Anaemia with their causes-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Anaemia with their causes
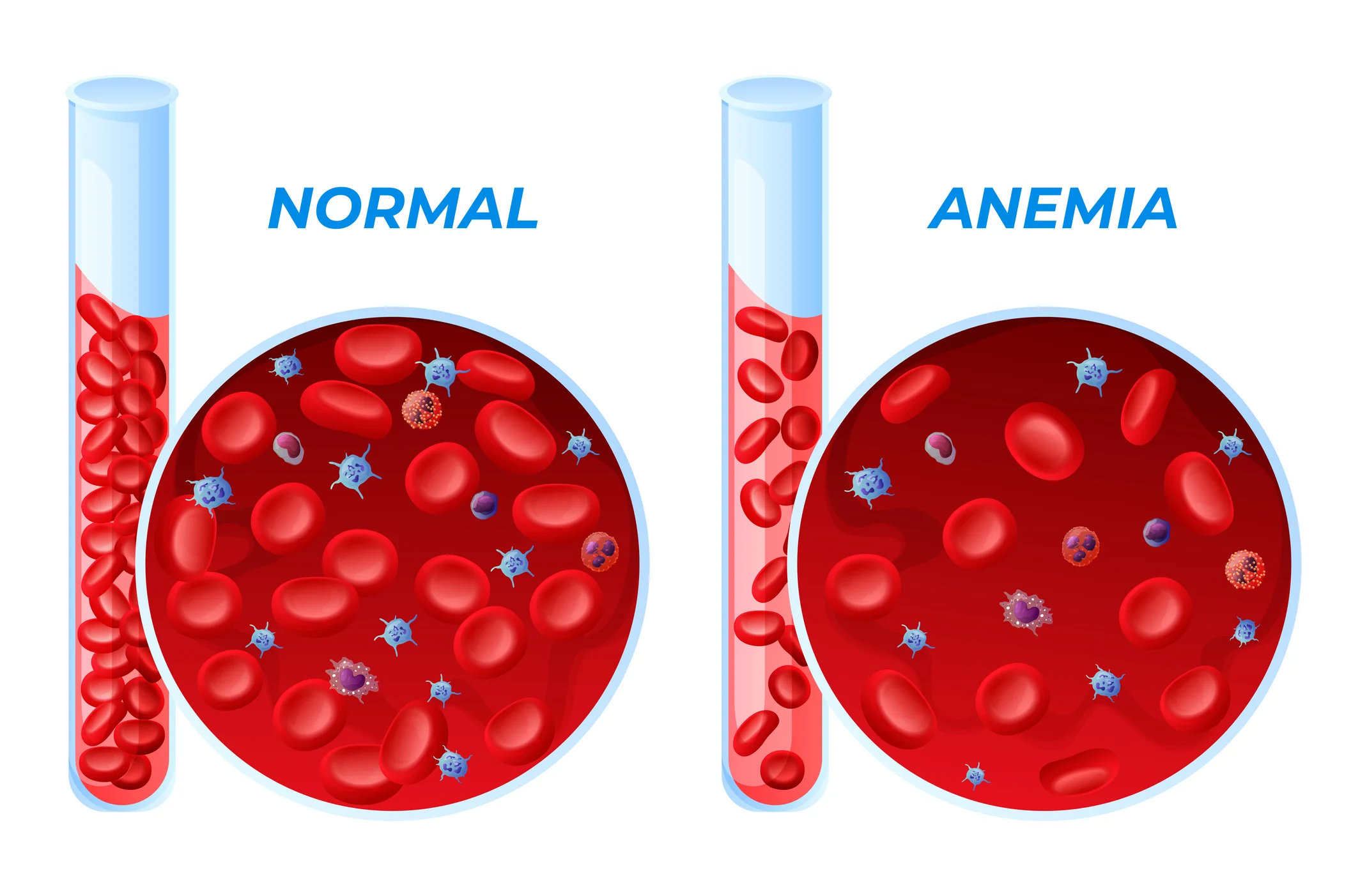
Anaemia
When the hemoglobin level in blood is below the lower limit/extreme of the normal range for the age and sex of the individual is called anaemia.
or,
Decrease the hemoglobin concentration in the peripheral blood below the normal level in respect of age & sex is called anaemia
The normal Range
In adult male: 14-18 gm/dl of blood.
In adult female: 12-15.5 gm/dl of blood.
Classification of anaemia:
Aetiological classification of anaemia:
- Iron deficiency anaemia (Most common in Bangladesh)
- Blood loss anaemia.
- Aplastic anaemia
- Megaloblastic anaemia
- Hemolytic anaemia.

Causes of anemia:
| Anemia | Causes |
| Malnutrition. | |
| 1. Iron deficiency anemia | Hookworm infestation |
| Frequent pregnancies | |
| Excessive menstrual bleeding. | |
| 2. Blood loss anemia | Rapid hemorrhage. |
| Chronic blood loss. | |
| Excessive X-ray treatment | |
| 3. Aplastic anemia | Certain industrial chemicals. |
| Gamma ray radiation. | |
| Drug. e,g-Chloramphenicol | |
| 4. Megaloblastic anemia | Deficiency of Vit B12& Folic acid |
| Deficiency of intrinsic factor | |
| 5. Hemolytic anemia | RBC membrane defect |
| Enzyme deficiency. | |
| Auto immune diseases etc. |
Haemoglobin (hb)
Hemoglobin is contained in red blood cells. It consists of the protein ‘globin’ united with the pigment heam’ and ‘Globulin’ is a polypeptide. Haemoglobin Carries oxygen from lungs to tissue & carries carbon-dioxide from the tissue to lung
Function:
- Haemoglobin is an oxygen carrier from lung to tissues
- It is a carbon dioxide carrier from tissues to lung
- It gives red color to the blood.
- It maintains the shape of the red blood cell
- It acts as a buffer
- Haemoglobin interacts with other ligands.
Normal Range of Hb:
In adult male : 14-18 gm/dl of blood.
In adult female: 12-15.5 gm/dl of blood.
At birth: About 23 gm/dl of blood.
At one month: About 10.5 gm/dl of blood.
At one year: About 12 gm/dl of blood.
Leukemia
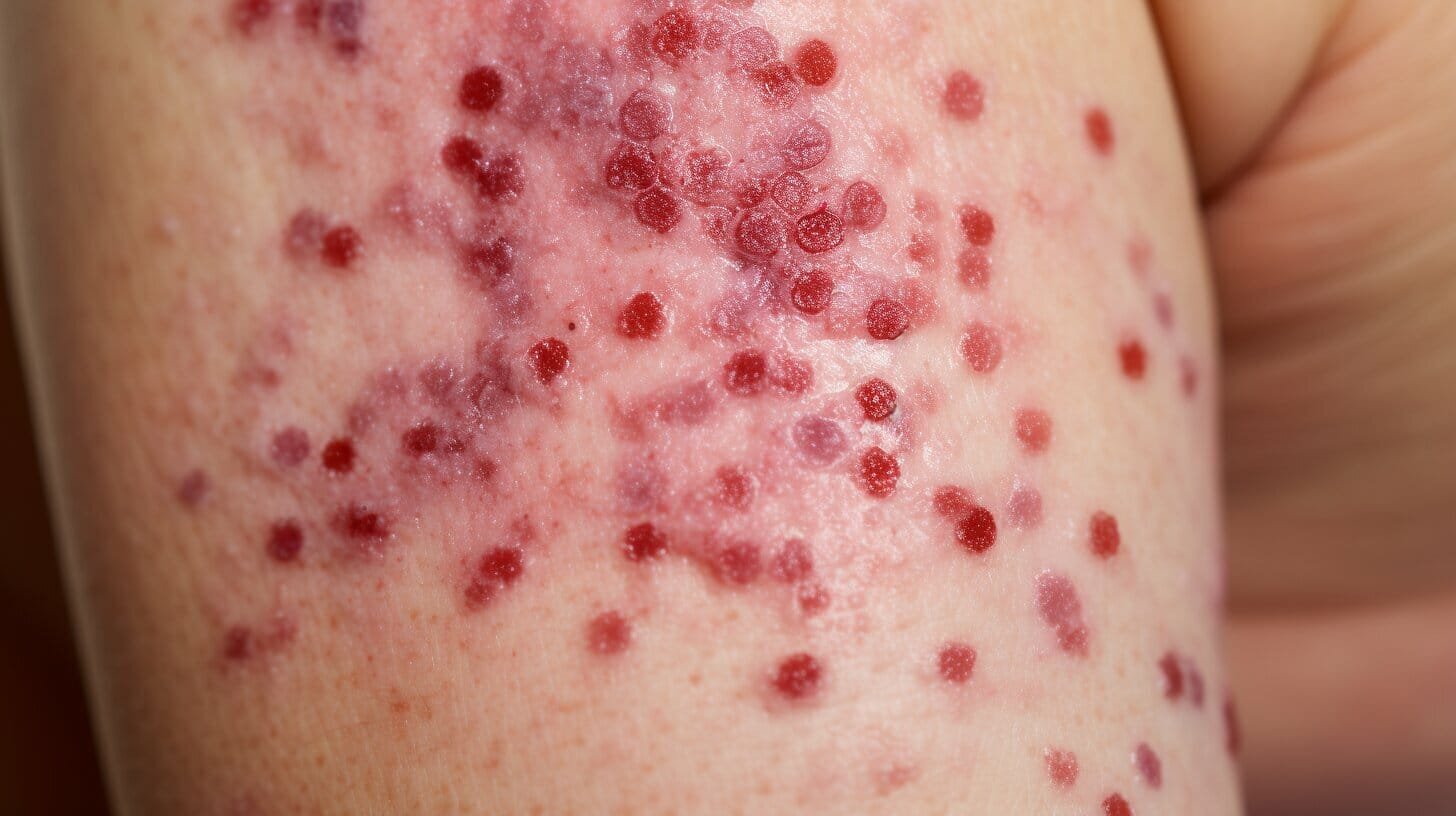
The term leukemia refers to a group of red bone marrow cancers in which abnormal white blood cells multiply uncontrollably. The accumulation of the cancerous white blood cells in red bone marrow interferes with the production of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
As a result, the oxygen- carrying capacity of the blood is reduced, an individual is more susceptible to infection, and blood clotting is abnormal. In most leukemias, the cancerous white blood cells spread to the lymph nodes, liver, and spleen, causing them to enlarge.
(Ref:-J. TORTORA,The essentials of anatomy and physiology, 8 edition-P-372)
Read more:
