Growth hormone-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Growth hormone
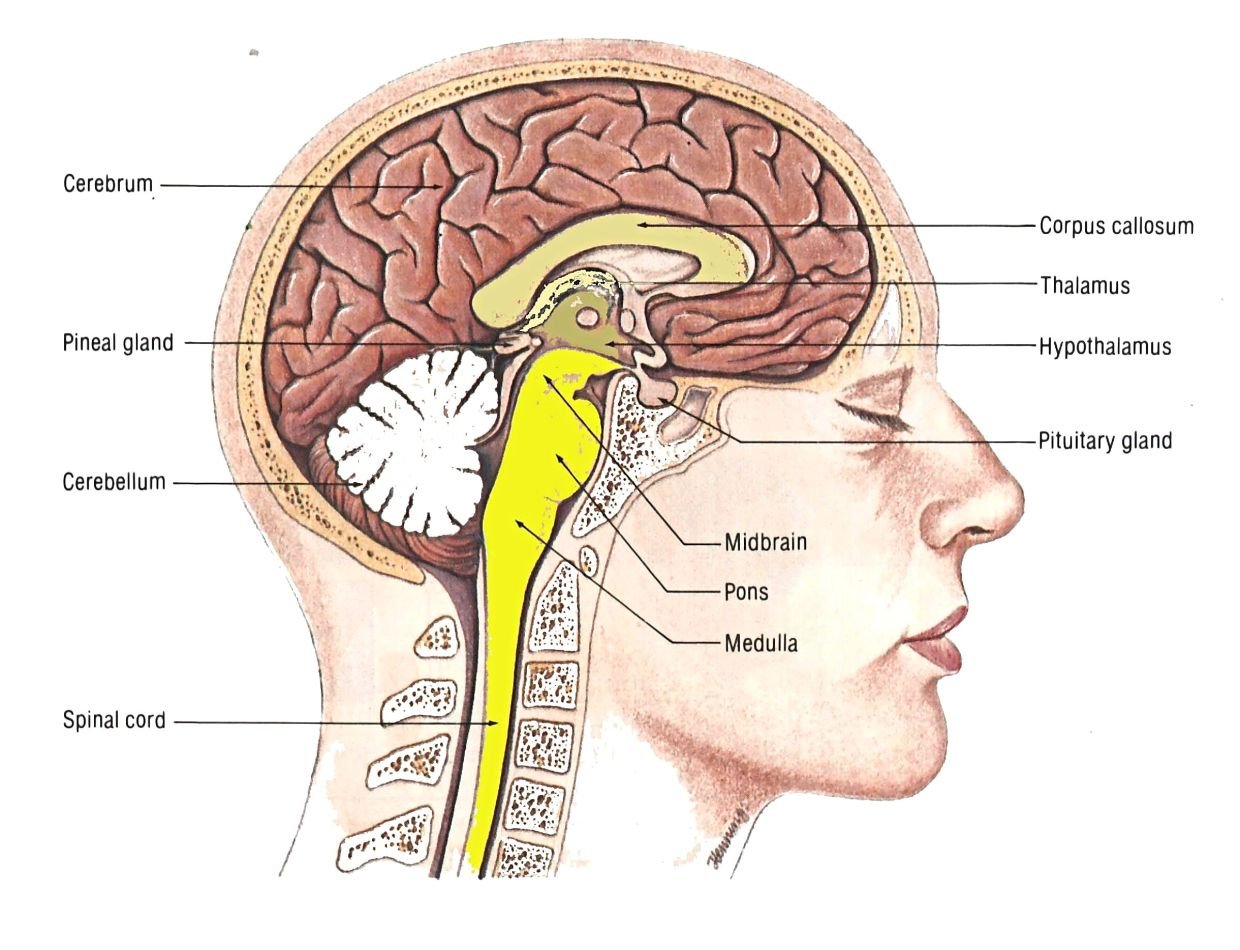
The growth hormone is produced by the anterior pituitary. It is made up of 191 amino acids that make a long single-chain polypeptide. It is synthesized in somatotropic cells found in the anterior pituitary gland These cells also store and release the hormone
The growth hormone is responsible for the regulation of several physiological processes such as growth and metabolism. It is also used as a drug in animals and plants
Function of Growth Hormone
Growth hormone performs the following important functions:
- It maintains normal body structure and metabolism
- Maintains, builds, and repairs healthy tissue in the brain and other organs.
- The growth hormone is utilized widely in medicines that heal the growth disorders in children and hormone deficiency in adults
- The growth hormone enhances growth in adolescents and children.
- It also contributes to the regulation of body fluids, fat metabolism, sugar and also the functions of the heart
- The growth hormone reduces body fat by increasing bone density and muscle mass
Adrenal glands
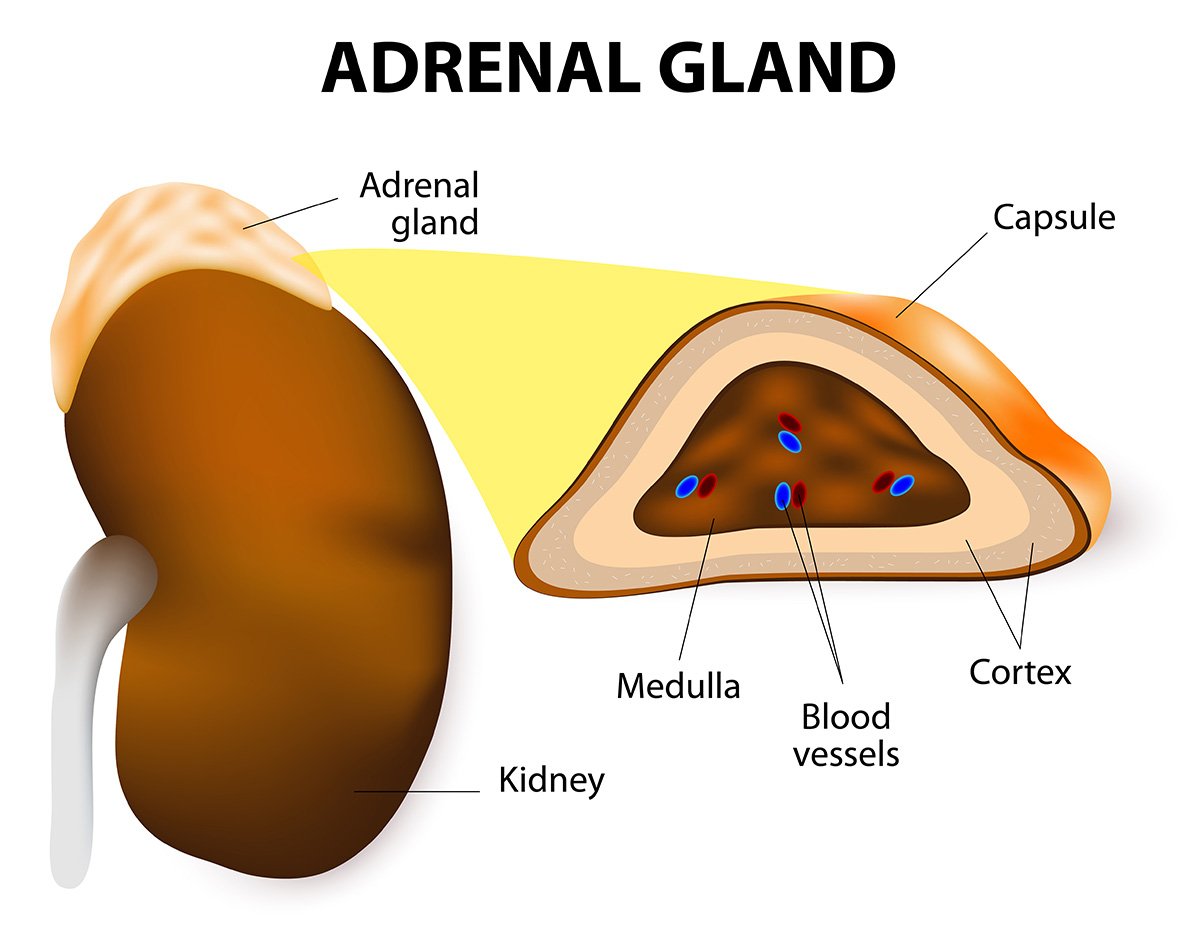
There are two adrenal glands, one lying topor the superior borders of the kidneys of each kidney. Each adrenal gland has regions that producedifferent hormones: the outer adrenal cortex, which makesup 85% of the gland, and the inner adrenal medulla, that function as separate glands.
Adrenal Cortex Hormones
The adrenal cortex consists of three distinct layers or zones, each of which synthesizes and secretes different steroid hormones.
- The outer zone or Zona glomerulosareleases hormones called mineralocorticoids because they affect mineral homeostasis
- The middle zone or Zona fasciculatareleases hormones called glucocorticoids because they affect glucose homeostasis.
- The inner zone orZona reticularisreleases androgens/Sex hormones (steroid hormones that have masculinizing effects).
Adrenal Medulla
The innermost region of each adrenal gland, the adrenal medulla, consists of sympathetic postganglionic cells of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) that are specialized to secretehormones. The two main hormones of the adrenal medullae are epinephrineand norepinephrine (NE), also called adrenaline and noradrenaline.
Function:-
These two hormones from the adrenal medulla increase the cardiac output and heart rate, dilate coronary blood vessels, increase mental alertness, increase the respiratory rate, elevatethe metabolic rate and increase blood levels of glucose and fatty acids.
(Ref:- Stuart Ira Fox, 12th ed, P-335 + J. TORTORA,8th edition, P-344, 345)
