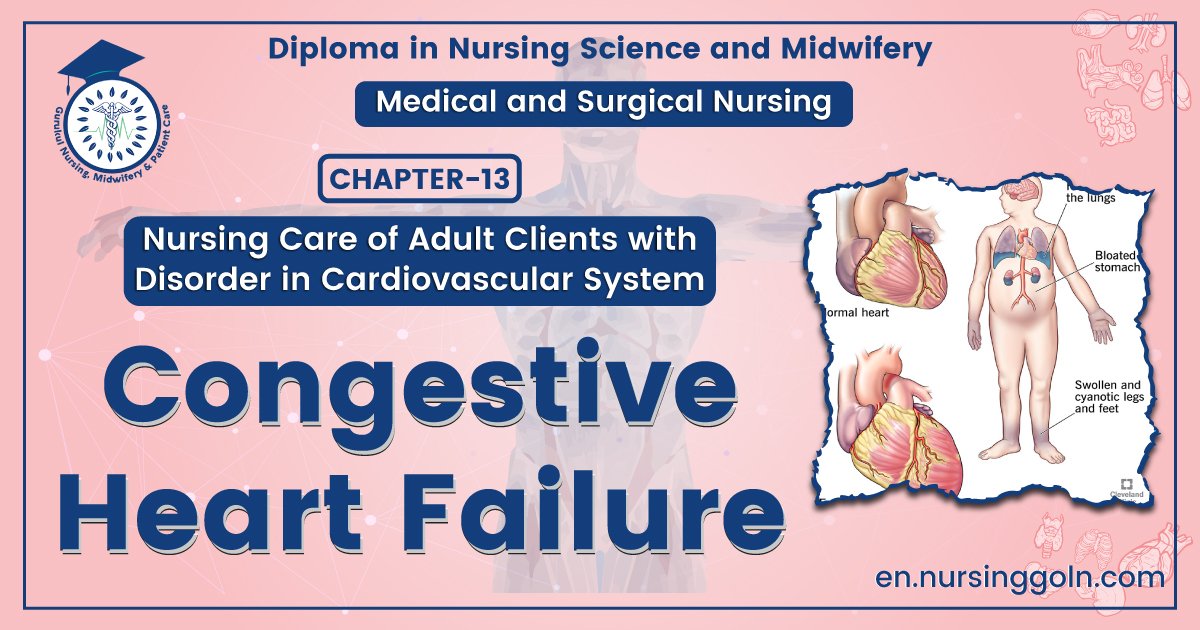
Congestive heart failure – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Congestive heart failure
Definition of Congestive Cardiac Failure
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a condition in which the heart’s function as a pump is inadequate to meet the body’s needs.
Or,
Congestive cardiac failure is the heart failure resulting from oedematous congestion, either pulmonary on systemic circulation.
Management of Congestive Cardiac Failure (CCF)
Clinical Feature
Symptoms
1. Dyspnoea/Breathlessness
2. Cough with frothy sputum/expectoration, sometimes stained with blood.
3. Feature of low cardiac output: Fatigue, restlessness, poor effort tolerance, cold & clammy skin, hypotension,oliguria, uraemia,confusion, convulsion
4. Cardiac cachexia in chronic heart failure.
5. Generalized swelling which started in the legs/bilateral leg swelling
6. Features of cause-H/O chest pain, palpitation, HTN.
Sign’s
1. General examination
- Patient is odematous (pitting) & puffy.
- Patient is dyspnoeic and is in propped up position.
- Pulse: Tachycardia
- Blood pressure- Hypotension
- Bilateral leg odema.
- Elevated JVP
2. Precordium
- Apex beat: Shifted downwards & outwards with heaving character (Cardiomegaly)
- Loud pulmonary component of 2nd heart sound- if there is pulmonary HTN.
3. Lungs
- Bilateral basal crepitations.
- Feature of pleural effusion
4. Abdomen.
- Tender hepatomegaly
- Ascites.
5. Features of causes- Murmur (Valvular heart diseases)
Investigations
1. The chest X-ray P/A view:
2. ECG: It may reveal ventricular hypertrophy, atrial fibrillation, IHD & valvular heart diseases
3. Echocardioghraphy
- Complete blood count if polycythemia & chronic corpulmonalae.
- Blood urea and serum creatinine- to see the renal function.
- ANP & BNP
4. Cardiac MRI, coronary angiography for IHD & cardiac biopsy for cardiomyopathies.
Treatment
General measures
1. Bed rest (to increase renal blood flow)
2. Diet-
- Good general nutrition
- Weight reduction in obese
- Avoidance of high salt containing food and added salt
3. Should give up alcoholism and smoking
4. Regular moderate exercise within limit of symptoms
5. Vaccination, if possible influenza and pneumococcus.
Specific measures
Drug therapy
1. Diuretics
- Frusemide (5-10mg/hour) can be used alone or in combination with thiazides.
- Spironolactone.
2. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI): Ramipril, Captopril, Enalapril,
3. Angiotensin receptor blocker:
- Losartan 50-100mg once daily
- Candesartan 4-16 mg daily or
- Valsartan 40-160 mg daily
4. Beta blocker. (Bisoprolol starting dose-1.25mg daily, increased gradually over a 12 weeks & target dose 10mg daily) :in chronic heart failure
5. Digoxin: To provide in pt. with heart failure not controlled by Diuretics, ACEI, beta blocker or heart failure with atrial fibrillation.
6. Amiodarone if symptomatic arrhythmia is there with heart failure & poor left ventricular function
7. IV inotropic & vasopressor if not respond to oral therapy.
- Non pharmacological treatment of Heart failure
- Implantable cardiac defibrillators & resynchronization therapy
- Coronary revascularization
- Heart transplatation.
- Ventricular assist device.
Rx of the cause
Monitoring
- Clinical (Pulse, temperature, BP, Resp. rate) & body weight
- Input-output chart
- Renal function test.
- Blood sugar.
- ECG
- Functional capacity by-
- Exercise tolerance test
- Echocardiography
Pathophysiological Condition of Congestive Cardiac Failure
Damage to the myocardium due to MI, CAD, Valvular disorders/Pericarditis
↓
Impaired ventricular function
↓
Fall in cardiac output
↓
Activate neuro hormonal mechanism
↓
Vasoconstriction, Salt or water retention of sympathetic activation by angiotensin II
↓
Increase myocardial contractility
↓
Prolonged sympathetic stimulation
↓
Myocardial necrosis
↓
Heart failure