Common terminology of endocrine system-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
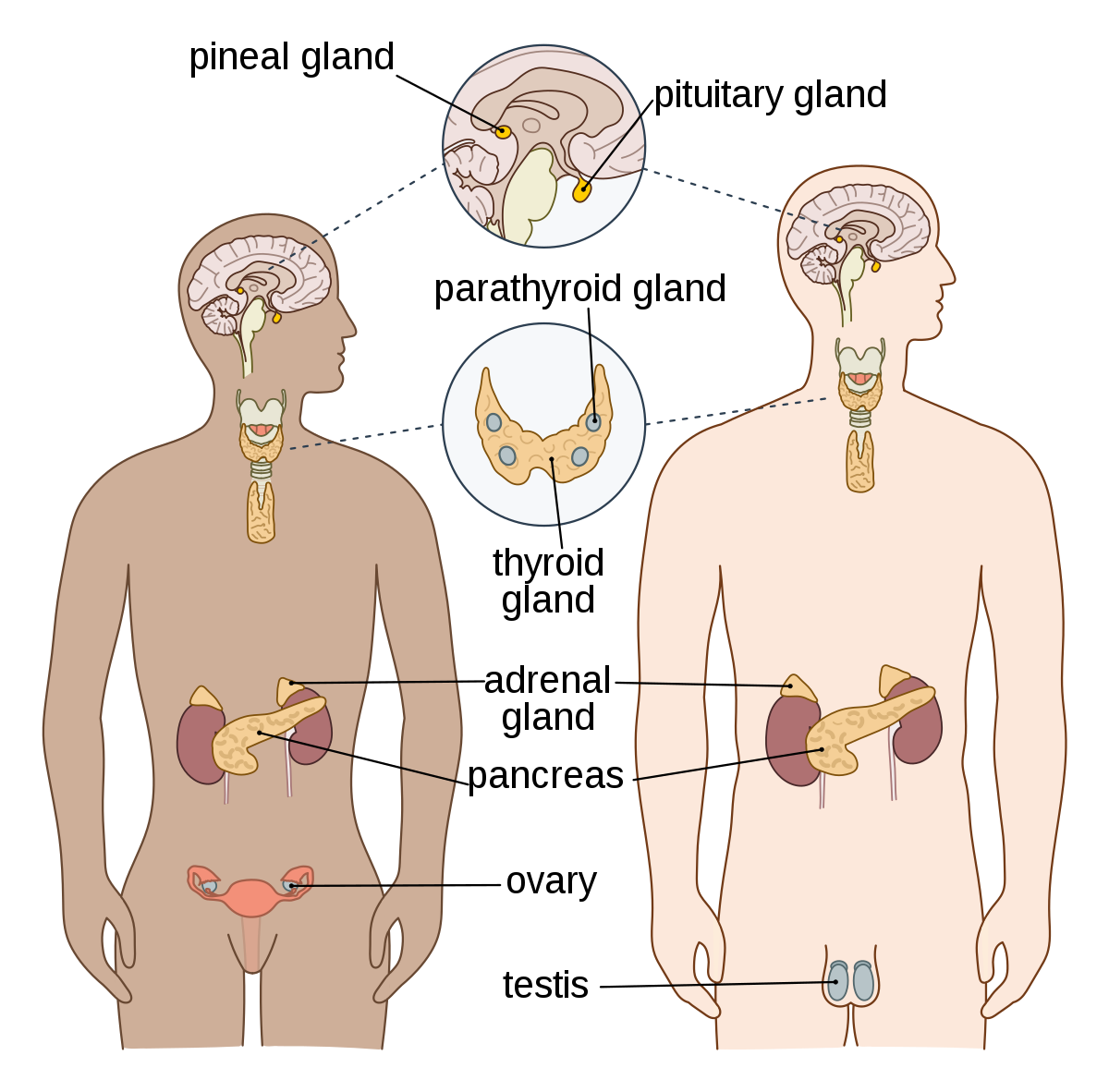
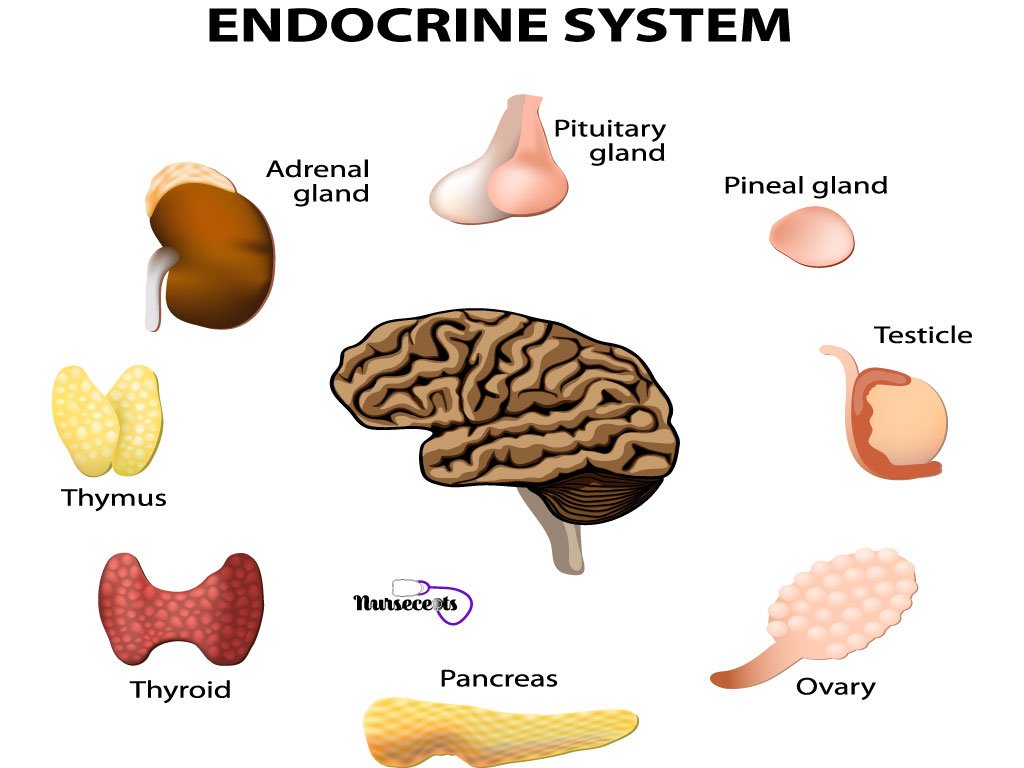
Common terminology of endocrine system
Acromegaly disease characterized by enlarged features especially of theface and hands, caused by hypersecretion of the pituitarygrowth hormone after puberty, when normal bone growthhas stopped, most often caused by a pituitary tumor.
Adrenalectomy; excision of the adrenal glands.
Addison’s disease: is caused by inadequate secretion of both glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, which results inhypoglycemia, sodium and potassium imbalance, dehydration, hypotension, rapid weight loss. and generalized weakness.
Antagonist: Drugs or substances that bind with receptors but have no activating effects on them are called antagonist.
Anabolic steroids: are synthetic androgens (male hormones)that promote protein synthesis in muscles and other organs. Use of these drugs by bodybuilders, weightlifters, and othersis prohibited by most athletic organizations.
Cretinism: is the condition caused by severe hypothyroidism during fetal life, infancy or childhood. Children who are hypothyroid from birth or before birth are called Cretins. This condition is characterized specially by failure of body growth and by mental retardation Skeletal growth in the children with cretin is more inhibited than soft tissue growth.
Cushing’s syndrome: An excessively high level of corticosteroids in the blood causes Cushing’s syndrome. Cushing’s syndrome is characterized by changes in carbohydrate and protein metabolism, hyperglycemia. hypertension, and muscular weakness. Metabolic problems give the body a puffy appearance and can cause structural changes characterized as “buffalo hump” and “moon face.”
Diabetes mellitus: Diabetes mellitus is a clinical syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia due to absolute or relative deficiency of insulin.
Diabetes insipidus: It is a clinical condition characterized by passage of large volume of watery/ dilute urine. It occurs due to deficiency of ADH.
Dwarfism: It is the condition resulting from hypo activity of the growth hormone in children.
Gestational diabetes: occurs in about 4% of pregnancies due to insulin secretion that is inadequate to meet the increased demand imposed by the ferus. Women who do not develop gestational diabetes have a sufficiently increased insulin secretion during pregnancy, probably due to the proliferation of beta cells in the islets.
Gynecomastia: (gyneco woman, mast breast) Excessive development of mammary glands in a male Sometimes a tumor of the adrenal gland may secrete sufficient amounts ofoestrogen to cause the condition.
Goiter: enlargement of the thyroid gland caused by thyroiddysfunction, tumor, lack of iodine in the diet, orinflammation.
Hirsutism: Presence of excessivebodily and facial hair in a male pattern, especially in women; may be due to excess androgen production caused by tumors ordrugs.

Hypercalcemia: an abnormally high level of calcium in the blood.
Hyperkalemia: an abnormally high level of potassium in the blood.
Hypophysectomy: excision of the pituitary gland.
Myxedema: The syndrome of adult hypothyroidism is generally known as myxedema or it is a clinical condition characterized by specific clinical features which develops in adult patients with almost lack of total thyroid function.
Polydipsia: excessive thirst.
Polyuria: excessive urination.
Polyphagia: Eating abnormally large amounts of food at a meal.
Thyroid crisis (storm): A severe state of hyperthyroidism that can belife-threatening It is characterized by high body temperature, rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, gastrointestinal symptoms(abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea), agitation, tremors, confusion, seizures, and possibly coma.
Thymectomy: excision of the thymus gland.
Virilizing adenoma (aden gland; oma tumor); Tumor of theadrenal gland that liberates excessive androgens, causing virilism(masculinization) in females. Occasionally, adrenal tumorcells liberate estrogens to the extent that a male patient developsgynecomastia. Such a tumor is called a feminizing adenoma.
Pituitary dwarfism: a condition of congenital hyposecretion of growth hormonethat slows growth and causes short, yet proportionate, starure (not affecting intelligence), often treated duringchildhood with growth hormone, other forms of dwarfismare most often caused by genetic defects .
Read more:
