Semen and sperm – The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Semen and sperm
Semen
Semen or seminal fluid refers to the fluid ejaculated during the orgasm at the time of male sexual act. It is the mixture of sperm and other secretions from the male reproductive organs. The volume of semen in a typical ejaculation is 2.5 to 5 milliliters, with 50 to 150 million sperm per milliliter. When the number falls below 20 million per milliliter, the male is likely to be infertile.
Components:
- Spermatozoa.
- Secretion of seminal vesicles.
- Secretion of prostste gland.
- Secretion of bulbourethral gland.
Volume. Average 2.5 to 3.5 ml per ejaculation.
Colour: Appearance of semen is milky due to prostatic fluid.
The sperm
- The sperm are released into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule and leave the testes. They then enter the epididymis where they undergo their final maturation and become capable of fertilizing a female gamete.
- Sperm production begins at puberty and continues throughout the life of a male.
- The entire process, beginning with a primary spermatocyte, takes about 74 days. About 300 million sperm mature each day.
- After ejaculation, the sperm can live for about 48 hours in the female reproductive tract.
There are 3 parts make up the sperm as following.
- The head contains substances that help the sperm enter the egg.
- The mid piece contains structures that release the energy needed for the long trip through the female reproductive system.
- The tail is made of proteins that help the sperm move.
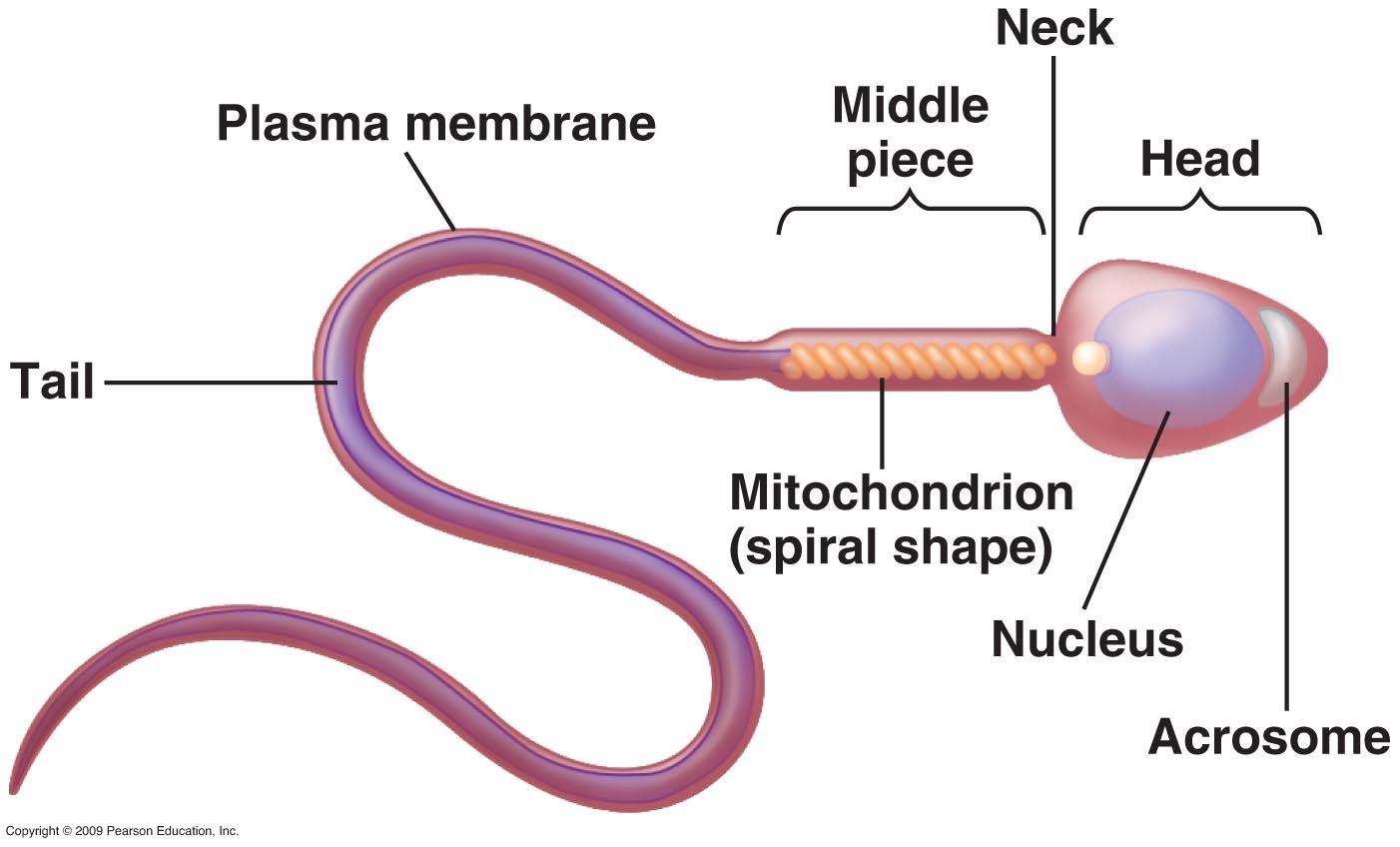
(Ref: K. Indu, I ed P-389,390)
Semen Analysis
| Characteristic | Reference Value |
| Volume of ejaculate | 1.5-5.0 ml |
| Sperm count | 40-250 million/ml |
| Sperm motility: Percentage of motile forms: | |
| 1 hour after ejaculation | 70% or more |
| 3 hours after ejaculation | 60% or more |
| Leukocyte count | 0-2,000/ml |
| PH | 7.2-7.8 |
| Fructose concentration | 150-600 mg/100 ml |
(Ref:-Stuart Ira Fox, Human Physiology, twelfth edition, P-716)
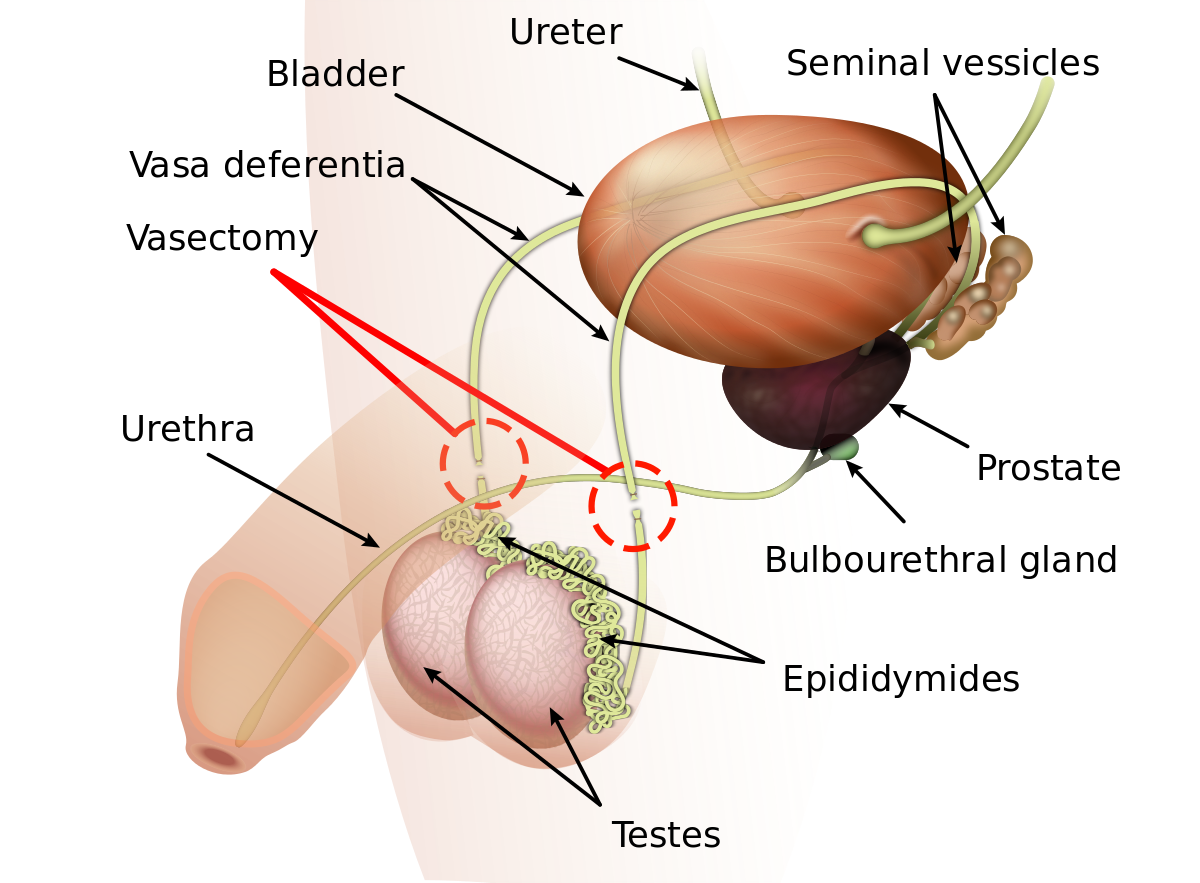
Vasectomy
Vasectomy is the permanent methods of male contraception or sterilization by a surgical procedure is called a vasectomy. In this procedure, each ductus (vas) deferens is cut and tied through an incision in the scrotum.