Amino Acid – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Amino Acid
Proteins are made up of simpler substances which are the building blocks of protein called amino acids.
Or,
Proteins are made by joining together a hundred or more much smaller things called amino- acids.
Classification of Amino Acids:
Amino acids are classified into two groups – essential (indispensable) and non-essential (dispensable)
Essential amino acids: –
These are the amino- acids, which cannot be synthesized in the body in sufficient quantity. And therefore, the dietary proteins must supply them.
These are:
- Leucine
- Isoleucin
- Lysine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Threonine
- Valine
- Tryptophan
Non-essential amino acids:
It can be synthesized by the body and they need not be supplied through diet.
These are –
1. Alanine.
2. Arginine.
3. Asparagine.
4. Aspartic acid.
5. Cysteine.
6. Cystine.
7. Glutamic acid.
8. Glutamine
9. Glycine.
10. Histidine
11. Hydroxyproline.
12. Proline.
13. Serine
14. Tyrosine
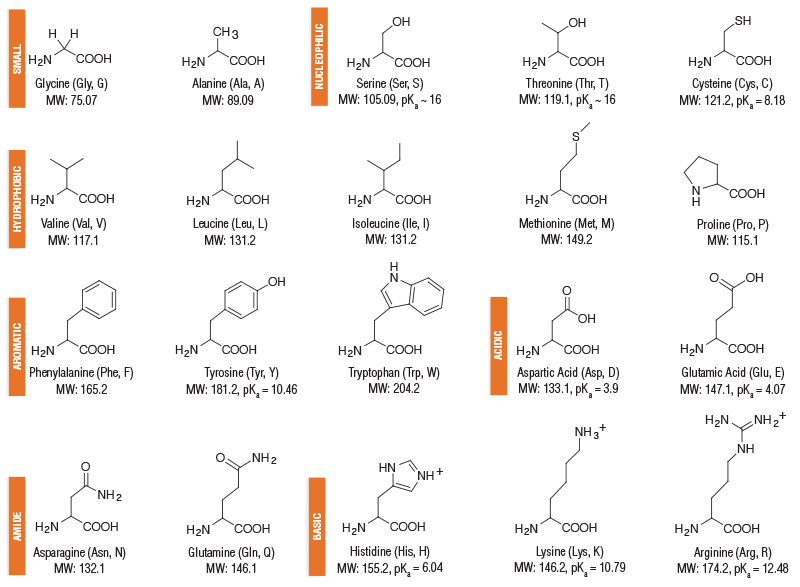
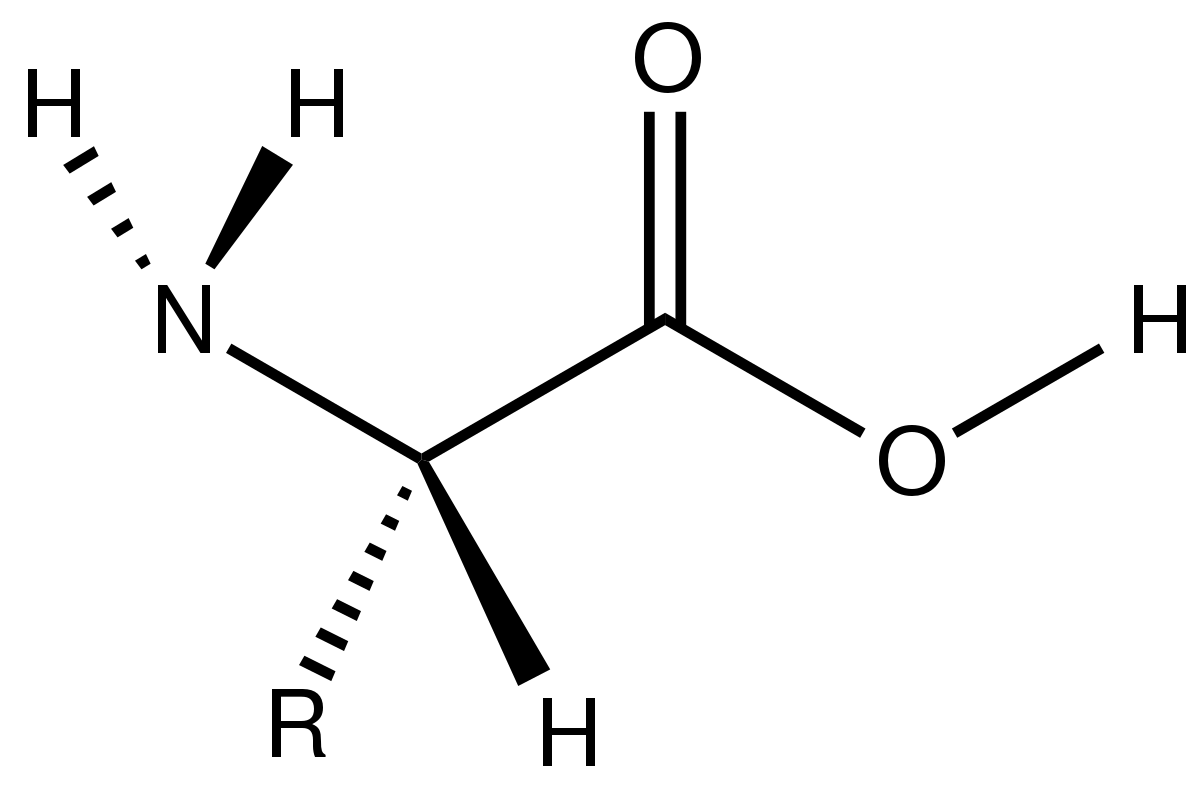
Fig: Structure of amino- acids

Essential amino acid requirements in adult:
Amino acid | FAO/WHO/UNU 2007 | |
| mg/kg/day | Each gram protein contains | |
| Histidine | 10 | 15 mg |
| Isoleucine | 20 | 30 mg |
| Leucine | 39 | 59 mg |
| Lysine | 30 | 45 mg |
| Methionine. | 10 | 16 mg |
| Cysteine | 4 | 6mg |
| Methionine + Cysteine | 15 | 22 mg |
| Threonine | 15 | 23 mg |
| Phenylalanine + Tyrosine | 25 | 38 mg |
| Tryptophan | 4 | 6 mg |
| Valine | 26 | 39 mg |
| Total EAA | 184 | 277 mg |
| Total protein | 0.66g/kg/day | |
Safe level of protein (Mean+1.96xSD) | 0.83g/kg/day | |

Read More….
