Avoid from unnecessary handling of ear. Cotton ball soaked with oil before bath.
- To avoid common cold.
- Avoidance of swimming & diving.
- Maintain aural hygiene.
- Avoidance of water entry.
- Again come after 2 weeks.
➤ Follow up of medical therapy:
- After 14 days, if patient comes with dried ear than the advice for permanent precaution or myringoplasty.
- After 14 days, If discharge persist do C/S of pus & change antibiotic accordingly e.g. ciprofloxacin.
- If still discharge persists &.x-ray shows hazy mastoids ear cells, then mastoid reservoir phenomenon is thought & treatment is cortical/simple mastoidectomy to drain mastoids diseases.
- If the ear dry for 3-6 months then myringoplasty operation done.
(Ref by-Synopsis/5th/113+ Lecture)
Read more: