Concept of Hypothyroidism – This course is designed to understand the concept of community health nursing: nurses’ roles and interventions in family health, school health, occupational health, environmental health, elderly health care, gender issues, disaster management and principles and terminology of epidemiology. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in community health nursing.
Concept of Hypothyroidism
Definition of Hypothyroidism:
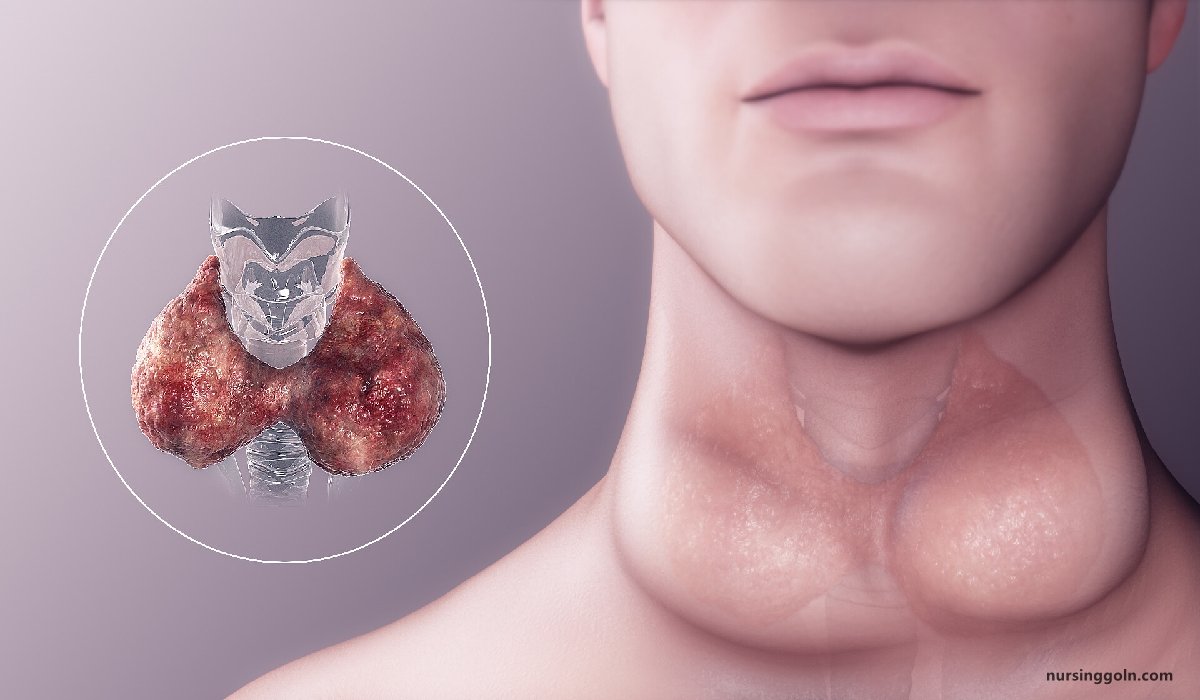
A clinical condition characterized by subnormal level of circulating thyroid hormones. It is associated with generalized non pitting oedema is called myxoedema.
Classification of Hypothyroidism
1. Primary: Here the abnormality is within thyroid gland, either structural or functional.
2. Secondary: Here the abnormality is in the hypothalamic-pituitary axis resulting in decreased production of TSH.
In another classification
- Goitrous: Associated with enlargement of thyroid gland..
- Nongoitrous: Not associated with enlargement of thyroid gland.
Causes of Hypothyroidism
1. Autoimmune
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- Spontaneous atrophic hypothyroidism
- Graves’ disease with TSH receptor-blocking antibodies
2. latrogenic
- Radioactive iodine ablation
- Thyroidectomy
- Drugs
- Carbimazole, methimazole, propylthiouracil
- Amiodarone
- Lithium
3. Transient thyroiditis:
- Subacute (de Quervain’s) thyroiditis
- Post-partum thyroiditis.
4. Iodine deficiency:
- e.g. In mountainous regions
5. Congenital:
- Dyshormonogenesis
- Thyroid aplasia
6. Infiltrative:
- Amyloidosis,
- Riedel’s thyroiditis,
- Sarcoidosis etc.
7. Secondary hypothyroidism:
- TSH deficiency
(Ref by: Davidson’s 741/21″)
Management of Hypothyroidism
Clinical feature
1. Fatigue
2. Increased sensitivity to cold
3. Constipation
4. Dry skin
5. Weight gain
6. Puffy face
7. Hoarseness
8. Muscle weakness
9. Elevated blood cholesterol level
10. Muscle aches, tenderness and stiffness
11. Pain, stiffness or swelling in your joints
12. Heavier than normal or irregular menstrual periods
13. Thinning hair
14. Slowed heart rate
15. Depression
16. Impaired memory
Investigation
1. Thyroid function tests
Total T4 & T3:
- T4 & T3-decreased.
- TSH-increased
Free T4 & T3-decreased.
2. Antithyroid antibodies
- Antimicrosomal /peroxidaseAb.
- Antithyroglobulin ab.
3. Thyroid scan, USG, FNAC.
4. Routine exam
- CBC- Anaemia
- Serum cholesterol & TG: Raised.
- Urine R/M/E.
- X-ray chest:
✓ Cardiomegaly
- ECG (>40 yrs):Low boltage ECG
✓ Ischaemia.
✓ Bradycardia.
- X-ray neck lateral and A/P view :
✓ Retrostemal extension
- Serum Na+ level:- decreased
Serum enzymes:
✓ Raised AST, CK & LDH.
Treatment
1. Oral thyroxin single dose/day.
Replacement dose: 50 µg/0.05 mg daily & then increased.
- 1st 3 wks-50 µg once daily
- 2nd 3 wks – 100 µg once daily
- Lifelong-150 µg once daily
Hypothyroidism with IHD:
- Start with low dose such as 25 µg/day.
2. If rapid response is required, tri-iodothyronine 20 µg 3 times daily,
Follow up:
- Regular thyroid function test-6 weekly & adjust thyroxin dose.
- Once the dose of thyroxin is established – thyroid function test-1-2 yearly.
(Ref by: Davidson’s 742/21 +750/20th)

Difference between Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism
| Traits | Hyperthyroidism | Hypothyroidism |
| 1. About | Also known as overactive thyroid | Also known as underactive thyroid. |
| 2. Most Common Cause | Graves’ disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter | Hashimoto’s disease, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis |
| 3. Other Causes | Thyroiditis, iodine deficiency, medication, thyroid nodules. | Thyroiditis, too much iodine, medication, genetics, hyperthyroidism treatments |
| 4. Diagnosis | Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test, thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) test, thyroid scan, radioactive iodine uptake test. | Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test, thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) test, thyroid scan, radioactive iodine uptake test. |
| 5. Treatment | Antithyroid medication (e.g., Methimazole) to slow overactive thyroid and, sometimes, beta blockers (e.g., Propranolol) to alleviate symptoms. | Synthetic thyroid hormone (e.g., Levothyroxine) or carefully monitored iodine supplementation. |
| 6. Occurrence | Less common. Roughly 1% of U.S. has overactive thyroid. Women more likely to suffer due to effects of pregnancy. | More common. Nearly 5% of U.S., could be as much as 20% if what is considered “normal” range is slightly adjusted. Women more likely to suffer due to effects of pregnancy. |
| 7. Appetite | Weight loss but increased appetite | Weight gain but loss of appetite |
| 8. Pulse | Tachycardia | Bradycardia |
| 9. Skin | Warm and moist | Dry and coarse |
| 10. Hair | Fine and soft | Thin and brittle |
| 11. Temperature Intolerance | Heat intolerance | Cold intolerance |