Sense of taste-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.

Sense of taste
Taste or gustation (gust = taste) is much simpler than olfaction because only five primary tastes can be distinguished:
- Sour,
- Sweet,
- Bitter,
- Salty, and
- Umami.
The umami taste is described as “meaty” or “savory.” All other flavors, such as chocolate, pepper, and coffee, are combinations of the five primary tastes, plus the accompanying olfactory and tactile (touch) sensations, Odors from food can pass upward from the mouth into the nasal cavity, where they stimulate olfactory receptors.
Because olfaction is much more sensitive than taste, a given concentration of a food substance may stimulate the olfactory system thousands of times more strongly than it stimulates the gustatory system. When you have a cold or are suffering from allergies and cannot taste your food, it is actually olfaction that is blocked, not taste.
Structure of Taste Buds
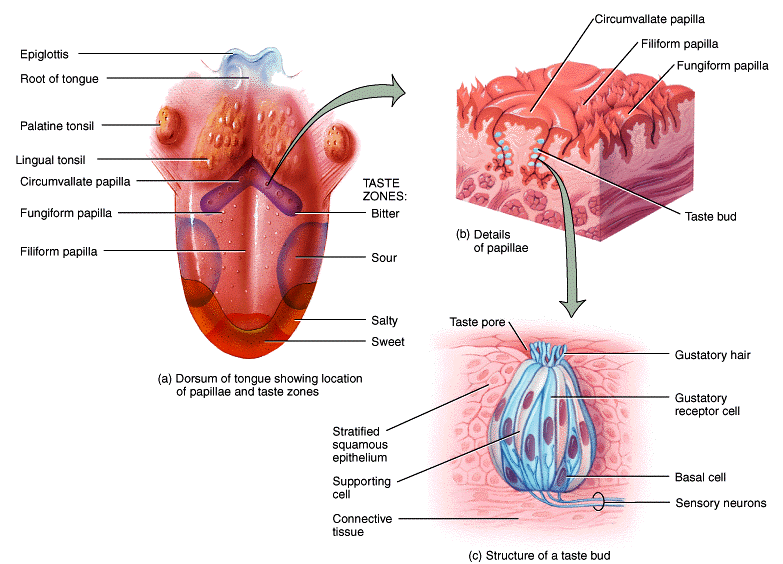
The receptors for taste sensations are located in the taste buds. Most of the nearly 10,000 taste buds of a young adult are on the tongue, but some are also found on the roof of the mouth, pharynx (throat), and epiglottis (cartilage lid over the voice box).
The number of taste buds declines with age. Taste buds are found in elevations on the tongue called papillae (singular is papilla), which provide a rough texture to the upper surface of the tongue.
Each taste bud is an oval body consisting of three types of epithelial cells:
◆ Supporting cells,
◆ Gustatory receptor cells, and
◆ Basal cells.
Modalities of Taste, and the substances causing primary taste sensation
Taste:
It is a function of taste buds that allows the person to select food with desire & need of the tissue.
Modalities of taste are four basic types:
- Sweet: At the tip of the tongue.
- Salt. Just behind the tip of the tongue at the dorsal surface.
- Sour: Along the edges of the tongue.
- Bitter Posterior part of the tongue.
Substances that causes primary taste sensation:
| Sweet | Organic substances e.g. Glucose, Sucrose, Esters etc. |
| Salt | Ionized salt e.g. NaCl, KCl, MgCl, etc. |
| Sour | Acids. |
| Bitter | Organic compounds e.g. Caffeine, Nicotine, Morphine etc. |
