Concept about Ewing’s sarcoma – An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
Concept about Ewing’s sarcoma
Ewing’s sarcoma:
Ewing’s sarcoma is a small round-cell tumor typically arising in the bones, rarely in soft tissues, of children and adolescents. Ewing’s sarcoma has retained the most unfavorable prognosis of all primary musculoskeletal tumors

Common sites of Ewings Sarcoma:
1) Pelvis (31.25%)
2) Femur(20.3)
3) Tibia(11%)
4) Humerus (9.4%)
5) Scapula (6.25%)
6) Ribs (4.7%)

Pathology of Ewings sarcoma:
Histologically, Ewing’s sarcoma is composed of a homogeneous population of small round cells with high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratios that are arrayed in sheets. Thereis scant cytoplasms, which is pale, vacuolated and characterized by faded boundaries. In contrast, the nuclei are clearly visualized by their intense color.
Mitotic activity is typically low, Cytoplasmic glycogen, which appears as periodic acid-Schiff-positive diastase-positive digestive granules, is also usually present. Cytogenetic or immune histochemical studies are often required to differentiate Ewing’s sarcoma from other small round-cell tumors. The t(11;22)(q24;q12) translocation, the most common translocation diagnostic for Ewing’s sarcoma, is present in more than 85% of cases. Other diagnostic
Clinical features of Ewings tumors:
1) Age: 4-25 years (80%)
2) Sex: more common in males.
3) Site: Pelvis, femur, tibia, fibula
4) Location: Diaphysis of the long bone
5) Intermittent pain-worse at night.
6) Skin is red, dilated veins may be present.
7) Constitutional symptoms: Fever, sweating, chills, anaemia, leucocytosis.
[Ref- John Ebnezar, Text Book of orthopedics, 4 edition.page-634]
Investigation of Ewings sarcoma:
1) Plain x-ray:
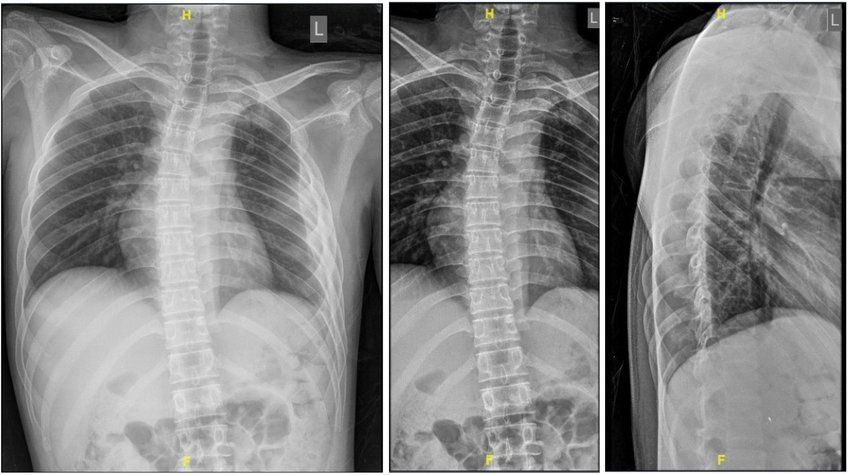
2) CT scan shows:

3) MRI shows:
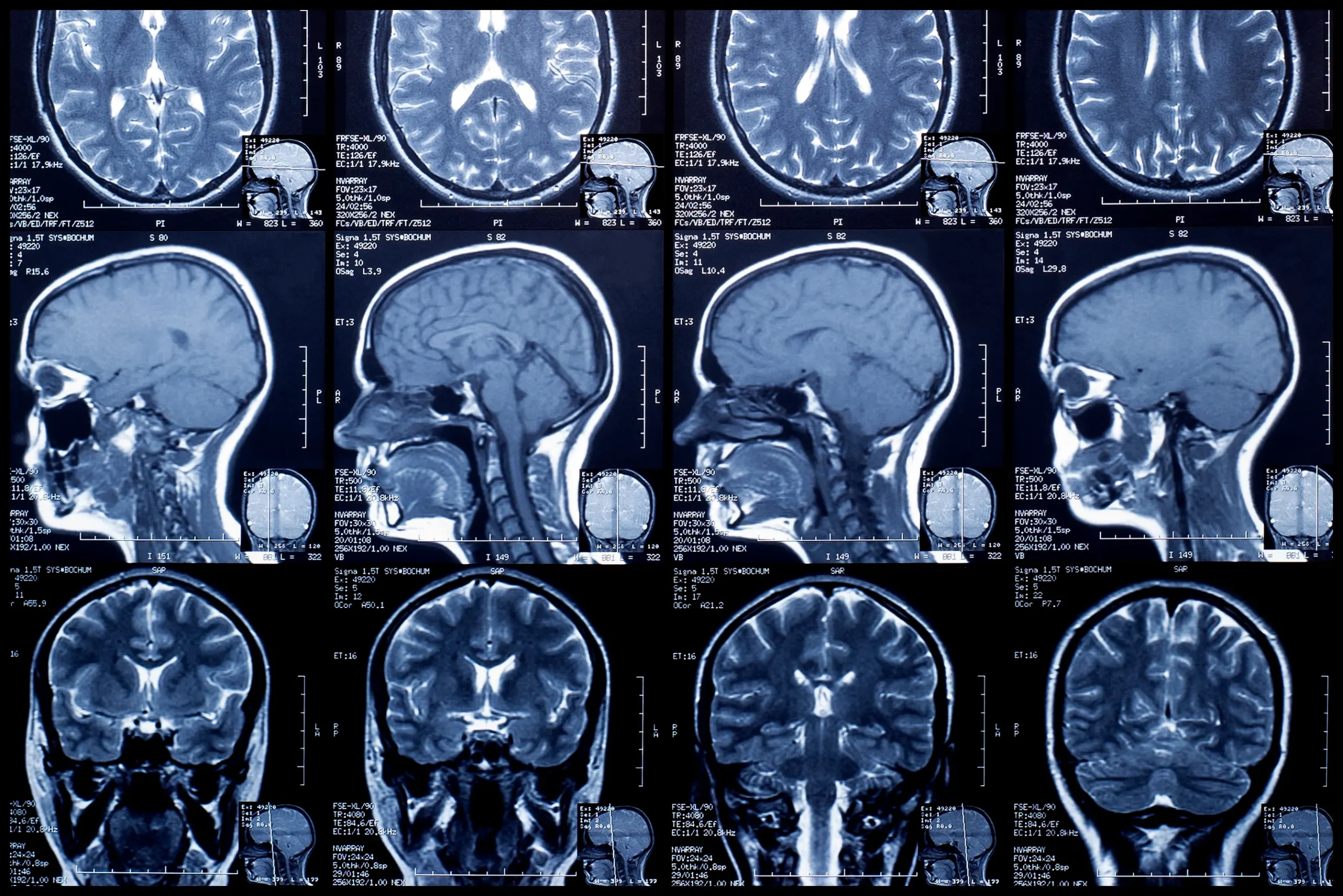
Management of Ewings sarcoma:
A. General management:
1. Complete bed rest.
2. Immobilization of the joint by cast.
3. Maintenance of personal hygiene.
4. Assess the level of pain and manage it.
5. Knowledge giving about care.
B. Medical management:
1. Analgesics
2. Carry out investigation to confirm the diagnosis.
3. Chemotherapy.
4. Surgery.
C. Nursing care:
1. Keep the patient in rest.
2. Reassure the patients and his or her family members.
3. Provide symptomatic treatment according to doctor’s advice.
4. Advice to the patient and his or her family members to carryout chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
5. Intravenous fluid may be given.
6. Adequate vitamin and nutrient containing diet will be given.
7. Advice to intake blood building food and frequent small meal.
8. Maintain personal hygiene.
9. Regular check up vital signs of the patient.
10. Signs and symptoms will be observed and recorded on a chart.
11. Encourage to the patient and his or her family members for surgical treatment.
12. All investigations will be done and patient prepare for operation, when failure conservative treatment.
13. Pre-operative medication and care will be given.
14. Patient in kept under internal fixation of the bone.
15. Amputation may be done for save of life.
16. Post-operative medication and care will be given.
17. Discharge planning.
