Antigen and antibody-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
Antigen and antibody
Antigen:
Antigen may be defined as a high molecular weight foreign substances (protein or polysaccharide in nature) when introduced into a suitable route, produce antibody with which it react specifically.
Or,
Any substance, which binds with antibody, is called antigen.
Immunogen:
Immunogen may be defined as a high molecular weight foreign substance (protein or polysaccharide in nature) when introduced into a suitable host through a suitable route, produce immune responses e. Humoral or Cellular immunity or both. All immunogens are antigen, but all antigens are not immunogen.
Antibody:
Antibodies are the substances (immunoglobulin), which are produced in response to an antigen and bind with that antigen specifically
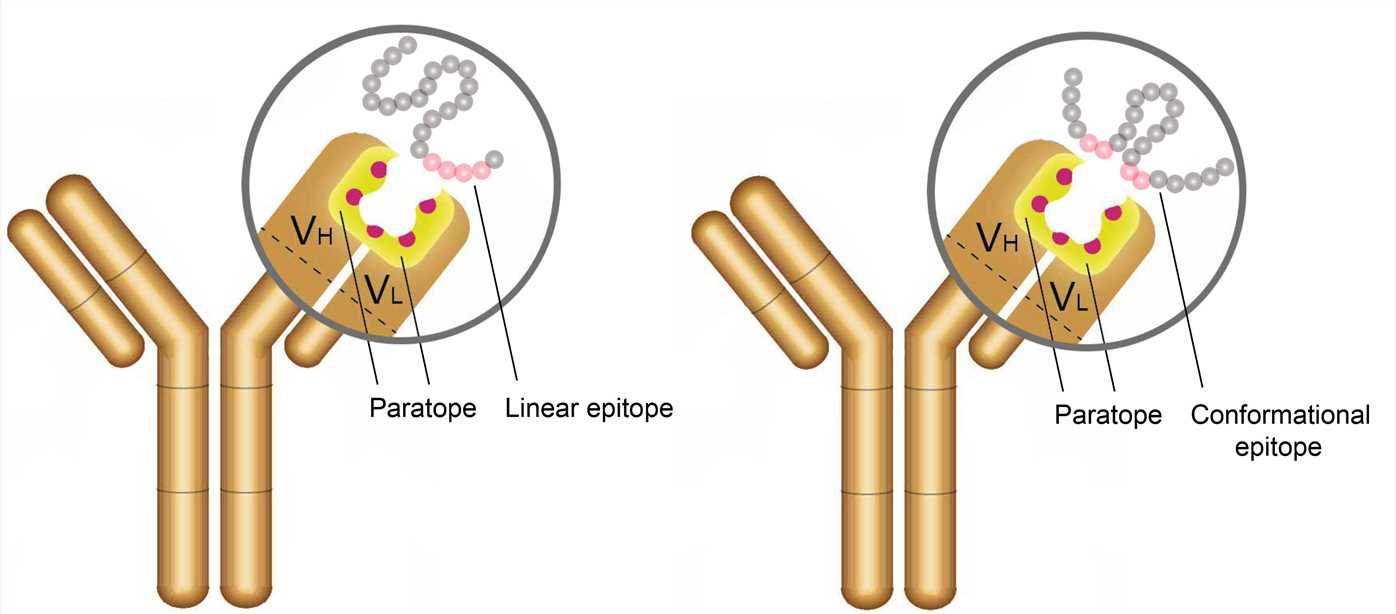
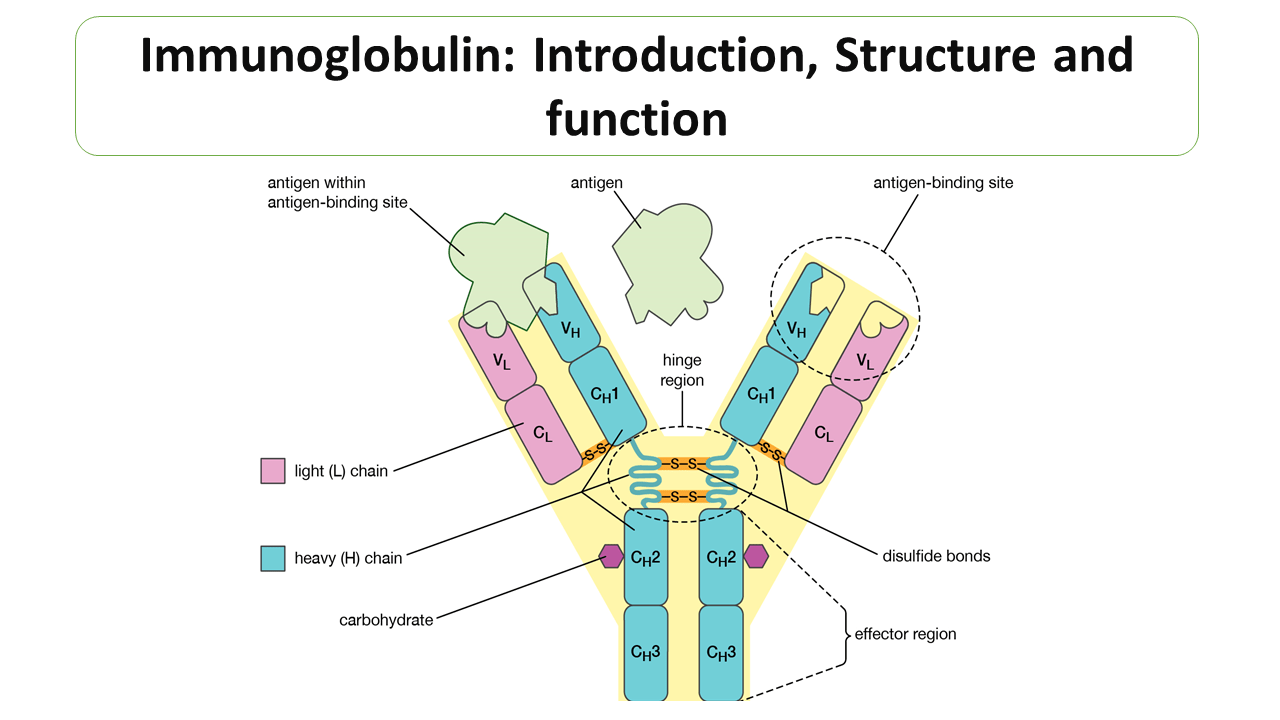
Immunoglobulin
Definition:
Immunoglobulins are plasma protein which structurally similar with antibodies but they may not endowed with antibody.
Classes:
There are five general classes of immunoglobulin:-
1. Immunoglobulin- ‘G’ (Ig-G)
2. Immunoglobulin- ‘A’ (lg-A)
3. Immunoglobulin- ‘M’ (Ig-M)
4. Immunoglobulin- ‘E’ (Ig-E)
5. Immunoglobulin- ‘D’ (Ig-D)
| Immunoglobulin | Functions |
| IgG | Main form of antibodies in circulation: production increased after immunization; secreted during secondary response. |
| IgA | Main antibody type in external secretions, such as saliva and mother’s milk. |
| IgM | Function as antigen receptors on lymphocyte surface prior to immunization; secreted during primary response. |
| IgE | Responsible for allergic symptoms in immediate hypersensitivity reactions. |
| IgD | Function as antigen receptors on lymphocyte surface prior to immunization; other functions unknown. |
The Comparison of Active and Passive Immunity
| Characteristic | Active Immunity | Passive Immunity |
| Injection of person with | Antigens | Antibodies |
| Source of antibodies | The person inoculated | Natural– the mother, artificial– injection with antibodies |
| Method | Injection with killed or attenuated pathogens or their toxins | Natural-transfer of antibodies across the placenta, artificial-injection with antibodies |
| Time to develop resistance | 5 to 14 days | Immediately after injection |
| Duration of resistance | Long (perhaps years) | Short (days to weeks) |
| When used | Before exposure to pathogen | Before or after exposure to pathogen |
