Hearing Impairment – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
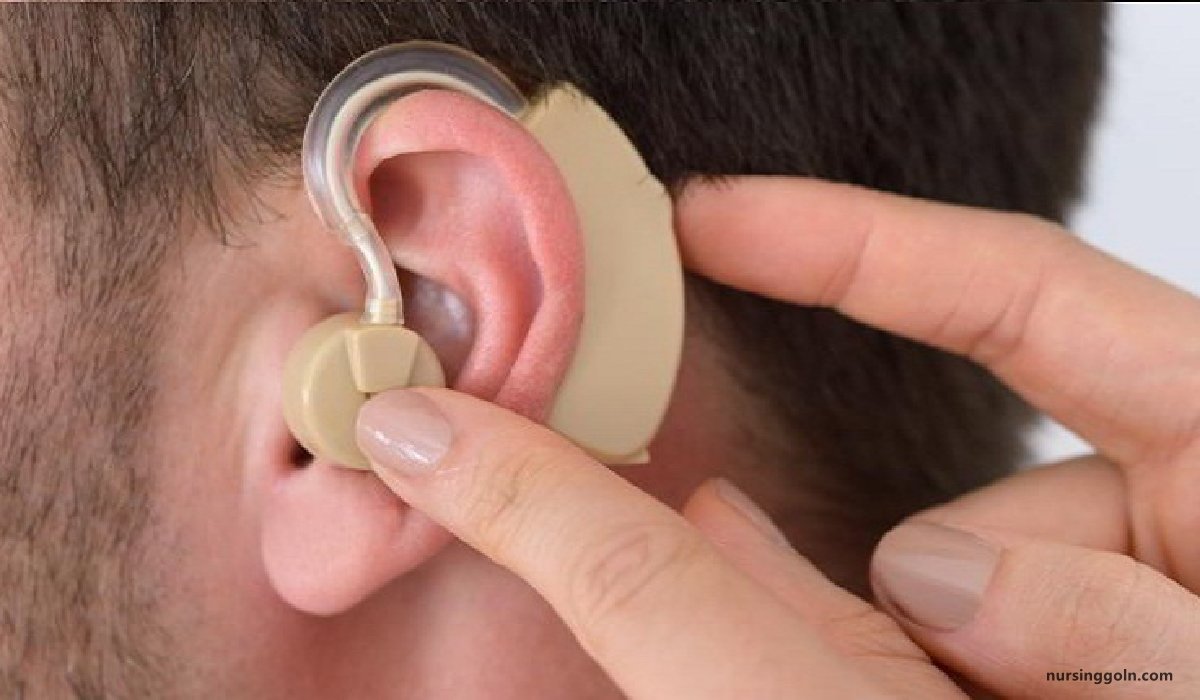
Hearing Impairment
Definition of Hearing Impairment:
Hearing loss, also known as hearing impairment, is a partial or total inability to hear. A deaf person has little to no hearing. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Difficulty using the telephone
- Loss of directionality of sound
- Difficulty understanding speech, especially of children and women whose voices are of a higher frequency.
- Difficulty discriminating speech against background noise (cocktail party effect)
- Sounds or speech becoming dull, muffled or attenuated
- Need for increased volume on television, radio, music and other audio sources
- Pain or pressure in the ears
- A blocked feeling
There may also be accompanying secondary symptoms:
- Hyperacusis, heightened sensitivity to certain volumes and frequencies of sound, sometimes resulting from “recruitment”
- Tinnitus, ringing, buzzing, hissing or other sounds in the ear when no external sound is present
- Vertigo and disequilibrium
- Tympanophonia, abnormal hearing of one’s own voice and respiratory sounds, usually as a result of a patulous eustachian tube or dehiscent superior semicircular canals
- Disturbances of facial movement (indicating possible tumour or stroke)
Causes of Hearing Impairment
Some diseases or circumstances that can cause deafness include:
- Chicken pox
- Cytomegalovirus
- Mumps
- Meningitis
- Sickle cell disease
- Syphilis
- Lyme disease
- Diabetes
- A treatment for tuberculosis (TB), streptomycin, that is believed to be a key risk factor
- Hypothyroidism
- Arthritis
- Some cancers
- Teenagers exposed to second-hand smoke
Types of Hearing Impairment:
There are three different types of hearing loss:
1. Conductive hearing loss: This means that the vibrations are not passing through from the outer ear to the inner ear, specifically the cochlea. This type can occur for many reasons, including:
- An excessive build-up of earwax
- Glue ear
- An ear infection with inflammation and fluid buildup
- A perforated eardrum
- Malfunction of the ossicles
- A defective eardrum

2. Sensorineural hearing loss: Hearing loss is caused by dysfunction of the inner ear, the cochlea, auditory nerve, or brain damage. This kind of hearing loss is normally due to damaged hair cells in the cochlea. As humans grow older, hair cells lose some of their function, and hearing deteriorates. Long-term exposure to loud noises, especially high- frequency sounds, is another common reason for hair cell damage.
3. Mixed hearing loss: This is a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. Long-term ear infections can damage both the eardrum and the ossicles. Sometimes, surgical intervention may restore hearing, but it is not always effective.