Definiton of Tuberculosis – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Definiton of Tuberculosis
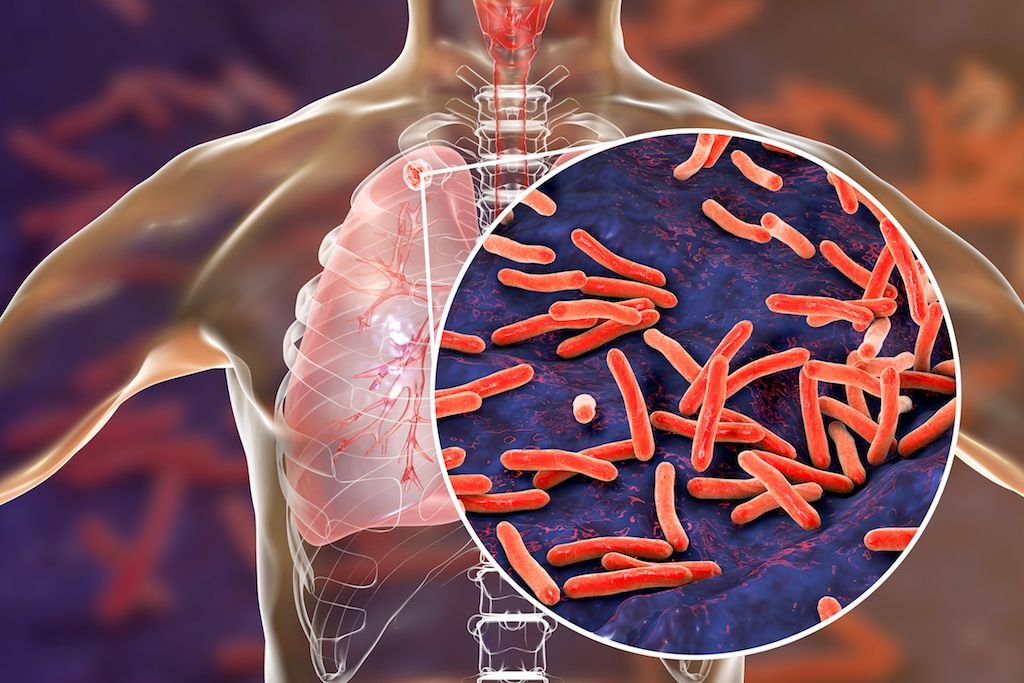
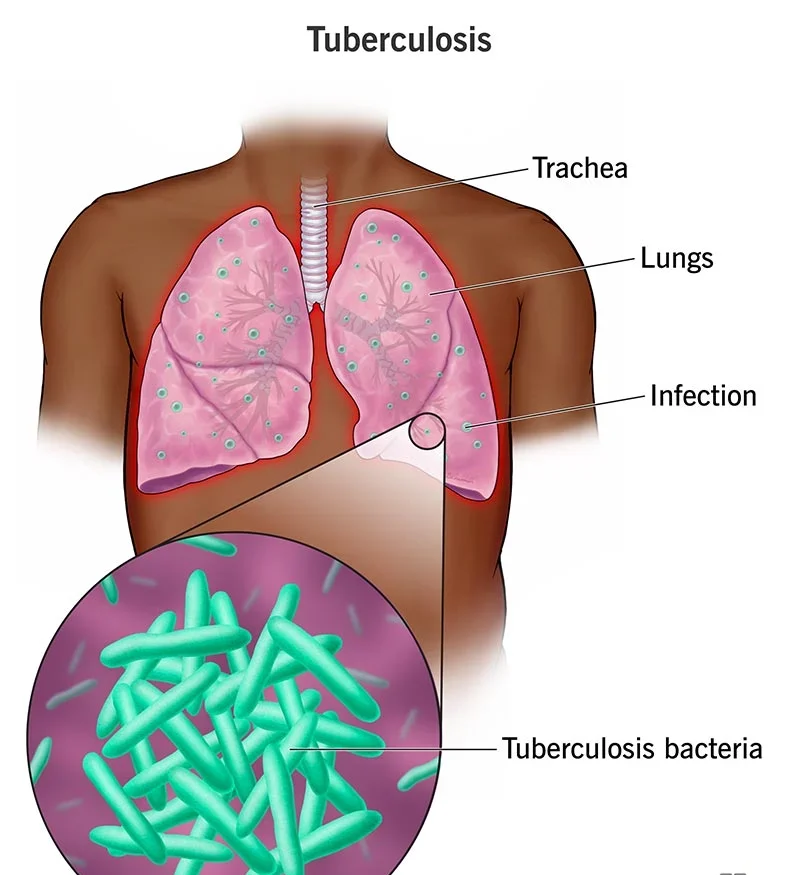
Tuberculosis is a chronic bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterial tuberculosis or M, bovis, which is transmitted by respiratory droplet and spread from person to person via air. South East Asia region has the highest number of cases among all WHO regions. India alone accounts for 20% of the global burden of the disease. As most cases occur in the younger age group, a large number of women with pregnancy would invariably be affected.
Effect of Pregnancy on Tuberculosis:
There is no evidence to show that pregnancy makes women more likely to develop tuberculosis or have a poorer prognosis if tuberculosis is diagnosed during pregnancy, provided if they are treated promptly.
Effect of Tuberculosis on Pregnancy:
It is difficult to decide that how much effect the disease per she has on pregnancy, or from the malnutrition, anemia and poor living conditions that predispose to developing the disease. Data shows that women, who are diagnosed and start treatment before pregnancy or in early part of pregnancy,
have a better pregnancy outcome as compared to those who are diagnosed late in pregnancy and in postpartum period. Neonates born to women with tuberculosis were found to have higher risk of prematurity, low birth weight and perinatal death.
Diagnosis:
Symptoms and Signs
Typical symptoms includes cough, weight loss, fatigue, night sweats and anorexia. However, some patients may have very few symptoms.
Laboratory Findings
2. Tuberculin skin test. It is done with purified protein derivate (PPD) and important screening test for tuberculosis. An induration of ≥10 mm is usually considered positive but in HTV infected persons 25 mm is taken as positive. A strongly positive mantoux (Mx) response is suggestive of active disease, India and in areas where the disease is endemic, the tuberculin positivity is high because of either due to latent infection or due to BCG vaccine.
3. Chest X-ray is useful for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis, which may show infiltration or cavities.
4. Bacteriological examination: Definitive diagnosis is made after positive identification of the bacilli by Ziehl-Neelson staining and a positive culture. A specimen can be obtained from sputum or secretion observed by bronchoscope or gastric lavage.
Treatment:
The indications of treatment are the same in pregnacy as those in the nonpregnant women. Treatment should not be delayed due to fetal or maternal concerns, whatever may be the period of gestation. Most of the drugs used as first line treatment for tuberculosis like Isoniazid, Rifampicin, and Ethambutol have been found to be safe with incidence of congenital malformation well within the range of control population.
Pyrazinamide has also been used in pregnancy but its safety profile has not been proven beyond doubt. Hepatotoxicity is the common adverse effect in patient on Antitubercular treatment reported in 10% of patients. So liver function tests should be done every month.
| 2. Women with active tuberculosis should receive the following drugs orally daily for a minimum period of 9 months. | ||
| Drug | Daily doses-PO | Major side effects |
| Isoniazid (pyridoxine) | 5 mg/kg upto 300mg 50mg daily | Hepatitis, peripheral neuropathy, hypersensitivity. |
| Rifampicin | 10 mg/kg upto 600mg. | Nausea, vomiting. hepatitis, orange discoloration of urine and secretion, febrile reaction. |
| Ethambutal | 15 mg/kg upto 2.5 gm | Skin rash, optic neuritis, decreased visual activity. |
| Pyrazinamide | 15-30mg/kg upto 2gm. | Hepatotoxicity, skin rash, arthralgias, hyperuricemias, G.L. upset. |
Most treatment plans have 3 drug regimen Isoniazid, ethambutoi and rifampicin for 8 weeks and isoniazid and rifampicin for 9 months. Pyridoxine 50 mg. should be given to prevent INH induced neuritis due to vitamin deficiency.
Obstetric Management:
It includes
- Adequate rest and nutrition,
- family support,
- correction of anemia if present and
- Regular follow-up visit.
Other management is no different from other pregnant women, once tuberculosis is well managed, with antituberculosis drugs.
Breastfeeding:
In only active lesions the breastfeeding is contraindicated. Baby should be isolated from the mother following delivery and baby should be given prophylactic Isoniazid 10-20 mg/kg/day for 3 months when the mother is suffering from active disease. But a women already on anti- tuberculosis drug, breastfeeding is not contraindicated. BCG should be given to the baby as early as possible.
Contraception:
Spacing can be achieved by any methods acceptable to the couple. Oral contraceptive should be avoided when Rifampicin is used. Puerperal sterilization should be considered if family is complete.
Chemoprophylaxis for Pregnant Women:
Isoniazid prophylaxis is highly effective and not shown to be teratogenic in standard dosage. Chemoprophylaxis is recommended in women with positive Mantoux test in the following situations:
- Documented recent conversion of tuberculin test within preceding two years.
- In close contact of persons with active tuberculosis.
- Immunocompromised, e.g . HIV positive,
- Liver function test must be performed monthly and pyridoxine should be supplemented to avoid the risk of peripheral neuropathy.