Jaundice In Pregnancy – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
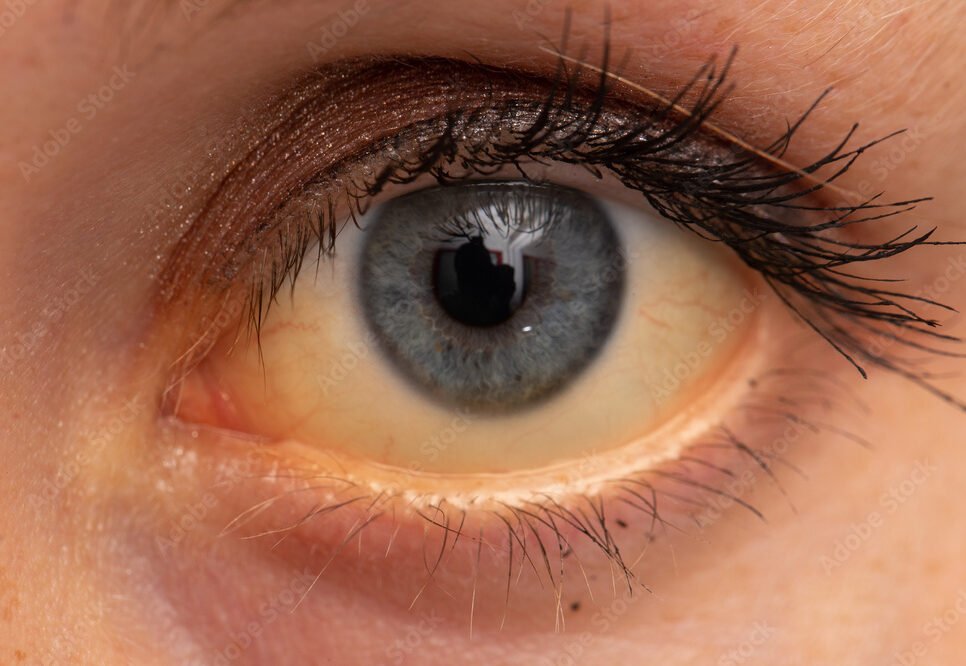
Jaundice In Pregnancy
Causes of jaundice in pregnancy:
A. Jaundice related with pregnancy:
➤ Severe pre-eclampsia.
➤ Acute fatty liver.
➤ Severe neglected hyperemesis gravidarum.
➤ Endotoxic shock.
➤Intrahepatic cholestasis.
B. Jaundice unrelated to pregnancy:
➤ Viral hepatitis.
➤ Haemolytic jaundice.
➤ Obstructive jaundice.
Management of jaundice in 2nd trimester:
Clinical features:
➤ Severe anorexia.
➤ Nausea and vomiting.
➤ Dark cloured urine.
➤ Yellowish discoloration of the skin and mucous membrane.
➤ There may be pain in the right hypochondriac region.
Investigations:
➤ CBC
➤ Serum bilirubin
➤ SGOT and SGPT
➤ Alkaline phosphatase
➤ Prothrombin time
➤ HBsAg
➤ USG of whole abdomen
Treatment:
➤ Complete bed rest,
➤ Isolate the patient from the others.
➤ Give nutritious diet rich in CHO
➤ If anorexia or vomiting is severe then I/V fluid.
Obstetric treatment:
➤ Careful monitoring of maternal and fetal condition.
Management of a pregnant woman with HBV infection:
General treatment:
➤ Complete bed rest.
➤ Isolation
➤ Blood sample should be collected with gloved hand. Disposable syringe should be used’.
➤ Give carbohydrate and protein rich diet. Fat restriction is not necessary’.
➤ Carefully avoid hepato-toxic drugs’.
➤ Regularly monitor blood electrolytes to prevent hypokalaemia, hypocalcaemia and monitor blood glucose to prevent hypoglycaemia
Obstetric management:
During labour:
➤ Avoidance of hepato-toxic drugs.
➤ Use prophylactic oxytocin.
➤ Administer vitamin K to raise prothrombin time.
After delivery:
➤ Breast feeding is not contraindicated.
➤ Immunize both mother and baby.
Prevention and immunization:
➤ Hepatitis B infection can be prevented by vaccination and is safe in pregnancy.
Immunization of the mother:

Passive immunity:
➤ 1 dose: Soon after exposure, sero negative pregnant woman should have hepatitis B immunoglobulin,
➤ 2nd dose: After 1 month of the 1″ dose.
Active immunity:
➤ Recombinant DNA vaccine (3 doses at 0, 1 and 6 months) after delivery.
➤ Immunization of the newborn:
➤ Passive immunization: All infants born to HBsAg positive mothers should have HBIG (Hepatitis B immunoglobulin) within 12 hours of birth.
➤ Active immunization: 3 doses at 0, 1 and 6 months after delivery
