Organ system-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Organ system
Human Organ Systems
Groups of organs working together to perform major activities of the body are called organ systems. There are 11 major organ systems in our human body.
- The integumentary system
- The muscular system,
- The skeletal system
- The Cardiovascular system,
- The Respiratory system,
- The Digestive system,
- The Nervous system
- The Urinary system
- The Endocrine system,
- The Lymphatic system/Immune system, and
- The Reproductive system.
Short description of organ system
ORGAN SYSTEMS AND SHORT DESCRIPTION
1. The Integumentary system
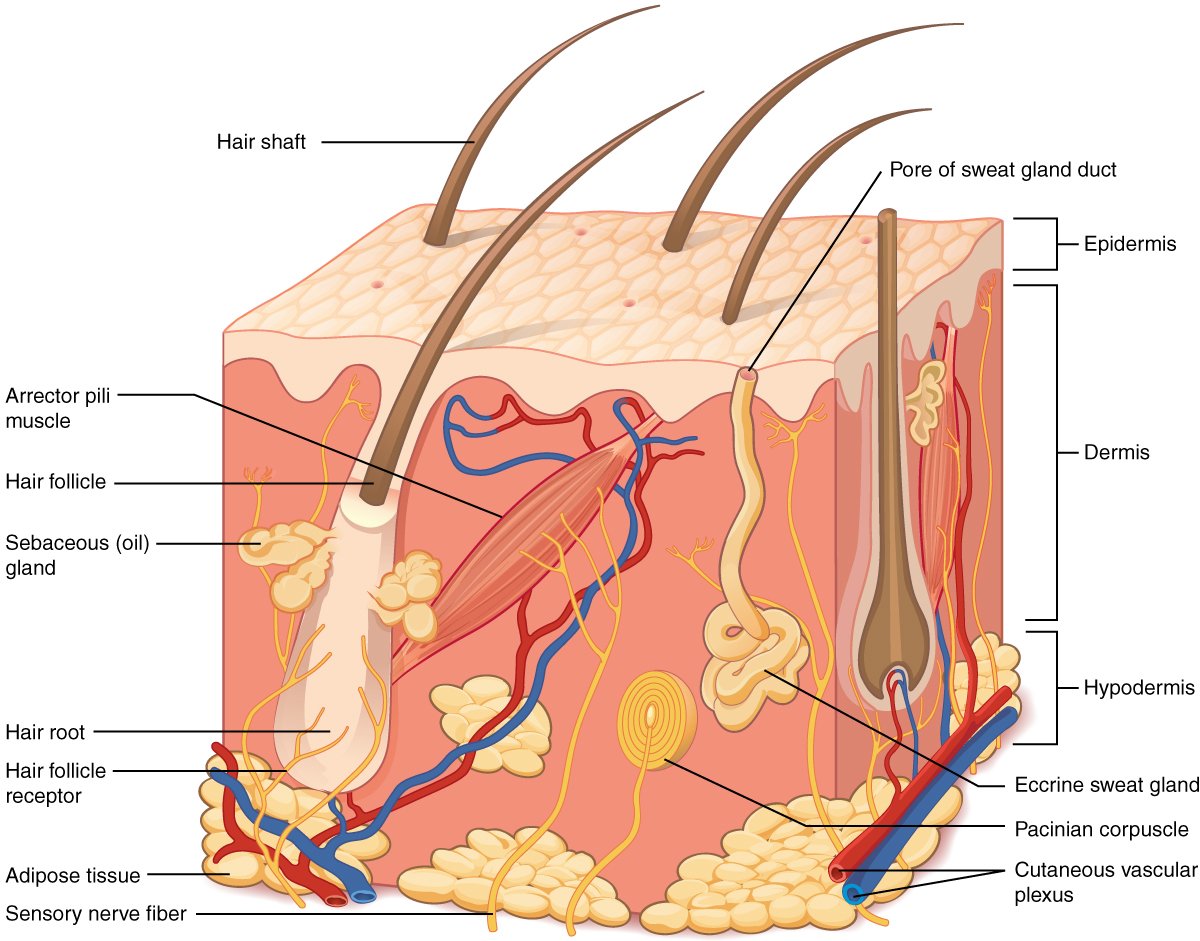
Components:
Skin and structures associated with it, such as hair, nails, and sweat and oil glands.
Functions:
- Helps regulate body temperature,
- O Protects the body,
- Eliminates some wastes,
- Helps make vitamin D,
- Detects sensations such as touch,
- O Pressure, pain, warmth, and cold.
2. The Muscular system

Components:
Specifically refers to skeletal muscle tissue, which is muscle usually attached to bones (other muscle tissues include smooth and cardiac).
Functions:
- Participates in bringing about body
- Movements such as walking;
- Maintains posture; and
- Produces heat.
3. The Skeletal system
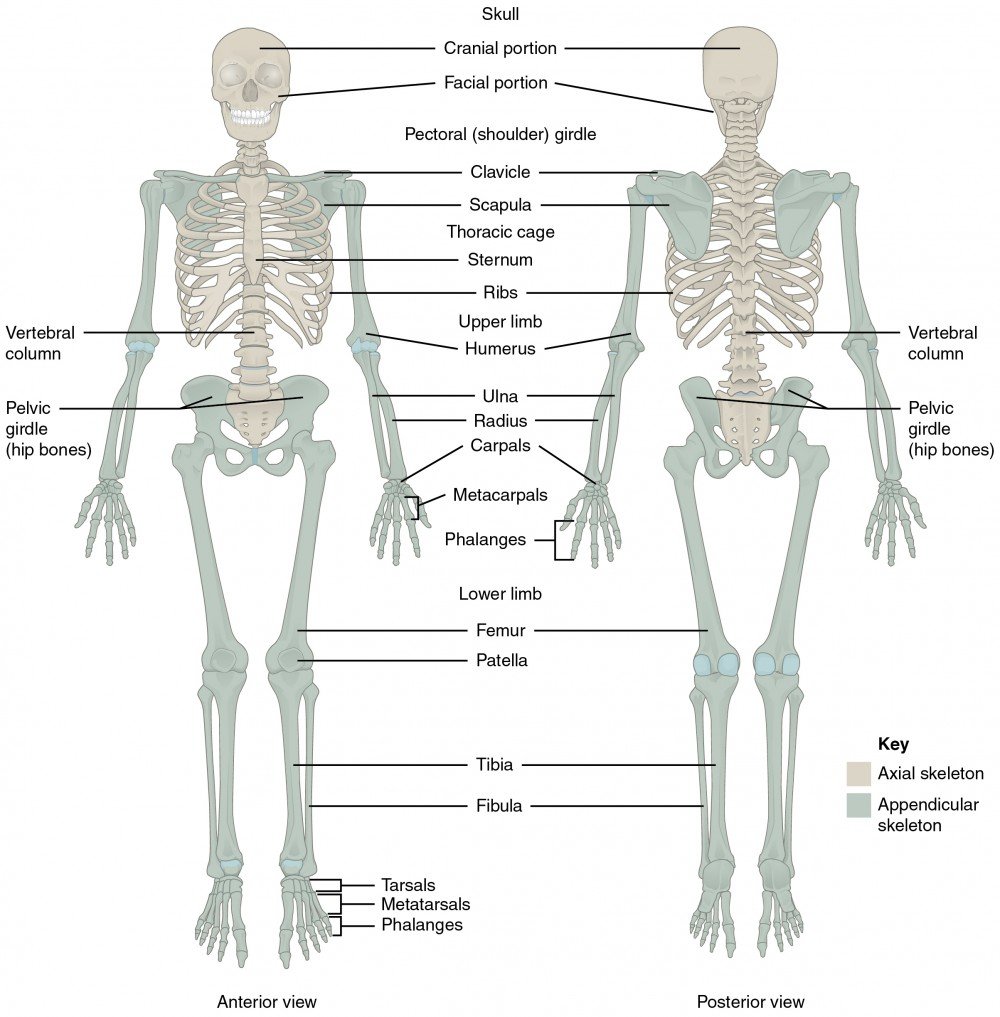
Components:
Bones and joints of the body and their associated cartilages.
Functions:
- Supports and protects the body,
- Provides a specific area for muscle attachment,
- Assists with body movements,
- Stores cells that produce blood cells, and stores minerals and lipids (fats).
4. The Cardiovascular system
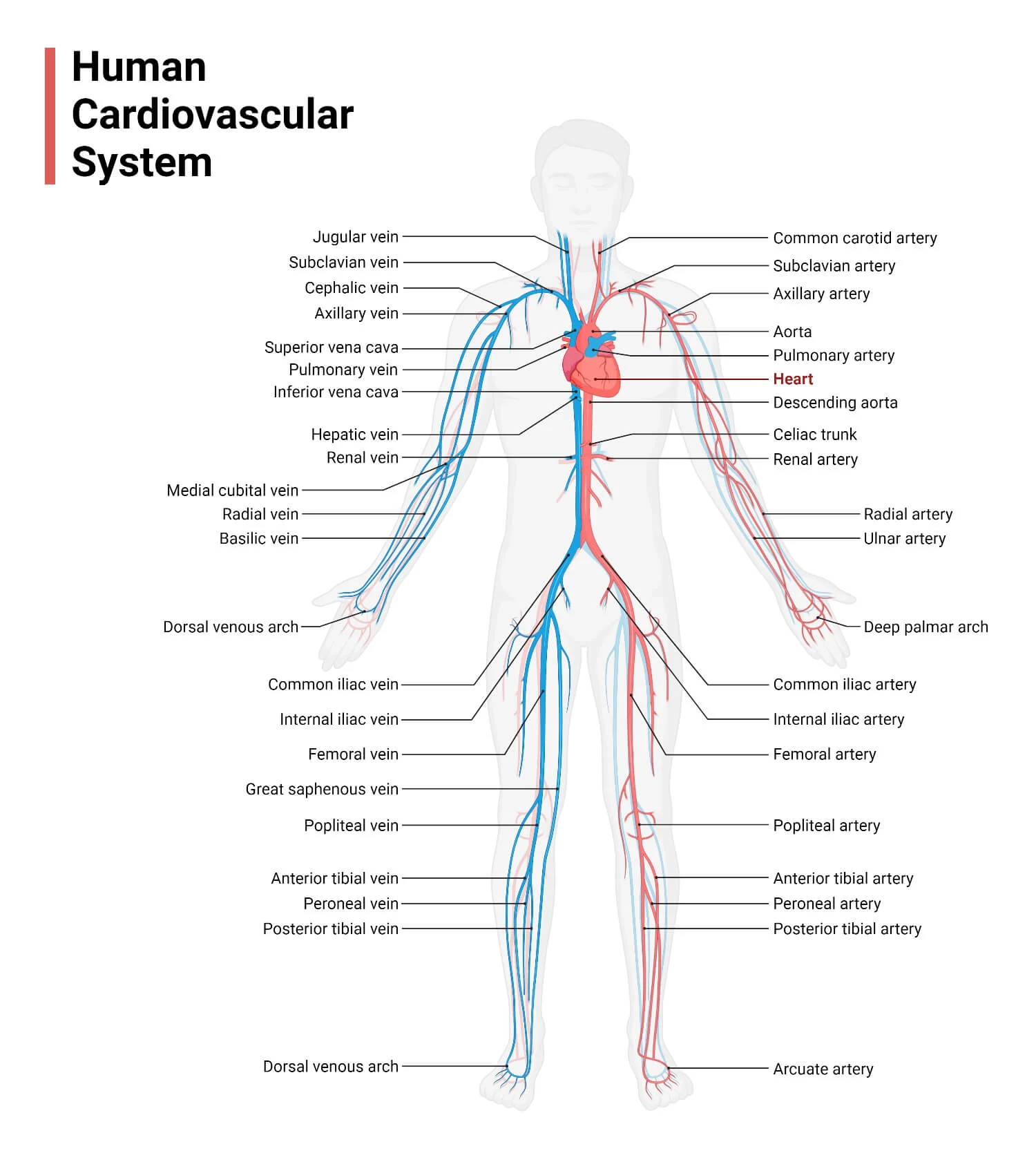
Components:
Blood, heart, and blood vessels.
Functions:
- Heart pumps blood through blood vessels blood carries oxygen and nutrients to cells and carbon dioxide and wastes away from cells, and
- Helps regulate acidity, temperature, and water content of body fluids,
- Blood components help defend against disease and mend damaged blood vessels.
5. The Respiratory system

Components:
Lungs and air passageways suchas the pharynx (throat), larynx (voice box), trachea (windpipe), and bronchial tubes leading into and out of them.
Functions:
- Transfers oxygen from inhaled air to blood and carbon dioxide from blood to exhaled air,
- Helps regulate acidity of body fluids,
- Air flowing out of lungs through vocal cords produces sounds.
6. The Digestive system
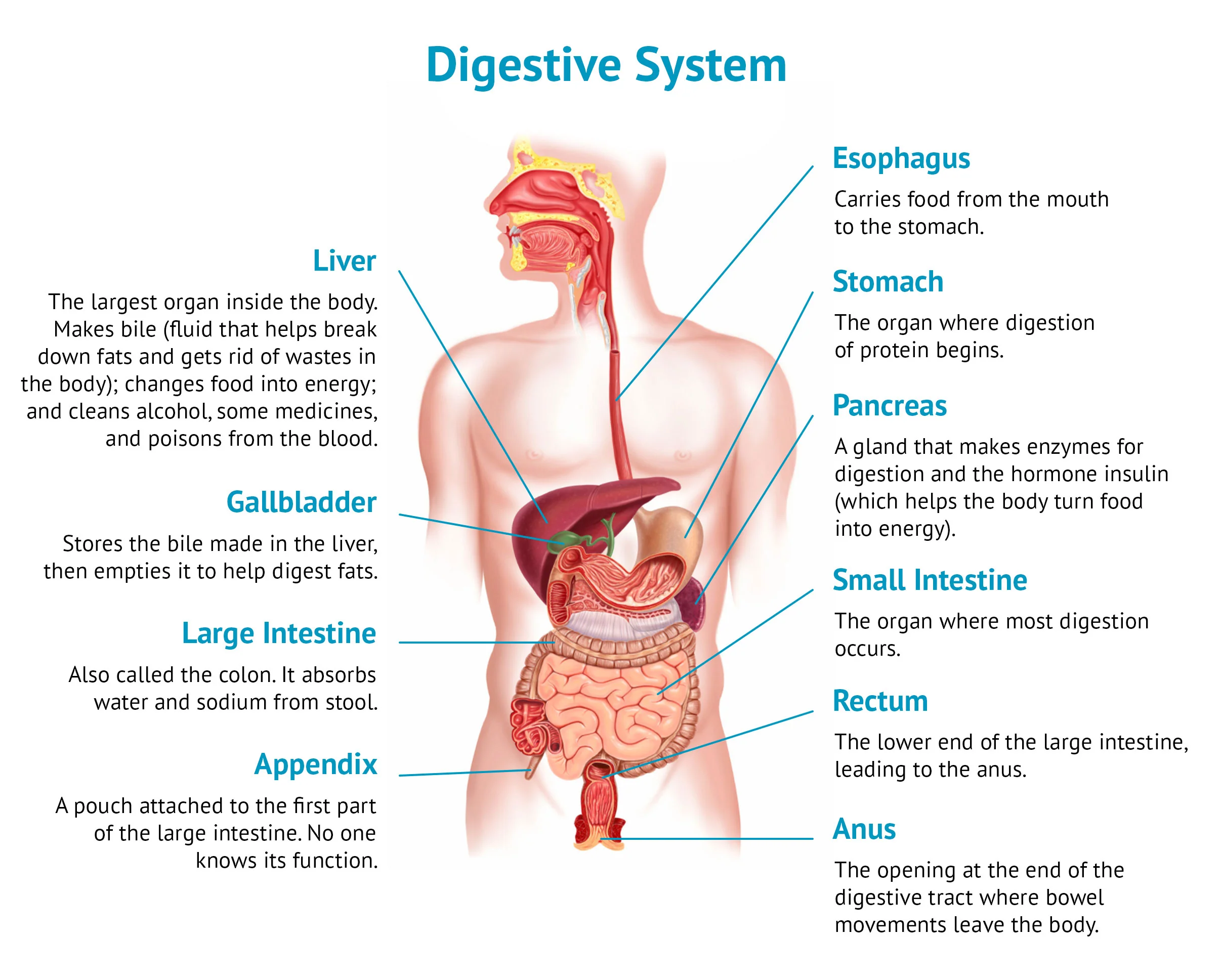
Components:
Organs of gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth, pharynx (throat), esophagus, stomach, small and largeintestines, rectum, and anus; Also includes accessory digestive organs that assist in digestive processes, such as the salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.

Functions:
- Physical and chemical breakdown of food,
- Absorbs nutrients and
- Eliminates solid wastes
7. The Nervous system
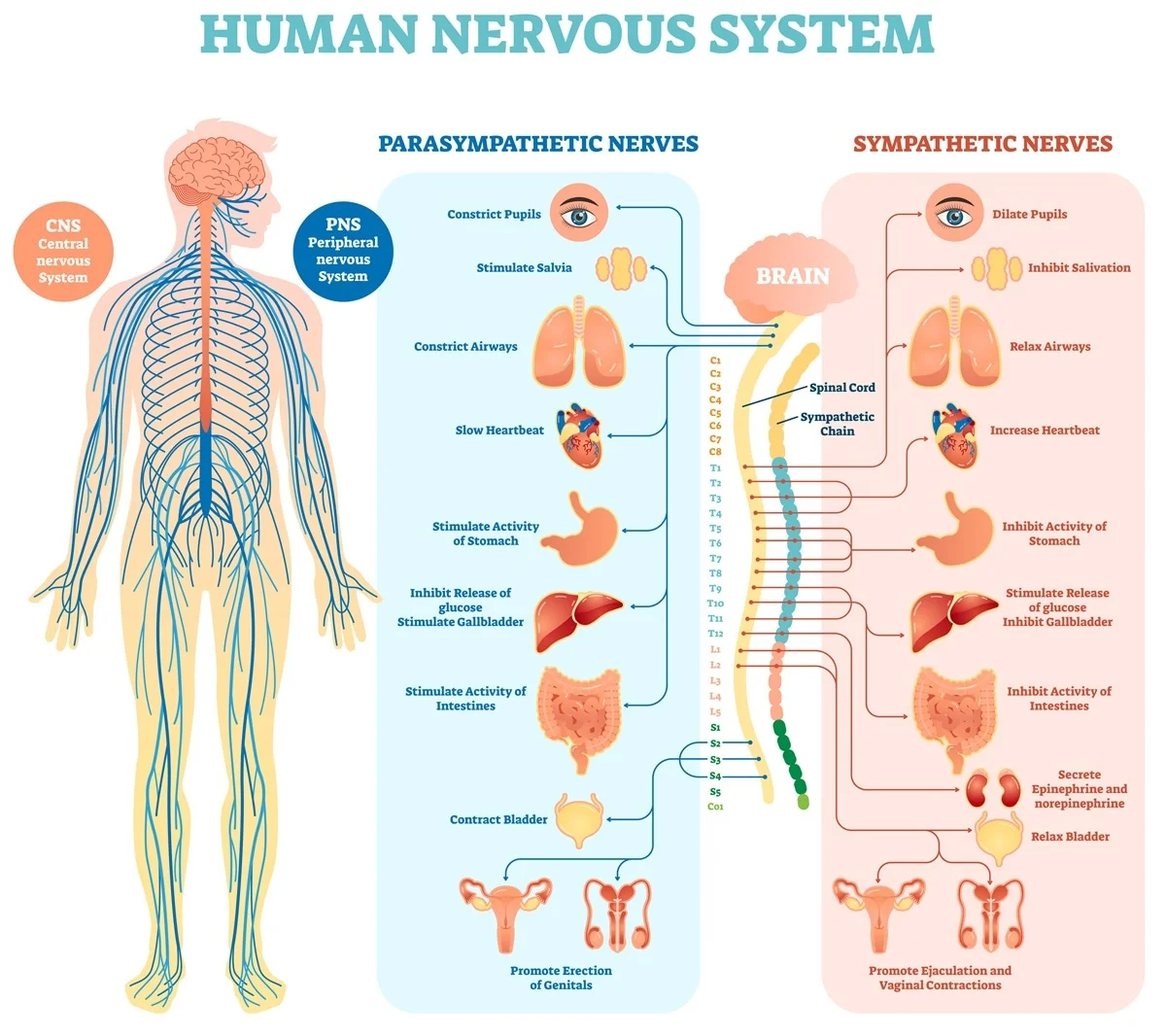
Components:
Brain, spinal cord, nerves, and special sense organs such as the eyes and ears.
Functions:
- Regulates body activities through nerve impulses by detecting changes in the environment,
- Interpreting the changes, and
- Responding to the changes by bringing about muscular contractions or glandular secretions.
8. The Urinary system
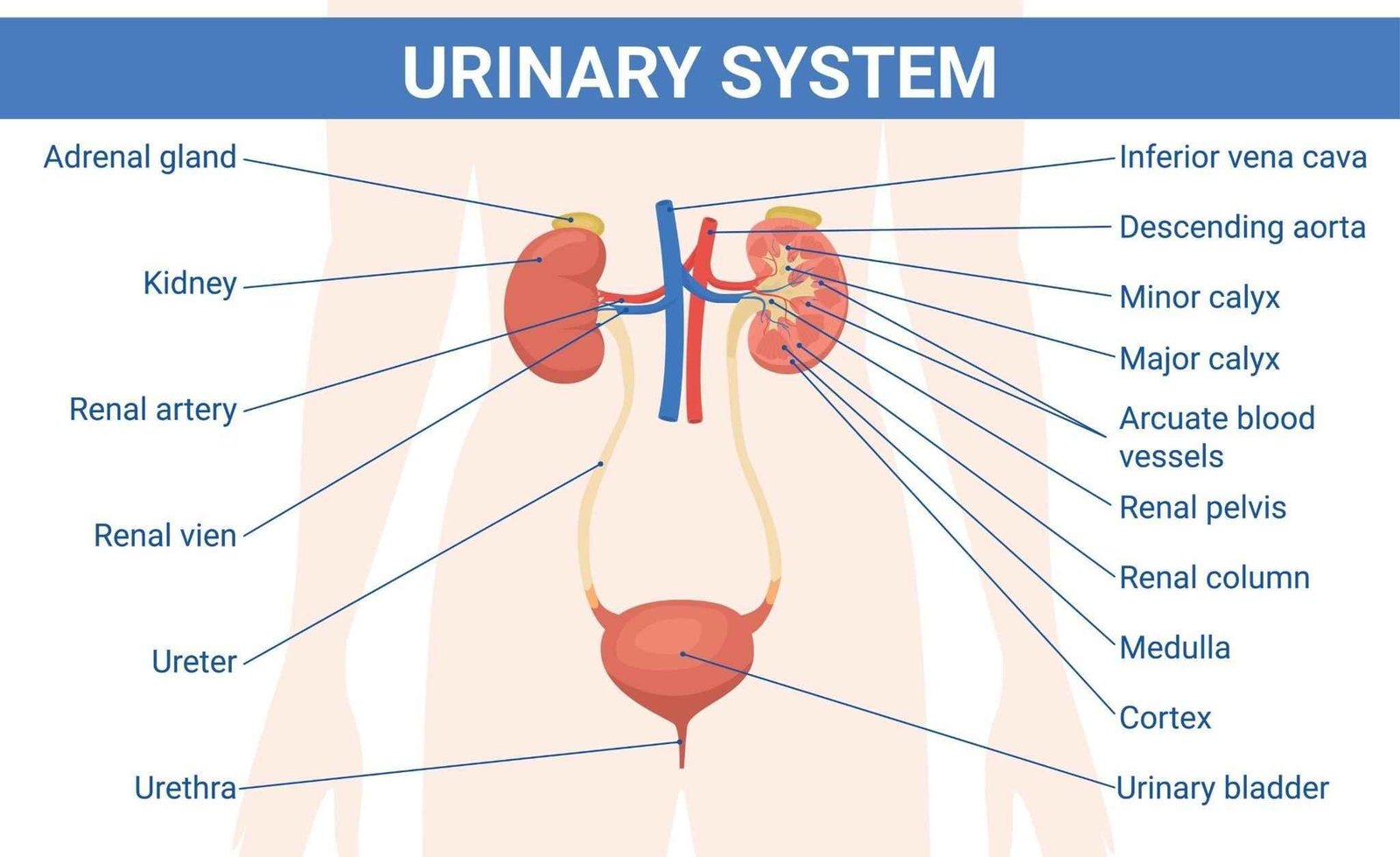
Components:
Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
Functions:
- Produces, stores, and eliminates urine;
- Eliminates wastes,
- Regulates volume and chemical compositionof blood;
- Helps regulate acid-base balance of body fluids; maintains body’s mineral balance;
- Helps regulate red blood cell production.
9. The Endocrine system

Components:
All ductless glands (Pituitary, thymus, thyroid, adrenal, ovaries, testes etc) and tissues that produce chemical regulators of body functions, called hormones.
Functions:
- Regulates body activities through hormones transported by the blood to various target organs.
10. The Lymphatic system and Immunity
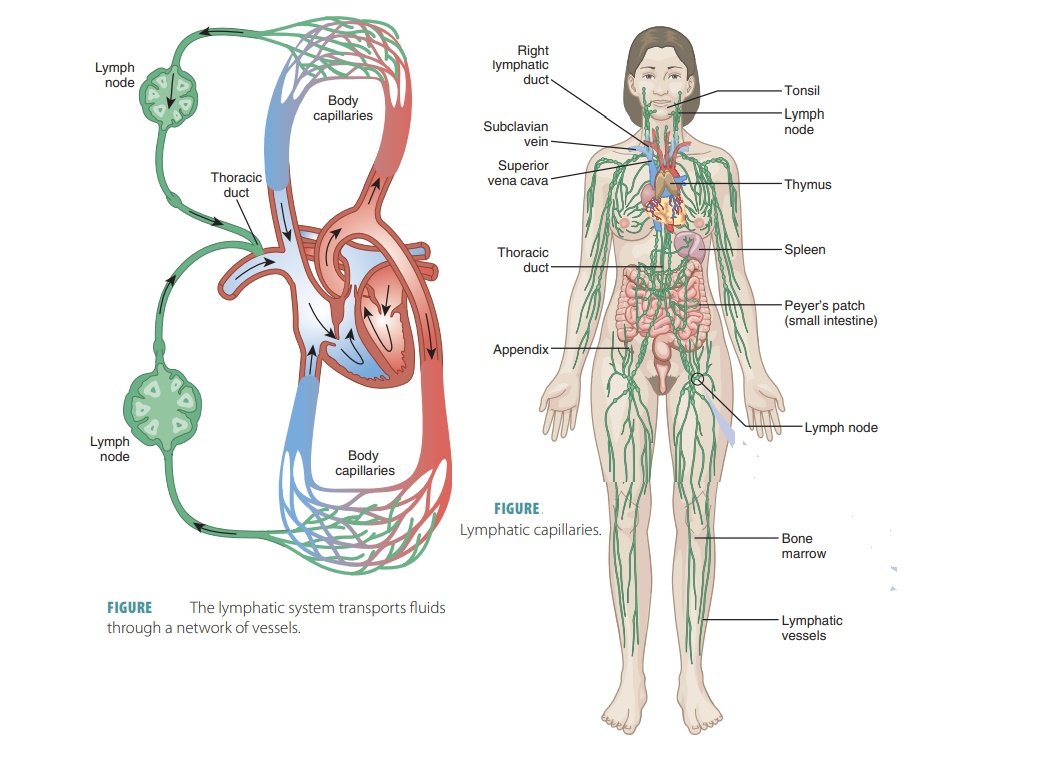
Components:
Lymphatic fluid (lymph) and vessels; spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, and tonsils; cells that carry out immune responses (B cells, T cells, and others).
Functions:
- Returns proteins and fluid to blood;
- Carries lipids from gastrointestinal tract to blood;
- Contains sites of maturation and proliferation of B cells and T cells that protect against disease-causing microbes.
11. The Reproductive system

Components:
Gonads (testes in males and ovaries in females) and associated organs: uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina in females, and epididymis, ductus (vas) deferens, and penis in males. Also, mammary glands in females.
Functions:
- Gonads produce gametes (sperm or oocytes) that unite to form a new organism and
- Release hormones that regulate reproduction and other body processes,
- Associated organs transport and store gametes.
- Produce milk.
(Ref:– J. TORTORA, The essentials of anatomy and physiology, 8th edition, P-4, 5)
Read more:
