Endocrine system and endocrinology-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Endocrine system and endocrinology
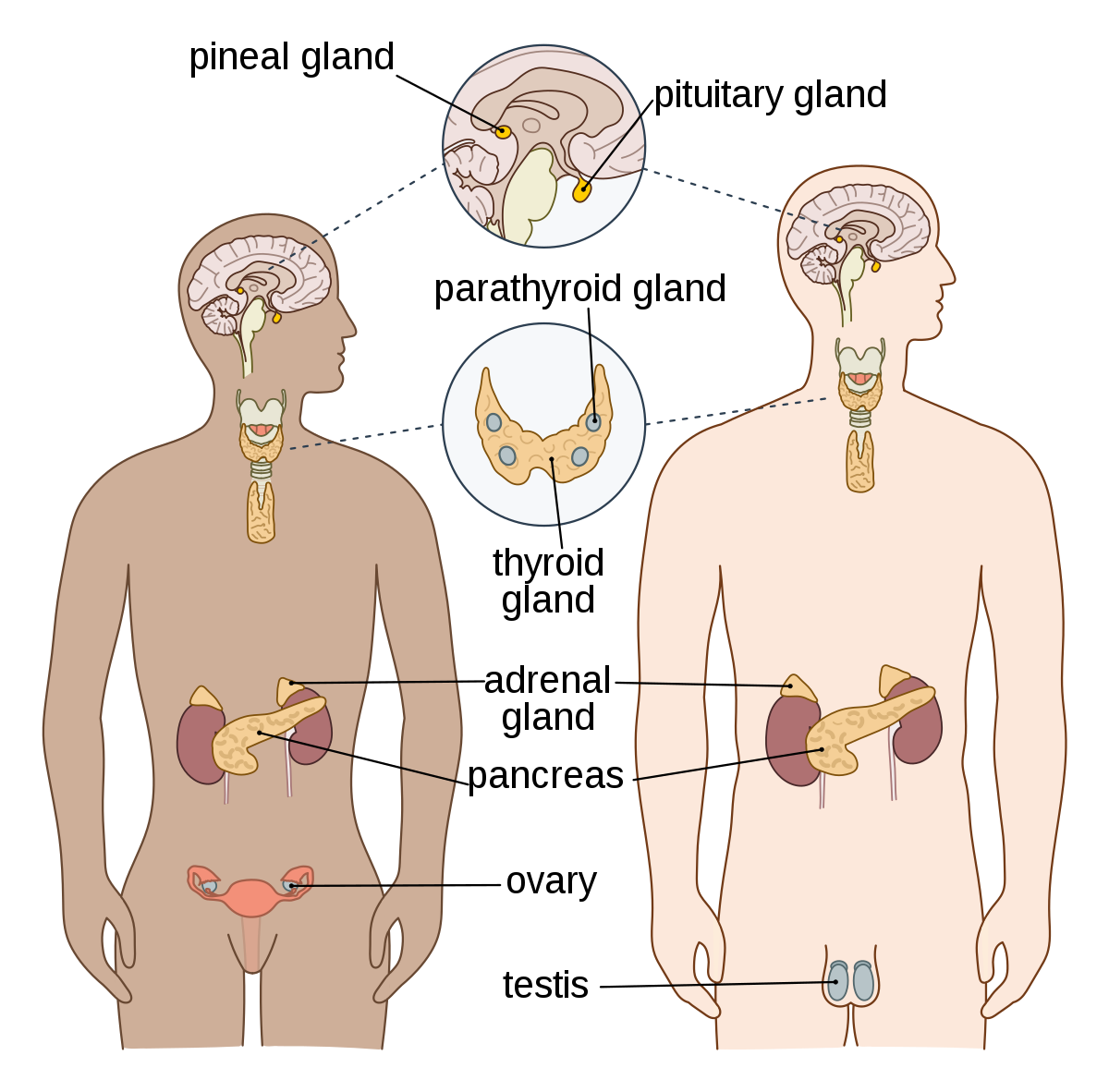
Endocrine system
The endocrine system consists of several endocrine glands plus many hormone-secreting cells in organs that have functions besides secreting hormones.
In contrast to the nervous system, which controls body activities through the release of neurotransmitters at synapses, the endocrine system releases hormones into interstitial fluid (fluid that surrounds cells) and then into the bloodstream.
The circulating blood then delivers hormones to virtually all cells throughout the body, and cells that recognize a particular hormone will respond. The nervous system and endocrine system often work together. For example, certain parts of the nervous system stimulate or inhibit the release of hormones by the endocrine system.
(Ref: J. TORTORA, 8th edition, P-329)
The endocrine system which denotes “internal” secretion of substances (hormones) which are released into the circulation by various endocrine glands and act at a site distant from their site of origin and is mainly concerned with different metabolic functions of the body especially the chemical reaction.
Endocrinology
Endocrinology – Endocrinologyis the scientific and medical specialty concerned with hormonalsecretions and the diagnosis and treatment of disordersof the endocrine system.
Endocrine gland
The word “endocrine” come from the Greek and means ‘internal secretion.
Definition:
The endocrine glands are the ductless glands that secrete chemical substances called hormone directly into the blood, which is transported by the circulation to its target cells in distant organs. Some of the endocrine glands produce single hormone, others two hormones or more, the pituitary gland, for example, produces a number of hormones which control the activity of many of the other endocrine organs, for this reason the pituitary gland has been described as “the master gland of the body” (See the figure # 6.1)
(Ref: Ross & Wilson 9th ed, P-214+P.Evelyn, 16h,P-276
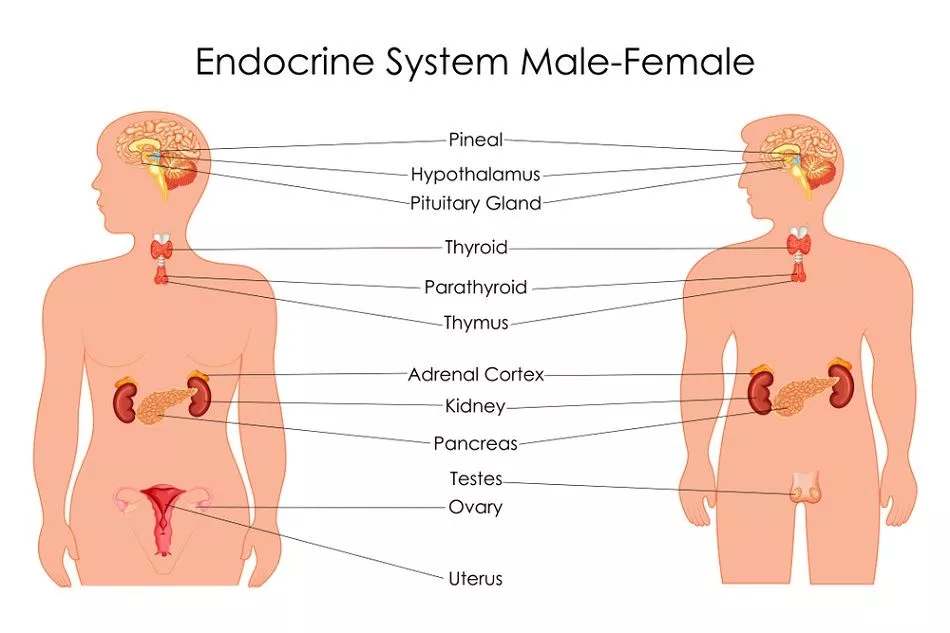
The major endocrine glands of the body are……
- 1- Hypothalamus
- 1- Pituitary gland
- 1-Thyroid gland
- 4-Parathyroid glands
- 2-Adrenal (suprarenal) glands
- The pancreatic islets (islet of langerhans)
- 1-Pineal gland
- 1-Thymus gland
- 2-Ovaries in the female
- 2-Testes in the male
(Ref: Ross & Wilson 9th ed, P-214+P.Evelyn, 16
