Common disorders and common terminology-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Common disorders and common terminology
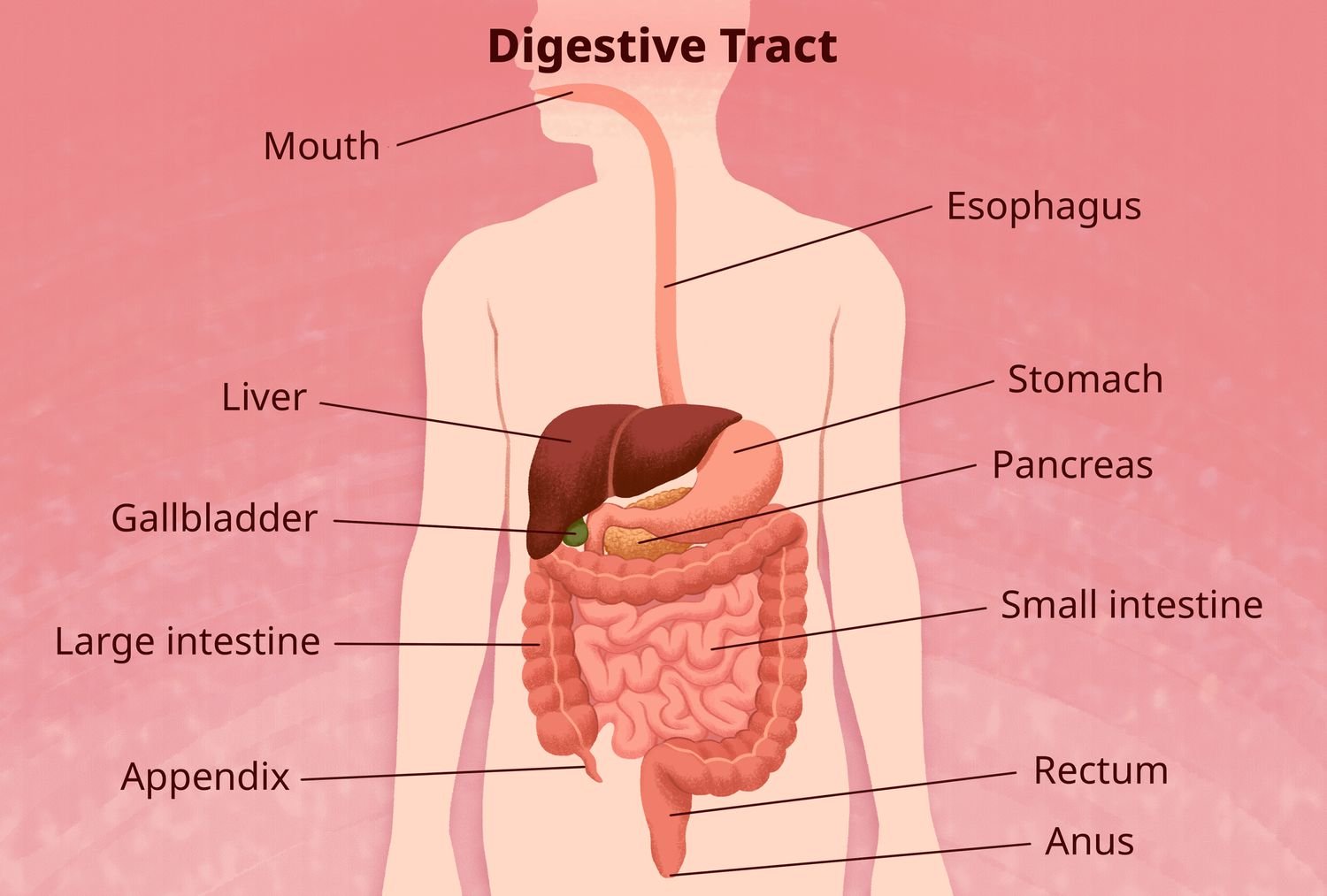
Dietary Fiber and the Digestive System
Dietary fiber consists of indigestible plant substances, such as cellulose, lignin, and pectin, found in fruits, vegetables, grains, and beans.
Insoluble fiber, which does not dissolve in water, includes the structural parts of plants such as fruit and vegetable skins and the bran coating around wheat and corn kernels: Insoluble fiber passes through the GI tract largely unchanged and speeds up the passage of material through the tract
Soluble fiber, which does dissolve in water, forms a gel that slows the passage of materials through the tract. It is found in abundance in beans, oats, barley, broccoli, prunes, apples, and citrus fruits.
It tends to slow the passage of material through the tract. People who choose a fiber-rich diet may reduce their risk of developing obesity, diabetes, atherosclerosis, gallstones, hemorrhoids, diverticulitis, appendicitis, and colon cancer Insoluble fiber may help protect against colon cancer, and soluble fiber may help lower blood cholesterol level.
Dental Caries
Dental caries, or tooth decay, involves a gradual demineralization (softening) of the enamel and dentin by bacterial acids. If untreated, various microorganisms may invade the pulp, causing inflammation and infection with subsequent death of the pulp. Such teeth are treated by root canal therapy.
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease refers to a variety of conditions characterized by inflammation and degeneration of the gums, bone, periodontal ligament, and cementum Periodontal diseases are often caused by poor oral hygiene, by local irritants, such as bacteria, impacted food, and cigarette smoke, or by a poor “bite.”
Peptic Ulcer Disease
Five to ten percent of the US population develops peptic ulcer disease (PUD) each year. An ulcer is a craterlike lesion in a membrane, ulcers that develop in areas of the GI tract exposed to acidic gastric juice are called peptic ulcers.
The most common complication of peptic ulcers is bleeding, which can lead to anemia. In acute cases, peptic ulcers can lead to shock and death Three distinct causes of PUD are recognized: (1) the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, (2) nonsteroidal anti- inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin, and (3) hypersecretion of HCI
Appendicitia
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix.Appendectomy (surgical removal of the appendix) is recommended in all suspected cases because it is safer to operate than to risk gangrene, rupture, and peritonitis
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer is among the deadliest of malignancies. An inherited predisposition contributes to more than half of all cases of colorectal cancer. Intake of alcohol and diets high in animal fat and protein are associated with increased risk of colorectal cancer, dietary fiber, retinoids, calcium, and selenium may be protective.
Signs and symptoms of colorectal cancer include diarrhea, constipation, cramping, abdominal pain, and rectal bleeding Screening for colorectal cancer includes testing for blood in the feces, digital rectal examination, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, and barium enema
Diverticular Disease
Diverticulosis is the development of diverticula, saclike outpouchings of the wall of the colon in places where the muscularis has become weak. Many people who develop diverticulosis have no symptoms and experience no complications.
About 15% of people. with diverticulosis eventually develop an inflammation known as diverticulitis, characterized by pain, either constipation or increased frequency of defecation, nausea, vomiting, and low-grade fever. Patients who change to high-fiber diets often show marked relief of symptoms.
Heartburn
The lower esophageal sphincter is not a true sphincter muscle that can be identified histologically, and it does at times permit the acidic contents of the stomach to enter the esophagus. This can create a burning sensation. comumonly called heartburn.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver caused by viruses, drugs, and chemicals, including alcohol Hepatitis A (infectious hepatitis), caused by the hepatitis A virus, is spread by fecal contamination of food, clothing, toys, eating utensils, and so forth (fecal-oral route). It does not cause lastingliver damage.
Hepatitis B, caused by the hepatitis B virus, is spread primarily by sexual contact and contaminated syringes and transfusion equipment. It can also be spread by any secretion via saliva and tears. Hepatitis B can produce chronic liver inflammation. Vaccines are available for hepatitis B and are required for certain individuals, such as health-care providers.
Hepatitis C. caused by the hepatitis C virus, is clinically similar to hepatitis B. It is often spread by blood transfusions and can cause cirrhosis and liver cancer. Hepatitis D is caused by the hepatitis D virus It is transmitted like hepatitis B.
A person must be infected with hepatitis B to contract hepatitis D Hepatitis D results in severe liver damage and has a fatality rate higher than that due to infection with hepatitis B virus alone spread like hepatitis A. Although it does not cause chronic liver disease, the hepatitis B virus is responsible for a very high death rate in pregnant women.

Anorexia nervosa
A chronic disorder characterized by self-induced weight loss, negative perception of body image, and physiological changes that result from nutritional depletion. Patients have a fixation on weight control and often abuse laxatives, which worsens their fluid and electrolyte imbalances and nutrient deficiencies. The disorder is found predominantly in young, single females, and it may be inherited Individuals may become emaciated and may ultimately die of starvation or one of its complications
Canker sore (KANG-ker)
Painful ulcer on the mucous membrane of the mouth that affects females more often than males, usually between ages 10 and 40, it may be an autoimmune reaction or result from a food allergy
Cholecystitis (chole bile, cyst bladder, -itis =inflammation of)
In some cases, an autoimmune inflammation of the gallbladder, other cases are caused by obstruction of the cystic duct by bile stones.
Cirrhosis
Distorted or scarred liver as a result of chronic inflammation due to hepatitis, chemicals that destroy hepatocytes, parasites that infect the liver, or alcoholism; the hepatocytes are replaced by fibrous or adipose connective tissue. Symptoms include jaundice, edema in the legs, uncontrolled bleeding, and increased sensitivity to drugs.
Colostomy (stomy provide an opening) The diversion of the fecal stream through an opening in the colon, creating a surgical “stoma” (artificial opening) that is affixed to the exterior of the abdominal wall. This opening serves as a substitute anus through which feces are eliminated into a bag wom on the abdomen.
Inflammatory bowel disease Disorder that exists in two forms: (1) Crohn’s disease, an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the distal ileum and proximal colon, in which the inflammation may extend from the mucosa through the sensa, and (2) ulcerative colitis, an inflammation of the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract, umally limited to the large intestine and usually accompanied by rectal.
Meeding gastrointestinal tract in which a person reacts to stress by developing symptoms (such as cramping and abdominal pain) associated with alternating patterns of darthea and constipation Excessive amounts of mucus may appear in feces, other symptoms include flatulence, nausea, and loss of appetite
Malocclusion
(mal bad, occlusion =to fit together) Condition in which the surfaces of the maxillary (upper) and mandibular (lower) teeth fit together poorly.
Nausca
Discomfort characterized by a loss of appetite and the sensation of impending vomiting. Its causes include local imtation of the gastrointestinal tract, a systemic disease, brain disease or injury, overexertion, or the effects of medication or drug overdose
Traveler’s diarrhea
Infectious disease of the gastrointestinal tract that results in loose urgent bowel movements, cramping, abdominal pain. malaise, nausea, and occasionally fever and dehydration. It is acquired through ingestion of food or water contaminated with fecal material typically containing bacteria (especially Escherichia coli), viruses or protozoan parasites are a less common cause.
Obesity
Obesity is the most common and most expensive nutritional problem. A convenient and reliable indicator of body fat is the body mass index (BMI), which is body weight (in kilograms) divided by the square of height (in meters). Values above 25 are abnormal Individuals with values of 25-30 are overweight, and those with values > 30 are obese.
Pancreatitis
(inflammation of the pancreas) may result when conditions such as alcoholism, gallstones, traumatic injury, infections, or toxicosis from various drags provoke activation of digestive enzymes within the pancreas.
Leakage of trypsin into the blood also occurs, but trypsin is inactive in the blood because of the inhibitory action of two plasma proteins, al- antitrypsin and o2-macroglobulin. Pancreatic amylase may also leak into the blood, but it is not active because its substrate (starch) is not present in blood. Pancreatic amylase activity can be measured in witre, however, and these measurements are commonly performed to assess the health of the pancreas.
Read more:
