Essential Nutrients – This book covers the entire syllabus of “Nutrition and Dietetics” prescribed by BNMC-for all Diploma in Nursing Science and Midwifery students. We tried to accommodate latest information and topics. This book is examination friendly setup according to the teachers’ lectures and examination’s questions. At the end of the book previous university questions are given. We hope in touch with the book students’ knowledge will be upgraded and flourished. The unique way of presentation may make your reading of the book a pleasurable experience.
Essential Nutrients
Definition of Essential Nutrients:
An essential nutrient is a nutrient required for normal human body function that either cannot be synthesized by the body at all, or cannot be synthesized in amounts adequate for good health and thus must be obtained from a dietary source.

Classification of Essential Nutrients:
There are 6 essentials nutrients. These are-

Concept about Nutrients
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excreted by cells to create non-cellular structures, such as hair, scales, feathers, or exoskeletons.
Some nutrients can be metabolically converted to smaller molecules in the process of releasing energy, such as for carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and fermentation products (ethanol or vinegar), leading to end-products of water and carbon dioxide. All organisms require water.
Essential nutrients for animals are the energy sources, some of the amino acids that are combined to create proteins, a subset of fatty acids, vitamins and certain minerals. Plants require more diverse minerals absorbed through roots, plus carbon dioxide and oxygen absorbed through leaves. Fungi live on dead or living organic matter and meet nutrient needs from their host.
Different types of organism have different essential nutrients. Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is essential, meaning it must be consumed in sufficient amounts, to humans and some other animal species, but not to all animals and not to plants, which are able to synthesize it.
Nutrients may be organic or inorganic: organic compounds include most compounds containing carbon, while all other chemicals are inorganic. Inorganic nutrients include nutrients such as iron, selenium, and zinc, while organic nutrients include, among many others, energy-providing compounds and vitamins.
Definition of Nutrients:
Nutrients are the constituents in food that must be supplied to the body in suitable amounts.
Or,
Nutrients are the constituents in food that must be supplied to the body in suitable amounts. These include water, proteins and the amino acids of which they are composed, fats and fatty acids, carbohydrates, minerals and vitamins.
(Ref by: H. Robinson’s Normal and therapeutic nutrition/4th/6)
Number – They are about 50 in number.
[OTHER DEFINITION – NICE TO KNOW]
- Nutrients are organic and inorganic complexes contained in food. There are about 50 different nutrients which are normally supplied through the food.
- The constituent in food is collectively known as nutrients.
Classification of Nutrients:
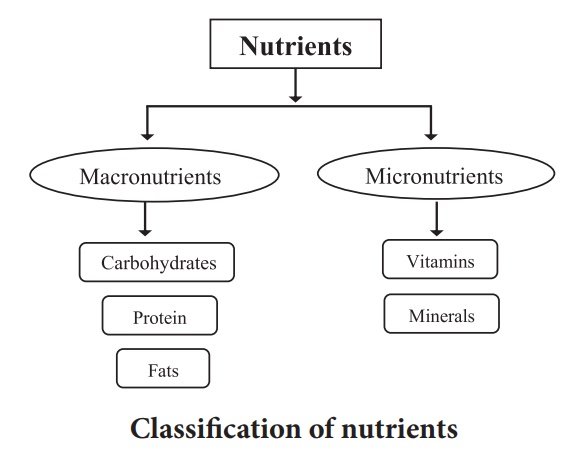
Macronutrients:
These are proteins, fats and carbohydrates which are often called “proximate principles” because they form the main bulk of food. They contribute to the total energy following intake in the proportions –
- Proteins: 7-15%0.
- Fats: 10-30%.
- Carbohydrates: 65-80%.
Micronutrients:
These are vitamins and minerals. They are called micronutrients because they are required in small amounts.
(Ref by: BT Basavanthappa’s Fundamentals of Nursing/24/464)
Functions of Nutrients:
1. Provide energy.
2. Promotion growth and maintenance.
3. Regulates body process: Lipids, protein, vitamins, minerals and water.
(Ref by: Rashid, Khabir, Hyder/5th/136)
Body Uses Nutrients:
- To build the body, produce fluids and repair tissues.
- To produce energy so that the body can keep alive and warm and so that it can move and grow.
- To help chemical processes.
- To protect the body from disease.
