Knee Arthroplasty – An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
Knee Arthroplasty
Knee arthroplasty:
Knee replacement surgery, also known asknee arthroplasty, is regarded as a modern surgical procedure that can accurately be described as “knee resurfacing”. This procedure entails restoring the weight bearing facade of the knee joint that is damaged, worn out, or diseased to relieve pain and movement disability. It is performed through the implant of an orthopedic metal and plastic component shaped as a joint so that the knee can move properly.
Arthroplasty is a field of medicine which deals with the surgical reconstruction and total replacement of degenerated joints. Arthroplasty uses artificial body parts (prosthetics). Arthroplasty literally means “the surgical repair of a joint”.
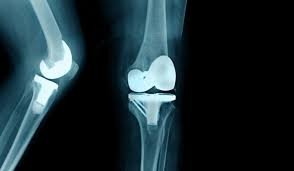
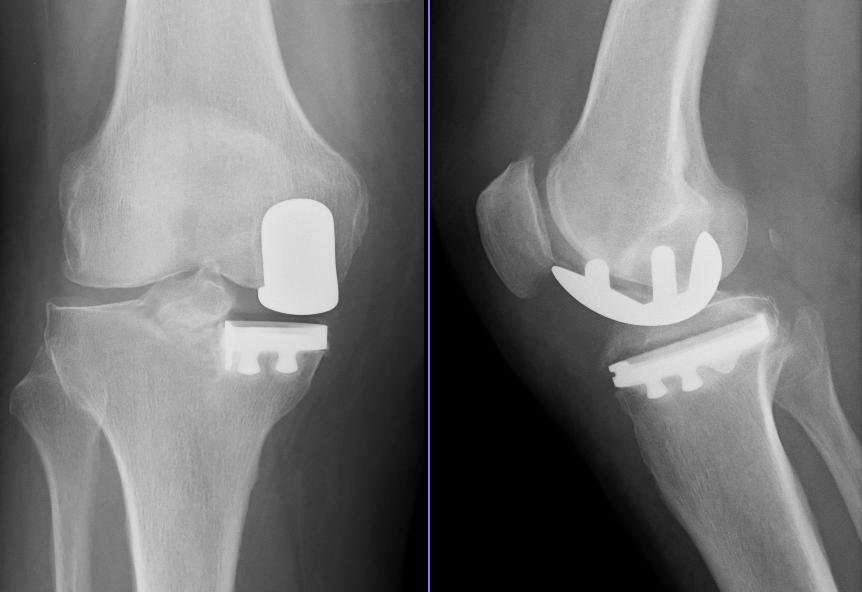
Types of knee arthroplasty:
Two major types of knee replacement sunguries
1) TKR (Total knee replacement): The surgery involves the replacement of both sides of the knee joint. It is the most common procedure. Surgery lasts between one and three hours. Experts say that the implant will last from 15 to 20 years. Despite having much less pain and better mobility, there will be scar tissue, which means there will always be some difficulty in moving and bending the knees. Most surgeons believe that TKR is a more reliable long term procedure.
2) PKR (Partial knee replacement) :This surgery is done when only one side of the knee joint is replaced. Hence, it does not last as long as a total replacement. Less bone is removed, so the incision is smaller.PKR is suitable foraround one in four people with osteoarthritis. Post-operative rehabilitation is simpler, there is less blood loss, lower risk of infection and blood clots. PKR in general includes a shorter hospital stay and recovery period.PKR often results in more natural movement in the knee. Most PKR patients are able to get up and about after their their operation more rapidly than TKR ones.
Indication for knee replacement arthroplasty: Today, a knee replacement surgery is considered a routine operation. Below are the three most common reasons for the procedure:
1. Osteoarthritis – This type of arthritis is age related caused by the normal long wear and tear of the knee joint. The majority of patients are over 50; however, younger people may be affected.
2. Rheumatoid arthritis – also called inflammatory arthritis, occurs when the membrane surrounding the knee joint is inflamated and thick. This inflammation becomes chronic and will damage the cartilage causing soreness and stiffness.
3. Post-traumatic arthritis – this type of arthritis is due to a severe knee injury. When the bones around the knee break or the ligaments tear, this will affect the knee cartilage. Sometimes, surgery is the best option.
Advice to the arthroplasty patients:
It is important that patients comply with the instructions given by doctors, nurses and the physical therapist.
1. Take iron supplements to aid wound healing and muscle strength.
2. Do everything possible to avoid a fall, which might mean further surgery.
3. Not bend down and lift heavy things, at least during the first few weeks.
4. Not to soak the wound until the scar is completely healed, otherwise there is a serious risk of infection.
5. Not to stay standing still for long periods. The ankles might swell.
6. Follow all the instructions carefully for all medications.
7. Follow the medical team’s advice on exercises to ensure rapid and proper mobility.
8. Have a footstool so that the affected leg may be elevated..
9. Make sure the shower has a secure handrail.
10. Make sure there are no loose carpet and wrinkly mats around the house, to prevent falls. 11. Look out for any signs and symptoms of infections, blood clots orpulmonary embolism.
12. If possible, have the bedroom downstairs.
13. When showering, use a stable, non-slippery bench or chair.
14. Use crutches, a walking stick, or a walker until the knee is strong enough to take your body weight.
15. In general six weeks after the operation, the person can resume normal day to day activities, but some pain and swelling will remain for up to 3 months.
