Organic Chemistry – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that is concerned with carbon and especially carbon compounds which are found in living things.
or
Organic chemistry is the chemistry sub-discipline for the scientific study of structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials (materials that contain carbon atoms).
or
Organic chemistry is the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and synthesis of organic compounds that by definition contain carbon.
Characteristics of Organic Compounds:
The general characteristics of Organic Compounds include:
- Can be isolated as well as prepared in laboratory
- Comprise almost 90% of all known compounds.
- Mostly built up of only three elements- carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Other elements like halogen, nitrogen as well as phosphorous are also present but to a lesser extent.
- Possess complex structures and high molecular weights
- Their properties are decided by certain active atom or group of atoms known as the functional group.
- They are mostly insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
- They are combustible in nature
- Chemical reactions involving organic compounds proceed at slower rates.
Characteristics due to Presence of Covalent Bonds
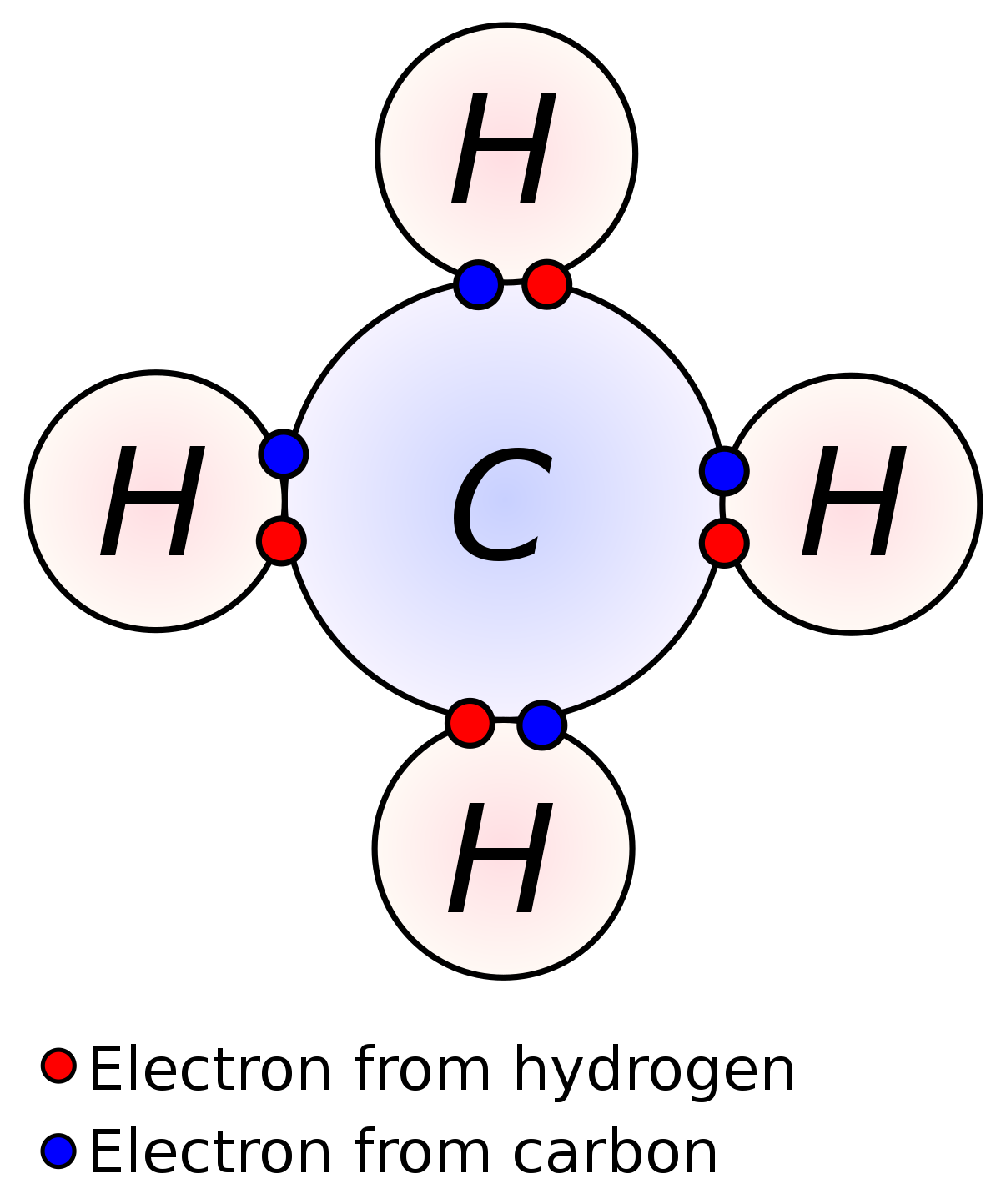
The presence of a covalent bond renders certain characteristics to the organic compounds. These include:
- Low melting points and boiling points in comparison to the inorganic compounds.
- Organic acids and bases are less stronger and thus they have a limited dissociation in an aqueous medium.
- They exhibit the phenomenon of isomerism in which a single molecular formula represents several organic compounds differing in physical and chemical properties.
- They are volatile in nature.
Importance of Organic Chemistry:
Importance of organic chemistry are as-
A. Medicine: Medicine is the prime store of organic compounds. Though not all but many drugs are made of organic substances. Like antibiotics, anticancer drugs, painkillers, anti- depressant, anesthetics, etc.
a) Drugs to cure disease: As said before many drugs used for the treatment of diseases are made of organic compounds.
b) Pathophysiology of the diseases: The study of disease is well supported by organic chemistry. Most diseases in humans have some course or pathway before complete death ensues.
c) To diagnose the disease: Here organic chemistry uses some diagnosing aids to detect the organic part of the deficiency or disturbed substance.
B. Food: Food materials are solely made of carbon compounds e.g. carbohydrates (CHO), proteins (NH2-CH-COOH), and fats (CH-COO-CH). Even vitamins are organic in nature. Among beverages alcohol is an organic substance
C. Cleansing agents: In industries and labs, organic solvents are widely used to clear of impurities. For example in drug extraction from plants, the fatty matter from the pulp is removed using petroleum ether. Thus organic chemistry through its knowledge of polarity, solubility, partition factors uses solvents to separate components for better use.
D. Sterilizing agents: Most of the sterilizing agents and disinfectants like phenol, formaldehyde etc are carbon compounds
E. Analytic substances: Most substances we use like drugs, pesticides, etc., are analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively using different types of titrations, chromatography techniques, and spectrophotometry. Here the reagent use like acids or bases or reductive oxidative species is organic in nature. Further, the endpoint indicators in titration are developed by organic chemistry.
F. Valuables: Diamonds, graphite, petroleum. Interestingly the carbon compounds are found to be highly valuable, durable and hardest in the world.
Diamond and graphite are both pure carbon alone compound without any other elements inside. They are both highly used and expensive. Their properties are studies in organic chemistry.

Nice To Know.
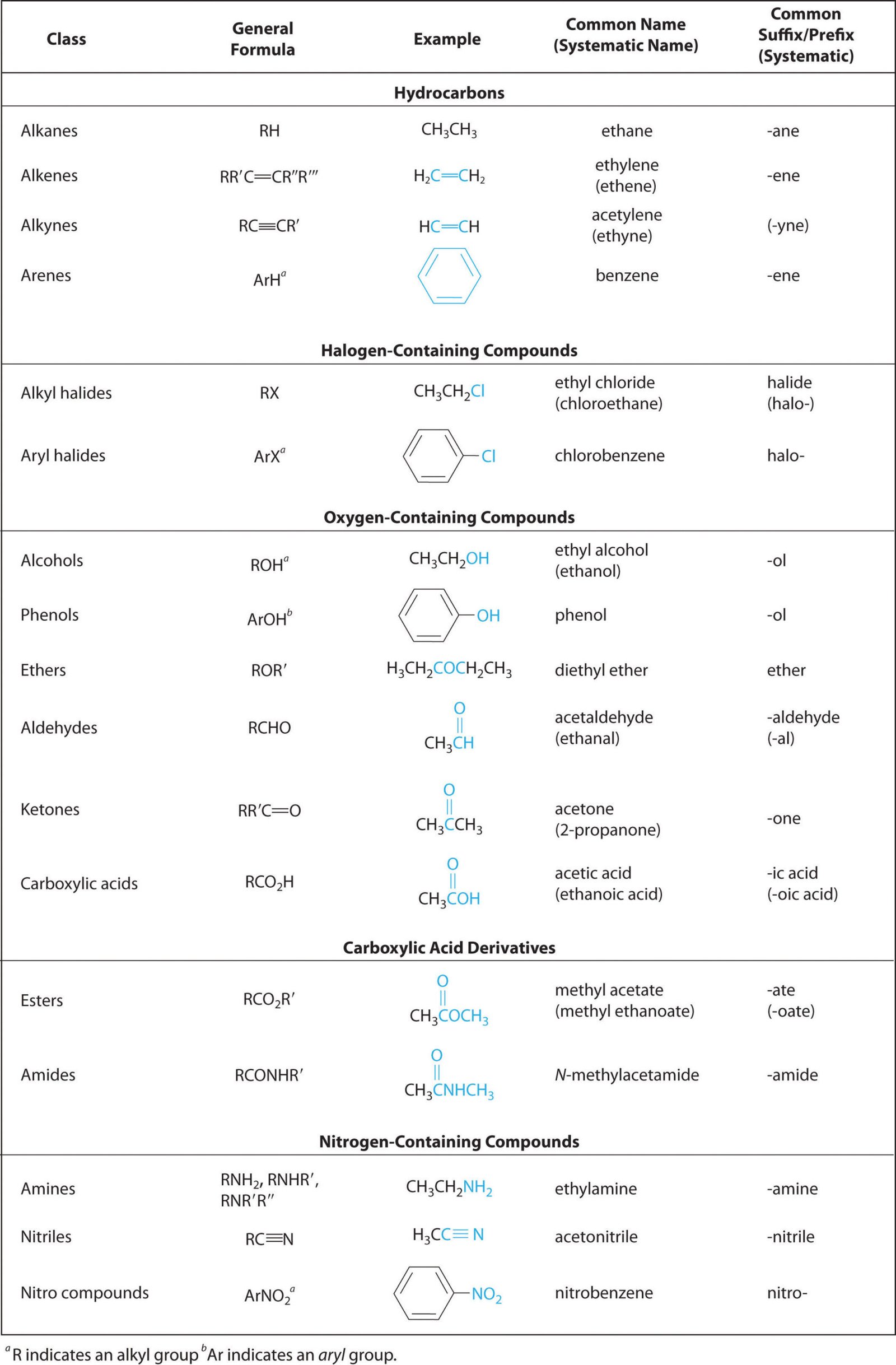
Functional Groups and Classes of Organic Compounds
Uses/Applications of Organic Chemistry:
Organic chemistry finds its application to a large extent in the field of medicine, pesticides, petroleum sector, textile etc.
A. For analysis: Not all organic substances are soluble in water. So they can be analyses by non-aqueous titration. For this they use organic solvents like pyridine, methanol, acetone etc.
Further other methods like chromatography, spectroscopy (infrared spectroscopy) also employ organic solvents for analysis. This analysis helps to test the given compound for its purity, quantity etc.
B. For synthesis: Organic chemistry helps us synthesis many compounds which are needed on a large scale. For example we find a drug molecule in nature by chance or as bi-product of some reaction. Then that drug molecule can be synthesized by knowledge of organic chemistry for large-scale use.
C. For better molecules: If a molecule is already been used for a long time. It can be replaced by similar molecule with slight change in its chemistry. This change is aimed at more effective performance. This is possible by substituting some organic functional groups.

Read More….