Concept about Oligohydramnios – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Concept about Oligohydramnios
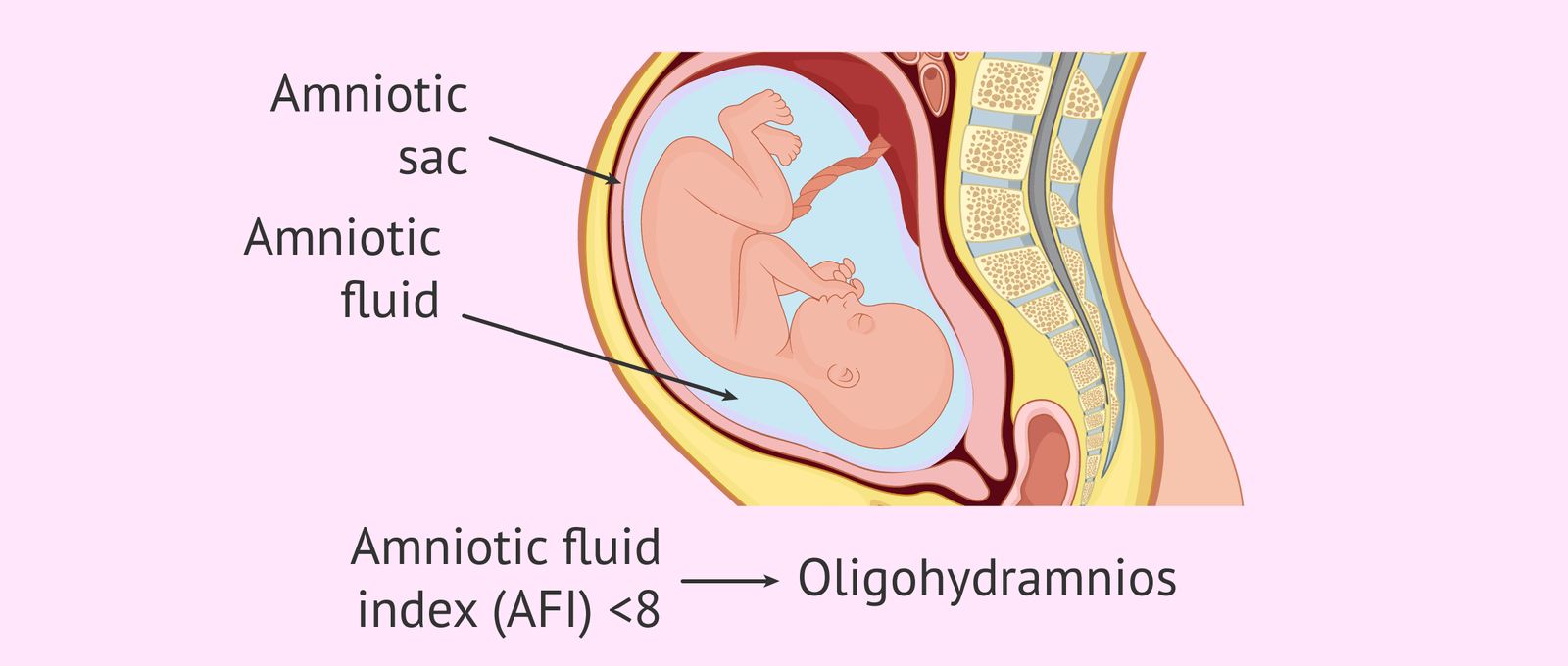
It is defined as the volume of amniotic fluid being less than 300 ml during the third trimester of pregnancy.
Causes of oligohydramnios
Cause are unknown but often associated with
➤ Renal agenesis or obstruction of the fetal urinary tract.
➤ Fetal Abnormalities: Absence of the kidney or any other kidney abnormality (renal agenesis, polycystic kidney) in the baby can also hamper urine production
➤ Genetic Factors: Inheriting abnormal genes in an autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant pattern.
➤ Placental insufficiency (IUGR).
➤ Premature rupture of membrane (PROM).
➤ Amnion nodosum.
➤ Hypertensive disorder, dehydration.
➤ Drug-Induced Causes: Using NSAIDs like indometacin and certain ACE (angiotensin- converting enzyme).
PROM is the common, labor may be protected and contractions are more painful.
Risk factors of oligohydramnios
The following medical conditions in the mother are considered to increase the risk of oligohydramnios:
➤ Chronic high blood pressure
➤ Dehydration
➤ Diabetes
➤ Preeclampsia
➤ Hypertension
➤ Lupus

Clinical features of oligohydramnios:
The signs and symptoms of oligohydramnios vary from person to person but some of the most common signs and symptoms are:
➤ Rapid growth of uterus.
➤ Abdominal discomfort.
➤ Leaking of the amniotic fluid.
➤ Little to no or decreasing fetal movement.
➤ Uterine contractions.
➤ Abnormal findings on a fetal monitor including fetal distress.
➤ Abnormal protuberance of fetal parts.
➤ Fetal malpresentation.
➤ Shorter symphysis-fundus height.
Diagnosis of oligohydramnios
➤ Ultrasound
This helps in:
✓ Checking fetal growth
✓ Ruling out other disorders (cystic dysplasia, ureteral obstruction, renal agenesis etc).
✓ Determine placental insufficiency (by using Doppler ultrasound).
The diagnostic criteria include:
✓ Amniotic fluid levels lower than 5 cm.
✓ Absence of a 2-3 cm deep fluid pocket.
✓ The total amniotic fluid volume below 500mL between 32nd and 36th gestational weeks.
➤ Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI): There are a number of tests available for measuring the amniotic fluid volume (AFV), with AFI being the most commonly used procedure. Around 8% of all pregnant women may have low amniotic fluid levels with 4% among them diagnosed with oligohydramnios.
➤ Maximum Vertical Pocket (MPV): This test allows doctors to check the amniotic fluid levels in the deepest part of the uterus.
➤ Sterile Speculum Examination
➤ It helps to detect any rupture of membranes (ROM) responsible for oligohydramnios.
➤ Maternal Blood Test
➤ Blood tests, like maternal serum screening, can be performed to detect low levels of col amniotic fluid in the uterus as well as to determine the chances of the baby being born with congenital disorders like Down syndrome and spina bifida.

Management of oligohydramnios:
Assessment:
Assess for the following:
1. Ballottement results in fluid waves.
2. Fundal height excessive for gestation
- Fetus difficult to outline with palpation
- Supine hypotension.
- Fetal abnormalities of central nervous system or GI tract
- Easy fatigability.
Analysis/Nursing Diagnosis:
1. Risk for fetal injury
2. Impaired physical mobility
3. Actual/risk for fluid volume deficit.
4. Anxiety.
5. Anticipatory grieving.
6. Altered family process.
7. Actual/risk for altered parenting.
8. Health seeking behaviors.
Planning:
1. Promote maternal comfort.
2. Promote maternal-fetal wellbeing.
3. Provide opportunities for counseling and support.
4. Provide education for self-care measures in increasing comfort.
Implementation:
1. Facilitate testing; amniocentesis, sonogram.
2. Assess FHR.
3. Anticipate premature labor and postpartumhemorrhage caused by over distention of the
uterine muscle.
4. Instruct and explain.
a. Nature of problem.
b. Need to obtain immediate medical attention for problems
c. Need to observe for pre-eclampsia.
Evaluation:
Ensure that the expectant mother
1. Verbalizes increased comfort.
2. Progresses to uneventful birth, as does her baby.
3. Verbalizes support
4. Verbalizes self-care measures.
Or/ (Another answer)
➤ Monitor maternal and fetal status closely, including vital signs and fetal heart rate patterns.
➤ Monitor maternal weight gain pattern, notifying the health care provider if weight loss occurs.
➤ Provide emotional support before, during, and after ultrasonography.
➤ Inform the patient about coping measures if fetal anomalies are suspected
➤ Instruct her about signs and symptoms of labor, including those she’ll need to reporta immediately.
➤ Reinforce the need for close supervision and follow up.
➤ Assist with amnioinfusion as indicated.
➤ Encourage the patient to lie on her left side.
➤ Ensure that amnioinfusion solution is warmed to body temperature, vilidegim
➤ Continuously monitor maternal vital signs and fetal heart rate during the amnioinfusionen procedure.
➤ Note the development of any uterine contractions, notify the health care provider, andiequi continue to monitor closely.
➤ Maintain strict sterile technique during amnioinfusion.
Treatment and Management of Oligohydramnios:
Women who have a healthy pregnancy, developing mild oligohydramnios towards the later stages often do not need any treatment. In such cases, the doctor monitors the fetal heart rate, lung development as well as the baby’s movements closely using ultrasound and other similar tests. Delivery is the most appropriate management option if oligohydramnios occurs during the last stage of pregnancy. More severe cases of pre-term oligohydramnios may require the following treatment measures:
➤ Amnioinfusion
It involves infusing sodium chloride solution (room-temperature) into the amniotic cavity using an intrauterine catheter to maintain normal amniotic fluid levels.
➤ Vesico-Amniotic Shunts
This treatment procedure involves diverting the fetal urine into the uterus in women with fetal obstructive uropathy that causes oligohydramnios. Vesico-amniotic shunts are quite effective in managing the low amniotic fluid levels; however, their efficacy in maintaining proper renal and pulmonary functions is still doubtful.
➤ Fluid Injections
Injecting fluids through amniocentesis prior to delivery. Although, the condition tends to return within a few weeks after administering the injection, it allows doctors to understand the fetal anatomy properly enabling them to better manage the problem in the future.
➤ Maternal Re-Hydration,
Using oral fluids and IV fluids to rehydrate the mother’s body helps to raise the amniotic fluid levels. Due to this reason, doctors often ask affected mothers to drink plenty of water
➤ Bed Rest
Prescribing complete bed rest to the mother, along with proper hydration, helps to promote the amniotic fluid production by increasing her intravascular space. Termination of pregnancy may be the only option in severe cases occurring during the first trimester.

Prevention of oligohydramnios:
Prevention is not possible in the idiopathic cases. However, taking certain measures may reduce its risks
➤ Consulting the doctor before taking any medications as well as vitamin or herbal supplements.
➤ Following a proper healthy diet (especially for women suffering from diabetes).
➤ Drinking enough fluids to prevent dehydration.
➤ Regular exercise.
➤ Giving up smoking.
➤ Visiting the doctor for regular check-ups to detect any fetal abnormality,
Complications of oligohydramnios:
A. Fetal:
➤ Abortion
➤ Fetal deformity (alteration in shape of the skull, club foot).
➤ Fetal compression syndrome.
➤ Fetal pulmonary hypoplasia, cord compression.
➤ Increased fetal mortality.
➤ Increased risk of fetal infections (in case of prolonged amniotic membrane rupture).
B. Mother:
➤ Prolonged labor
➤ Increased operative interference
➤ Pulmonary hypoplasia.
➤ Amniotic band syndrome
Consequences of oligohydramnios:
Oligohydramnios occurring during the first and the second trimester is more likely to cause serious complications than when it occurs during the third trimester [1]
➤ Birth Defects: Malformation or complete absence of some external or internal organs in the newborn (hip dysplasia, club foot).
➤ Premature Birth: Delivery before completing 37th week of pregnancy.
➤ Miscarriage: Death of the baby in the uterus before twenty weeks of pregnancy.
➤ Stillbirth: Death of the baby in the uterus after twenty weeks of pregnancy.
➤ Death of the baby shortly after birth.
Oligohydramnios can lead to the following problems when occurring during the third trimester:
➤ Fetal growth restrictions.
➤ Complications like an umbilical cord compression during labor or at the time of birth (the umbilical cord is responsible for carrying oxygen and food to the fetus, so its compression prevents the baby from getting enough nutrition and oxygen).
➤ Cesarean delivery (a surgical method to bring the baby out through a cut in the mother’s abdomen and uterus).
