Female sterilization & Menstrual Regulation – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Female sterilization & Menstrual Regulation
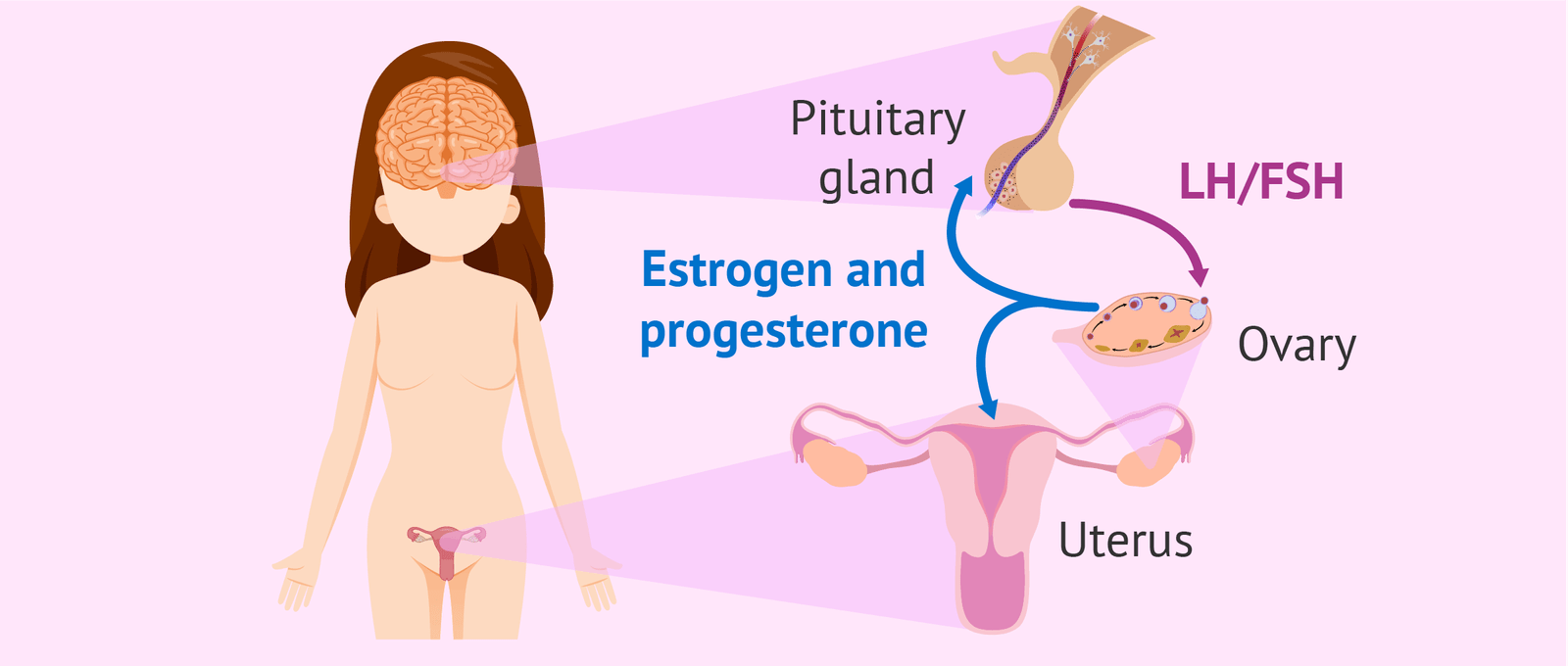
Definition of Female Sterilization:
Female sterilization involves the mechanical blockage of both fallopian tubes to prevent sperm reaching and fertilizing the oocyte.
Technique of Female Sterilization:
| Technique of tubai occlusion | Special features |
| A. Ligation |
|
| B. Electrocautery/ diathermy |
|
| C. Falope rings |
|
| D. Clips |
|
| E. Laser |
|
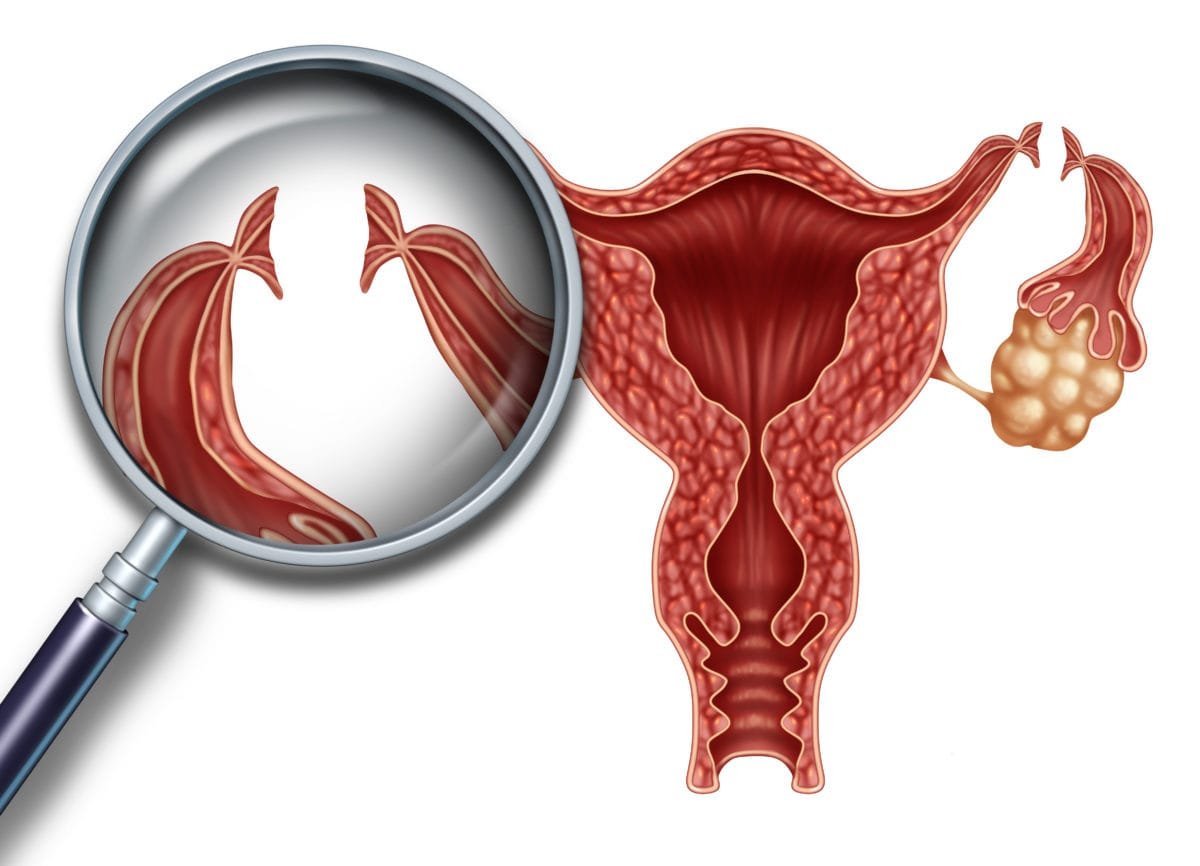
MR (menstrual regulation)
Definition of MR (menstrual regulation):
A relatively simple method of birth control is “MR” which consists of aspiration of the uterine contents 6 14 days of a missed period, but before most pregnancy tests can accurately determine whether or not a woman is pregnant.
Time of MR operation:
It is done within 8 weeks of pregnancy or 60 days from the 1st day of last menstruation.
Complication MR (menstrual regulation):
| A. Immediate |
|
| B. Late: |
|
Pre-Operative Preparation:
A. History: Menstrual, obstetrical, gynaecological & medical history.
B. Examination:
- G/E: pulse, BP, temperature, anaemia etc. I
- Abdominal exam, to exclude any pathology.
- PA/ exam to know about the size & position of the uterus, condition of the cervix and to exclude any pathology.
C. Investigations:
- Blood for TC, DC, H6%.
- Blood grouping and cross matching
- Urine for albumin, sugar.
- Pregnancy test.
- Pt. is explained the procedure, counseled about future contraceptive advice, proper consent taken
- After her bladder she is taken to taken to the OT.
Instruments Required for MR:
- Swab holding forceps
- Sims vaginal speculum (to expose the cervix)
- Volsellum forceps (to hold the anterior lip of the cervix)
- Karmanscannule (to employ suction)
- Karmans 50cc syringe (to employ suction)
Procedure of MR:
1. The pt. is placed in lithotomy position.
2. The lower abdomen, thighs, vulva, vagina & perineum are painted with antiseptic solution. (e,g. betadin solution)
3. The parts are draped with sterile sheets
4. Vaginal examination is performed to determine the size & direction of the uterus
5. Sim’s posterior vaginal speculum is introduced (to retract posterior vaginal wall) and an assistant is asked to hold
6. The anterior lip of the cervix is held and steadied with a volsellum (or Allis) forceps
7. The appropriate Karman’s plastic cannula 4-5 mm (corresponding) to the weeks of gestation) is inserted up to the fundus of the uterus.
8. Negative pressure of 50-70 mm Hg (vacuum) is created in the Karman’s syringe (outside
the uterus) and with held with the thumb block.
9. The syringe (pre-evacuated) innected to the Karman’s cannula and then the thumb block is released
10. The Karman’s cannula is rotated at the fundus and gradually withdrawn downwards, until it reaches the isthmus; thereafter it may be moved vertically up & down to confirm the grating sensation all around.
11. Signs of completion of evacuation:
- No further tissue is evacuated.
- Blood stained bubbles are seen in the cannula & syringe
- The internal os grips the cannula.
- Grating sensation is felt all over.
12. The syringe is disconnected from the cannula and the cannula is withdrawn. The volsellum and Sim’s speculum is withdrawn.
Post-operative MX:
1. Pt. is sent to the bed and should be rested for 1 hour for observation. After that she can go to home.
2. Vital signs (such as pulse, BP) and vaginal bleeding should be noted she leaves the hospital.
3. Antibiotic: Cephalosporins/ Ampicillin/ Amoxycillin + Metronidazole for 7 days.
4. Analgesic: maybe
5. Contraceptives: immediately (1-t day of MR)-ovacon.
6. Advice
- Avoidance of coitus for 15 days.
- Maintenance of personal hygiene.
- Heavy wt. lifting is avoided.
- Come after 2 weeks for follow up. If there is fever, vaginal bleeding, severe lower abdominal pain-come earlier.