Skin Traction – An orthopedic nurse is a nurse who specializes in treating patients with bone, limb, or musculoskeletal disorders. Nonetheless, because orthopedics and trauma typically follow one another, head injuries and infected wounds are frequently treated by orthopedic nurses.
Ensuring that patients receive the proper pre-and post-operative care following surgery is the responsibility of an orthopedic nurse. They play a critical role in the effort to return patients to baseline before admission. Early detection of complications following surgery, including sepsis, compartment syndrome, and site infections, falls under the purview of orthopedic nurses.
Skin Traction
Skin traction:
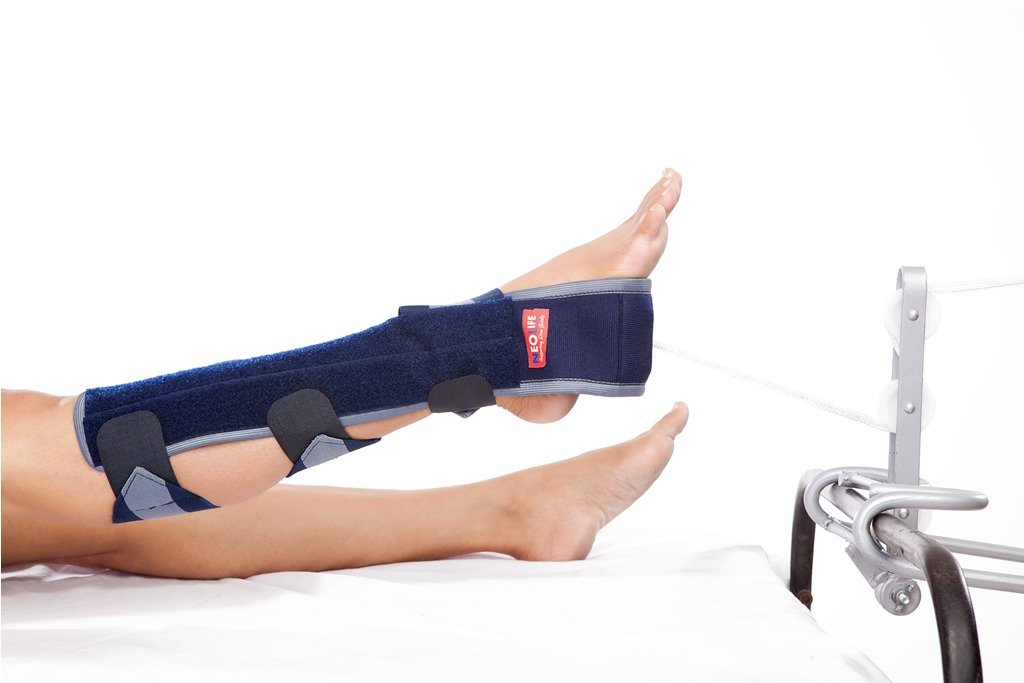
Skin traction isattached directly to the patients skin to immobilize a body part continuously or intermittently over a short or extended period.
(Ref-Lippincott, Adult Orthopedic Nursing, I edition,P-155)
Skin traction is one in which traction is applied over a large area of skin to exert a pulling effect on the injured limb and fix the bone in correct position.
Types of skin traction:
There are two types of skin traction such as,
1) Adhesive skin traction: Here adhesive material is used for strapping which is applied anteromedial and posterolateral on either side of the lower limb.
2) Non-adhesive skin traction: Useful in thin and atrophic skin and in patients sensitive to adhesive strap. It is less secure than the former.
(Ref-John Ebnezar’s “Orthopaedics for Nurses”, edition, P-66)
Indications of Skin traction:
1. Fracture of shaft of femur.
2. Fracture of neck of femur
3. Undisplaced fracture of acetabulam.
4. For low backache.
5. Correction of fixed flexion deformity of hip and knee.
6. Supra condylar fracture of humerus.
7. Intercondylar fracture of humerus.
8. After reduction of hip dislocation.
(Ref-John Ebnezar’s “Orthopaedics for Nurses”, 4″ edition, P-66)
Contraindications of skin traction:
There are some condition in which skin traction is neglected. These are given below:
1. Abrasions.
2. Lacerations.
3. Impaired circulation.
4. Dermatitis.
5. Marked shortening.
6. Allergy to plaster are some of the important contraindications for skin tractions.
(Ref-John Ebnezar’s “Orthopaedics for Nurses” 4″ edition, page-66)
Complications of skin traction:
There are some problems of skin traction. Specially for adhesive skin traction.
Most of the complications are skin related:
1. Allergy.
2. Excoriations around the malleoli.
3. Pressure sores around the malleoli. 4. Common peroneal nerve palsy.
5. Distal Oedema
6. Vascular obstruction
7. Peroneal nerve palsy
8. Skin Necrosis over bony prominence’s.
Equipments needed for skin traction:
1) Leucoplast/ Strape..
2) Roller bandage.
3) A wood havin central opening.
4) Measuring tape
5) A pulleys.
6) A rods for attached pulleys.
7) Strong ropes for hanging weight.
8) Appropriate weight.
9) Knife/Scissors to cut strape and ruller bandage.
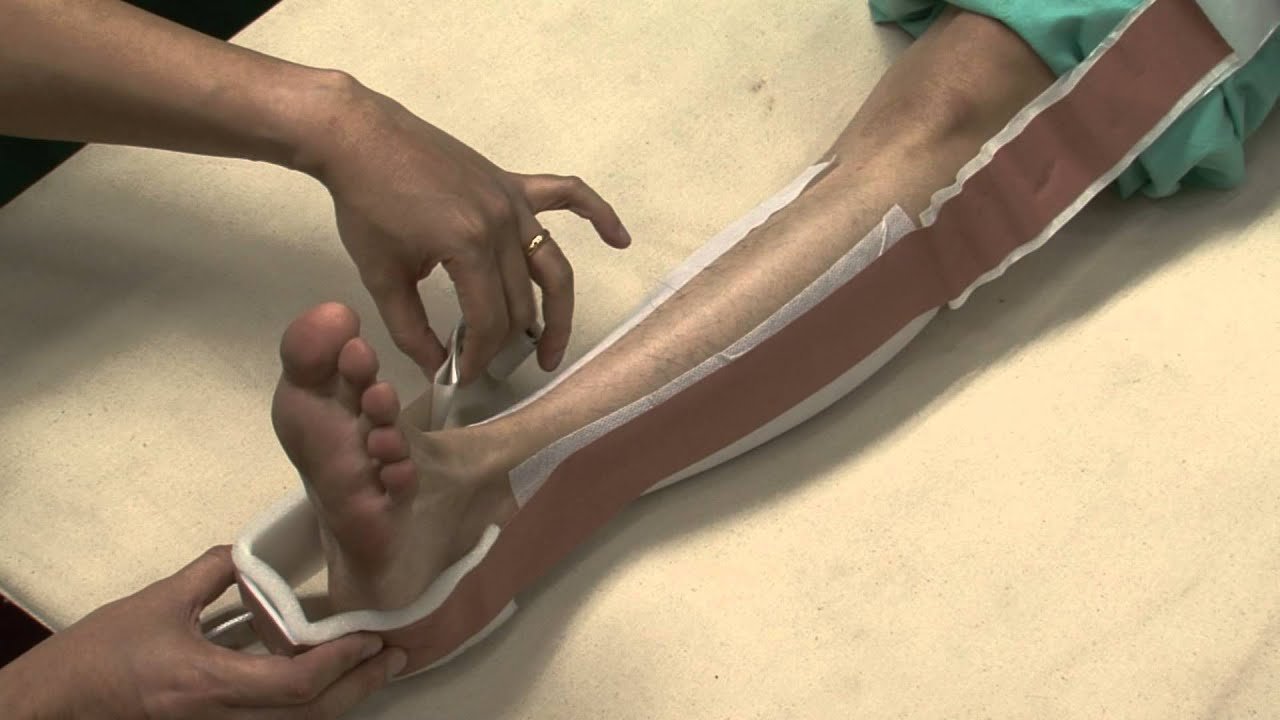
Procedure of application of Skin traction:
1. Greetings with the patients.
2. Give your activity in hospitals. e.g. staff nurse, Student nurse.
3. Explain the benefits of the skin traction.
4. Assure that it will not harm the patients and reduce the pain and swellings.
5. Keep the all equipments ready near the patients.
6. Two operators required, one exert continuous manual traction on the limb and other person apply skin traction.
7. During application patients should lie in flat position.
8. Clean the area of application Shaving the limb if more hair is present.
9. The assistance of this procedure will be seated at the foot end of the bed and exert a gentle steady manual traction on the limb.
10. Choose the correct size of strape/Leucoplast/Adhesive tape. 11. After measuring the length cut the strapping to required length.
12. Wrapping the limb medial to lateral.
13. A void the tighten of the Strape. Because it causes pressure sores. 14. Apply the retaining bandage, starting at distal to proximal
15. Then a rope is attached to a pulley and hanging a weight in the bed.
Nursing care of a patient surface with traction:
1. Patient should be kept in complete bed rest.
2. Affected part of the patient must be kept in comfortable position.
3. Assurance to the patient & his relatives.
4. General condition will be observed frequently & marked on a chart.
5. Personal hygiene especially skin care will be given frequently.
6. Position will be changed regularly for prevent pressure sore.
7. Bony prominence area will be checked frequently for signs of pressure or irritation.
8. The patient is allowed to move about rather freely in the bed.
9. Must be checked frequently to be sure the weight are hanging free & exerting the required amount of pull.
10. Care of the bowel & bladder.
11. Urinal & bed pan must be used carefully.
12. Aseptic precaution must be maintained for pin insertion / dressing.
13. Frequent fingered movement for improved blood circulation.
14. Sufficient fluid will be given maintain fluid balanced.
15. Nutrient & vitamin C will be given.
16. Medication will be given according to doctor’s.
Important skin traction:
1. Buck extension skin traction.
2. Dunlop s traction.
3. Gallows traction.

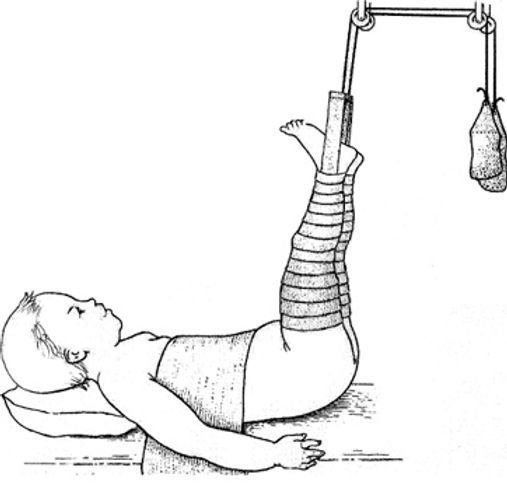
Buck Extension traction:
This is the commonest type of traction employed for lower limbs. It is used for Temporary treatment of –
1) Fracture of neck of femur.
2) Undisplaced fractures of actabulum. 3) After reduction of hip dislocation.
4) To correct minor fixed flexion deformity of hip and knee.
5) For low backache
(Ref-John Ebnezar’s “Text book of Orthopaedics” 4 edition, page-66)
Indication of Dunlop’s traction:
Used in upper limb-
1. Supracondylar fracture s of humerus.
2. Intercondylar fractures of humerus.
Indications of Gallow’s traction:
1. Traction of children < 2 years.
2. Fracture of shaft of femur.
If used in more than 2 years it causes vascular complications.
Read more:
