Functions of male and female reproductive system – The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Functions of male and female reproductive system
Reproduction is the process of producing a new human. And Sexual reproduction is the process by which organisms produce offspring by making germ cells called gametes. And the reproductive system is that systems by which the male and female gonads (testes in males and ovaries in females), associated ducts and glands, external and internal genitalia that function in the procreation (the sexual activity of conceiving and bearing offspring) of offspring.
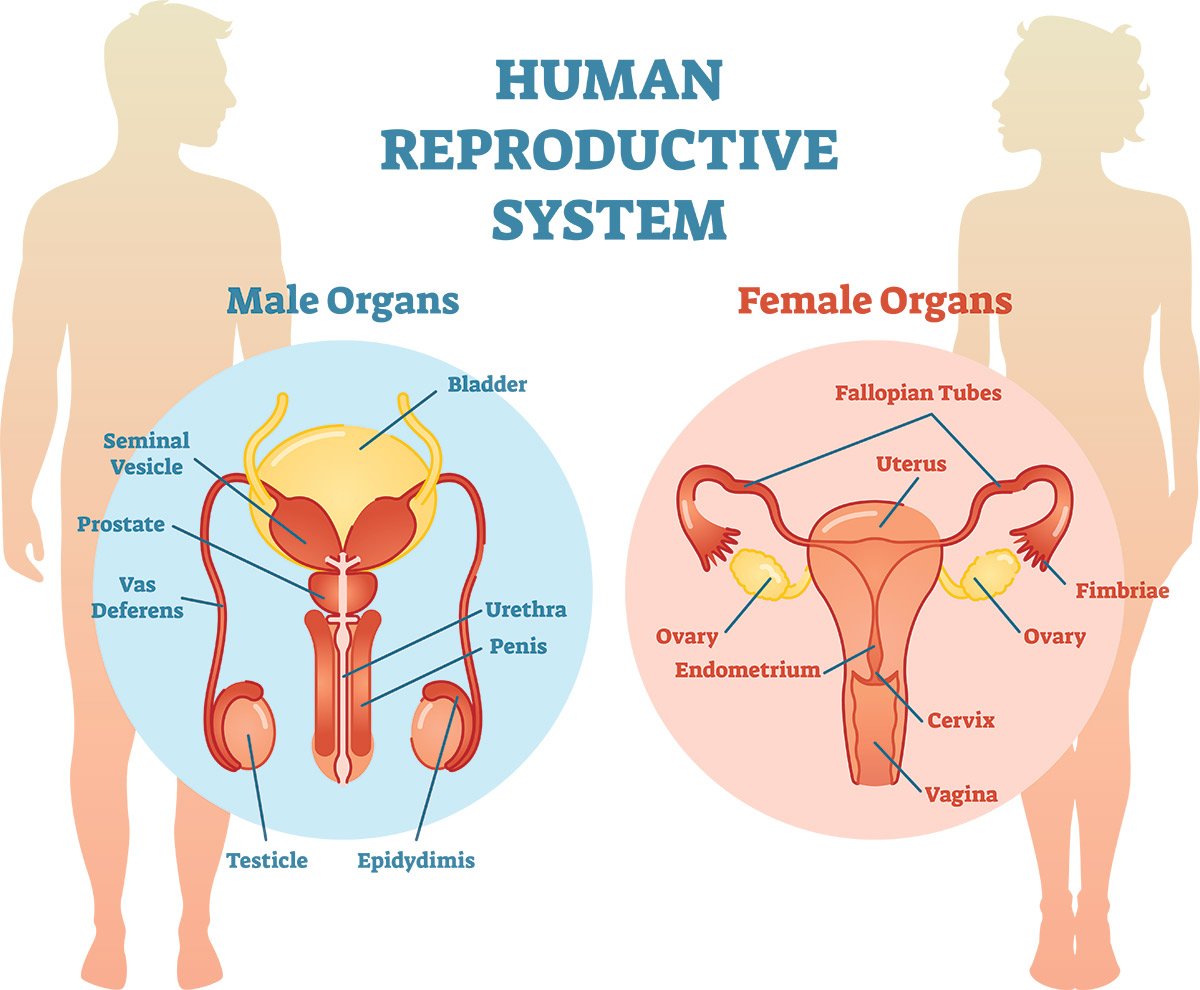
- In women these include the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, clitoris, and vulva.
- In men they include the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, ejaculatory duct, prostate, and penis.

The functions of male reproductive system.
Main functions of male reproductive system are
- Produce, maintain, and transport sperm (the male reproductive cells) and protective fluid (semen).
- Discharge sperm within the female reproductive tract during sex.
- Produce and secrete male sex hormones (eg: testosterone) responsible for maintaining the male reproductive system.
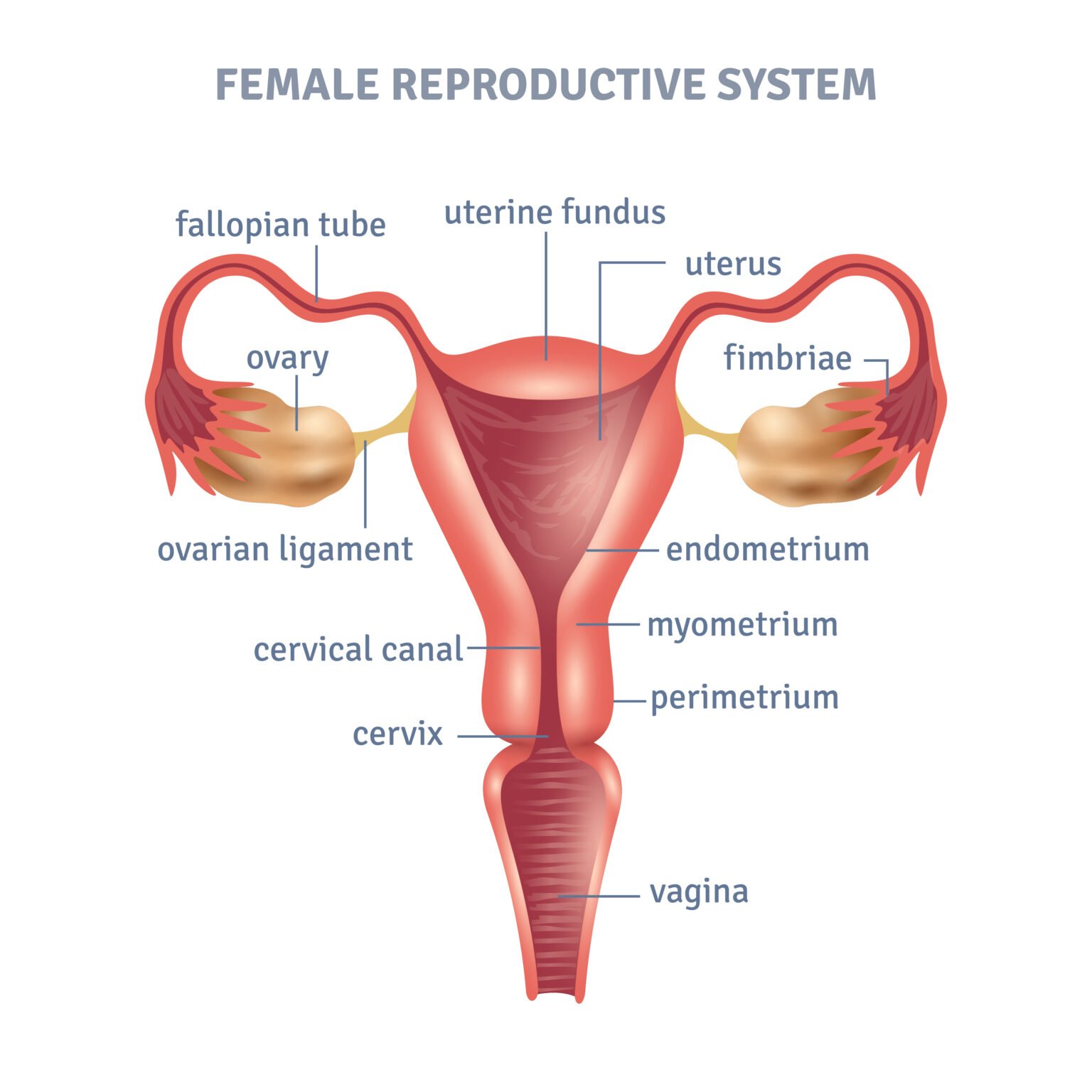
The functions of female reproductive system.
Main functions of female reproductive system are
- Formation of female gametes, (ova).
- Reception of male gametes, (spermatozoa).
- Provision of suitable environments for fertilization of the ovum by spermatozoa and development of the resultant fetus.
- Parturition (childbirth).
- Lactation, the production of breast milk, which provides complete nourishment for the baby in its early life.
(Ref: Ross & Wilson 9th /438-452p + K. Indu, 1″ edition,P-385-399)
Read more:
