Cell membrane-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Cell membrane

Structure of cell membrane:
Cell membrane is very thin elastic structure surrounds the cell s only about 7.5 to 10 nanometers thick and primarily made up of lipids, proteins & carbohydrates, which completely envelops the cell and is semi permeable.
It is generally referred to as ‘plasma membrane’. It is a lipid bi-layer interposed with sandwich of protein.
A. Lipid portion:
a. Composed of phospholipids and cholesterol.
b. The head end of the membrane contains the phosphate portion and is relatively soluble in water. (i.e. hydrophilic or polar) and faces towards the outer and inner aspect of the membrane.
c. The tail end are relatively insoluble in water. (i.e. hydrophobic or nonpolar) and lies centrally in the membrane.
B. Protein portion:
Two types –
a. Integral protein: It protrudes all the way through the membrane providing structural channels for the movement of water-soluble substances between ECF and ICF.
b. Peripheral protein: It attached to the integral protein. It acts mainly as enzyme.
Functions of cell membrane:
- Transports of substances.
- Maintains size & shape of the cells.
- Act as a receptor for various hormones and other chemicals
- Provide inter-cellular contact.
- Separates the cell from outer environment.
- Secretes waste products.
- Generates membrane potential.
- Participates in intracellular function.
- Participates in processing of antibody.
(Ref:: Guyton and Hall, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 13ª ed., P-13)
Gene
Gene: It may be defined as a specific sequence of nucleotide in the specific part of DNA which carries a particular genetic information.
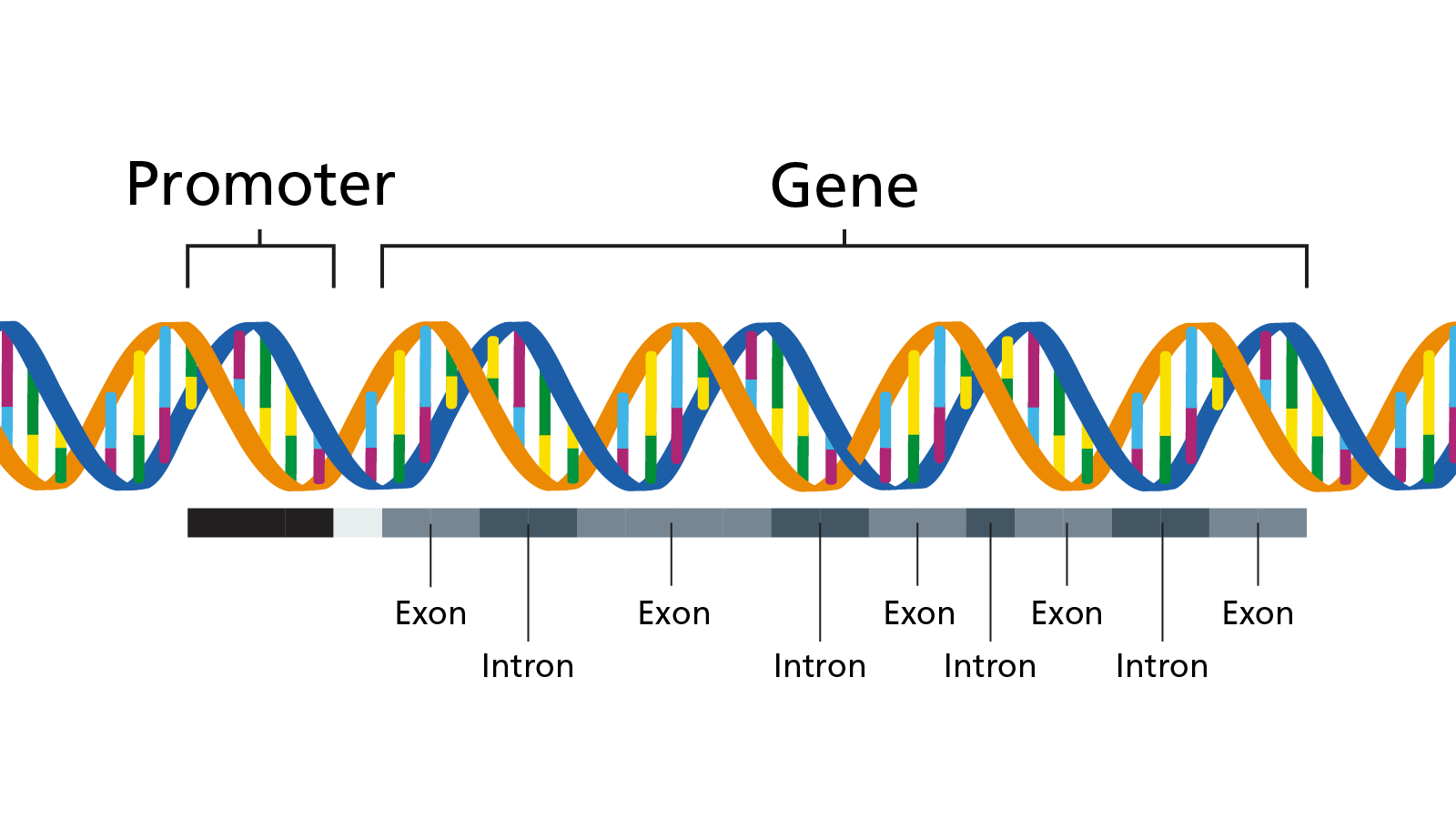
Well to know-
DNA present in:
- Chromosomes and
- Mitochondria
RNA present in:
- Nucleus (chromosome).
- Mitochondria.
- Ribosome and
- Endoplasmic reticulum
