Common terminology of nervous system-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
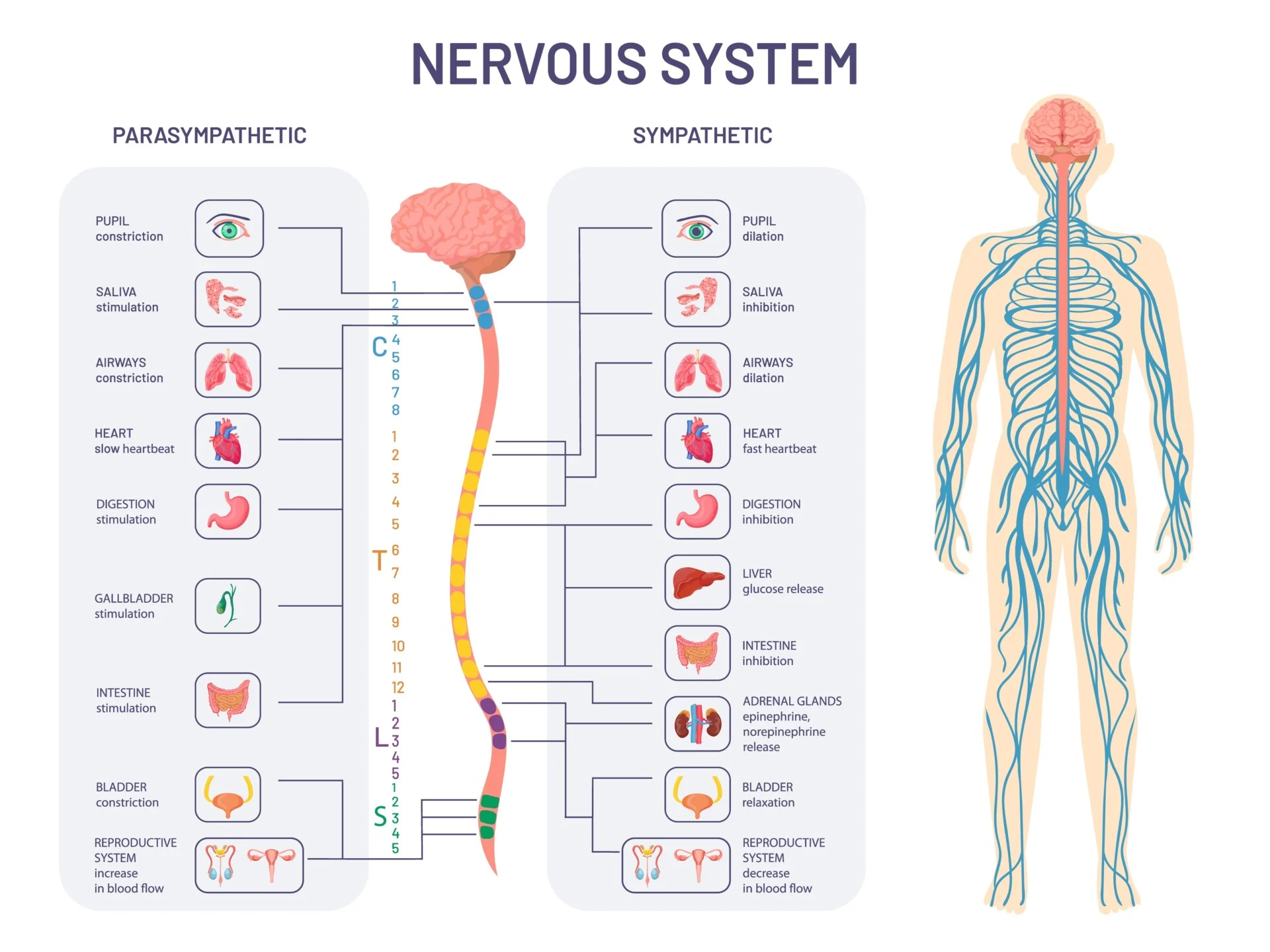
Common terminology of nervous system
Alzheimer disease or AD: is a disabling senile dementia, the loss of reasoning and ability to care for oneself, that afflicts about 11% of the population over age 65. The cause of most AD cases is still unknown, but evidence suggests it is due to a combination of genetic factors, environmental or lifestyle factors, and the aging process.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) (a without; myo muscle, trophic nourishment) is a progressivedegenerative disease that attacks motor areas of the cerebral cortex axons of upper motor neurons, and lower motor neuron cellbodies.
Analgesia (an without, algesia painful condition): Pain relief.
Anesthesia (esthesia feeling): Loss of sensation.
Cerebrovascular Accident: The most common brain disorder is acerebrovascular accident(CVA), also called a stroke or brain attack. A CVA is characterized by abrupt onset of persisting symptoms, such as paralysis or loss of sensation, that arise from destruction of brain tissue. Common causes of CVAs are hemorrhage from a blood vessel in the pia mater or brain, blood clots, and formation of cholesterol- containing atherosclerotic plaques that block brain blood flow.
Consciousness: A state of wakefulness in which an individual is fully alert, aware, and oriented, partly as a result of feedback between the cerebral cortex and reticular activating system.
Dementia (de away from; mentia mind): Permanent or progressive general loss of intellectual abilities, including impairment of memory, judgment, and abstract thinking, and changes in personality.
Diplegia (di = two) is paralysis of both upper limbs or both lower limbs
Encephalitis: An acute inflammation of the brain caused by either a direct attack by any of several viruses or an allergic reaction to any of the many viruses that are normally harmless to the central nervous system. If the virus affects the spinal cord as well, the condition is called encephalomyelitis.
Epidural block: Injection of an anesthetic drug into the epidural space, the space between the dura mater and the vertebral column, to cause a temporary loss of sensation. Such injections in the lower lumbar region are used to control pain during childbirth.
Hemiplegia (hemi half) is paralysis of the upper limb, trunk, and lower limb on one side of the body,
Meningitis: Inflammation of the meninges.
Monoplegia (mono one; plegia blow or strike) is paralysis of one limb only.
Nerve block: Loss of sensation due to injection of a local anesthetic, an example is local dental anesthesia.
Neuralgia (neur nerve; algia pain) Attacks ofpain along the entire length or a branch of a peripheral sensorynerve.
Neuritis: (neur nerve); itis inflammation) Inflammation of oneor several nerves, resulting from irritation caused by bone fractures.contusions, or penetrating Additional injuries. causes includeinfections; vitamin deficiency (usually thiamine); and poisonssuch as carbon monoxide, carbon tetrachloride, heavymetals, and some drugs.
Paraplegia (para beyond) is paralysis of both lower limbs.
Parkinson disease (PD): is a progressive disorder of the CNS that typically affects its victims around age 60. Neurons that extend from the substantia nigra to the putamen and caudate nucleus, where they release the neurotransmitter dopamine (DA), degenerate in PD.
The cause of PD is unknown, but toxic environmental chemicals, such as pesticides, herbicides, and carbon monoxide, are suspected contributing agents. Only 5% of PD patients have a family history of the disease.
Reye syndrome : Occurs after a viral infection, particularlychickenpox or influenza, most often in children от characterized teens by whohave taken aspirin; vomiting and brain dysfunction(disorientation, lethargy, and personality changes) thatmay progress to coma and death.
Shingles: is an acute infection of the peripheral nervous system caused by herpes zoster, the virus that also causes chickenpox. After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus retreats to a posterior root ganglion.
If the virus is reactivated, it may leave the ganglion and travel down sensory axons to the skin. The result is pain, discoloration of the skin, and a characteristic line of skin blisters. The line of blisters marks the distribution of the particular sensory nerve belonging to the infected posterior root ganglion.
Sciatica: A type of neuritis characterized by severe painalong the path of the sciatic nerve or its branches, may be causedby a slipped disc, pelvic injury, osteoarthritis of the backbone, orpressure from an expanding uterus during pregnancy.
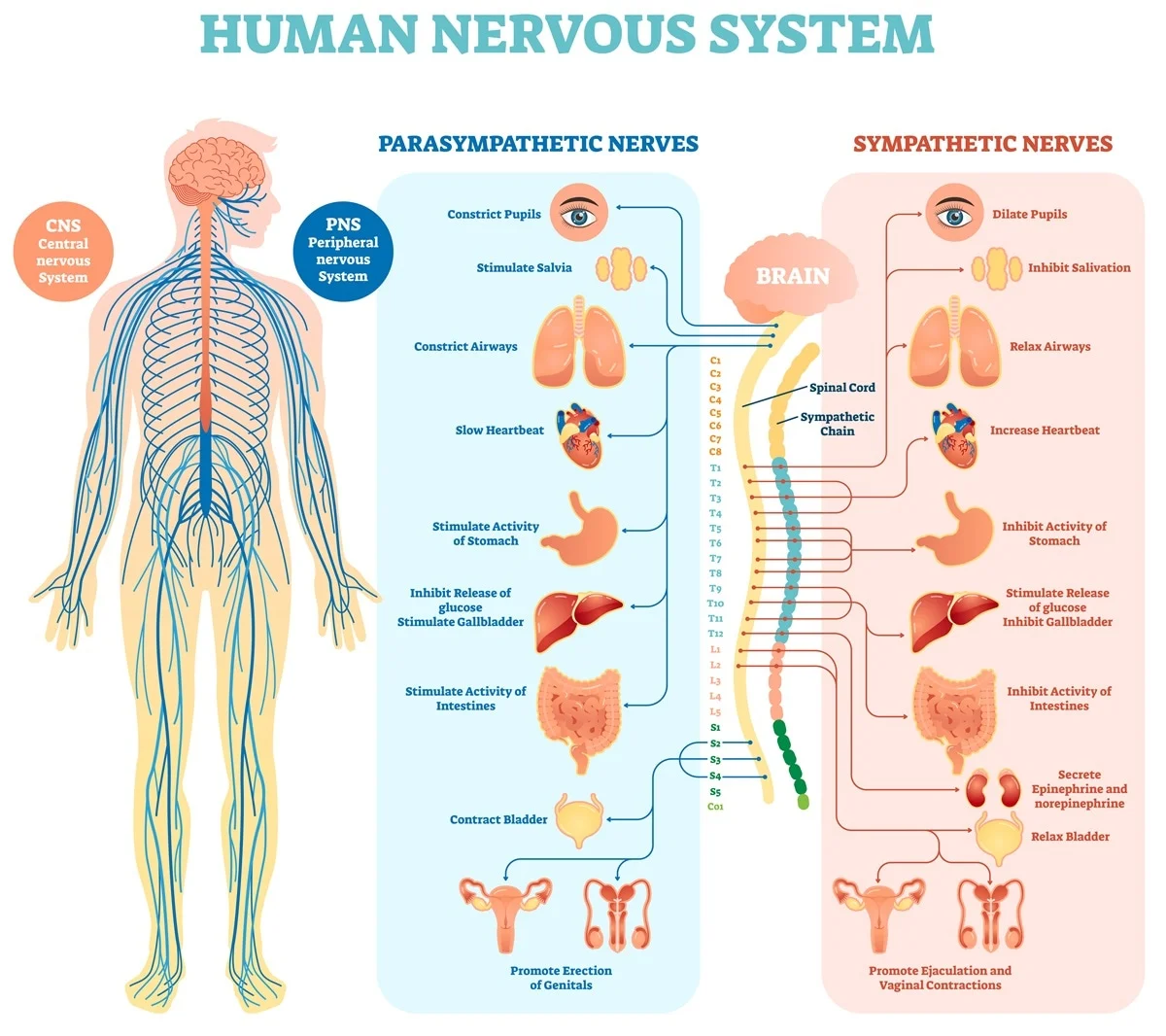
Transient Ischemic Attack: A (TIA) is an episode of temporarycerebral dysfunction caused by impaired blood flow to part of thebrain. Symptoms include dizziness, weakness, numbness, orparalysis in a limb or in one side of the body, drooping of oneside of the face; headache; slurred speech difficulty understandingspeech; and a partial loss of vision or double vision.
The onset of symptomsis sudden and reaches maximum intensity almost immediately.A TIA usually persists for 5 to 10 minutes and only rarelylasts as long as 24 hours. The causes of TIAs include blood clots, atherosclerosis, and certain blood disorders.
Quadriplegia (quad four) is paralysis of all four limbs.
