Today our topic of discussion is ” Nutrition and Diet “. Nutrition and diet are cornerstones of health, influencing everything from cellular metabolism to body composition and chronic disease risk. The adage “you are what you eat” encapsulates the fundamental truth that the quality of the nutrients ingested is directly proportional to the quality of health one experiences.
Nutrition is not just the act of eating; it is the science of how the body uses food to grow, repair, and maintain our cells and energy levels. This article will explore the myriad ways in which nutrition and diet impact metabolism and nutrition, offering insights into how to manage and optimize both for better health.
Nutrition and Diet : Metabolism and Nutrition
Understanding Nutrition
Nutrition is a multifaceted discipline that examines the nutrients necessary for proper human function, their sources, their biological uses, and how our bodies respond to various dietary patterns.
Macronutrients and Micronutrients
Macronutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, are essential for energy and structural components. Micronutrients, comprising vitamins and minerals, are crucial for the biochemical processes that drive metabolism.
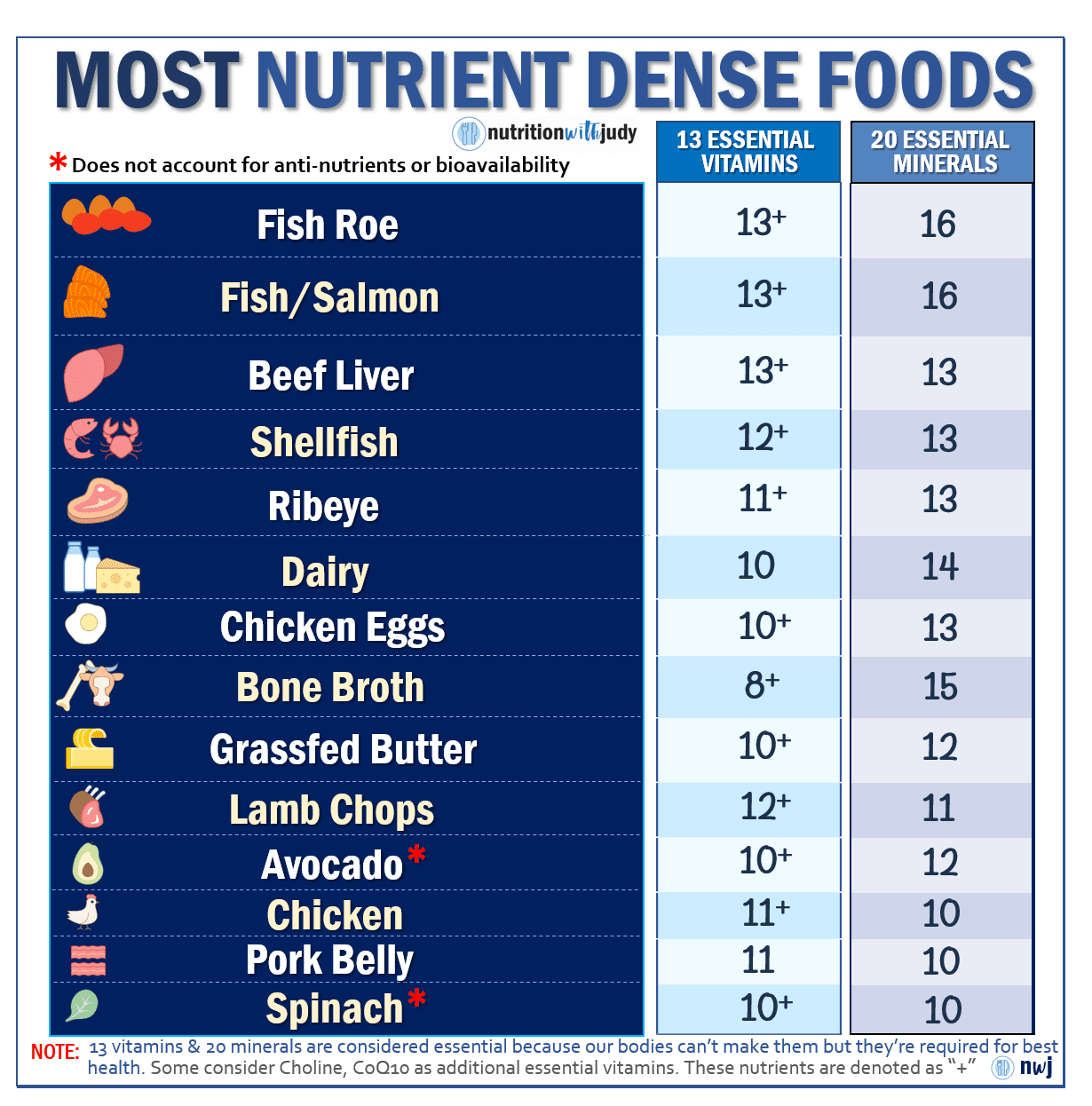
Nutrient Density and Bioavailability
The concept of nutrient density, which refers to the ratio of nutrients to calories in food, along with bioavailability, or the extent to which nutrients can be absorbed, are critical considerations for an effective diet.
Principles of Diet Planning
A well-planned diet is key to maintaining a balanced metabolic state and achieving specific health outcomes.
Dietary Guidelines
National and international dietary guidelines provide frameworks for building a nutrient-dense diet that can prevent chronic disease and promote longevity.
Personalized Nutrition
Understanding individual needs, including genetic predispositions, lifestyle, age, and health goals, is necessary for tailoring dietary plans for optimal nutrition.

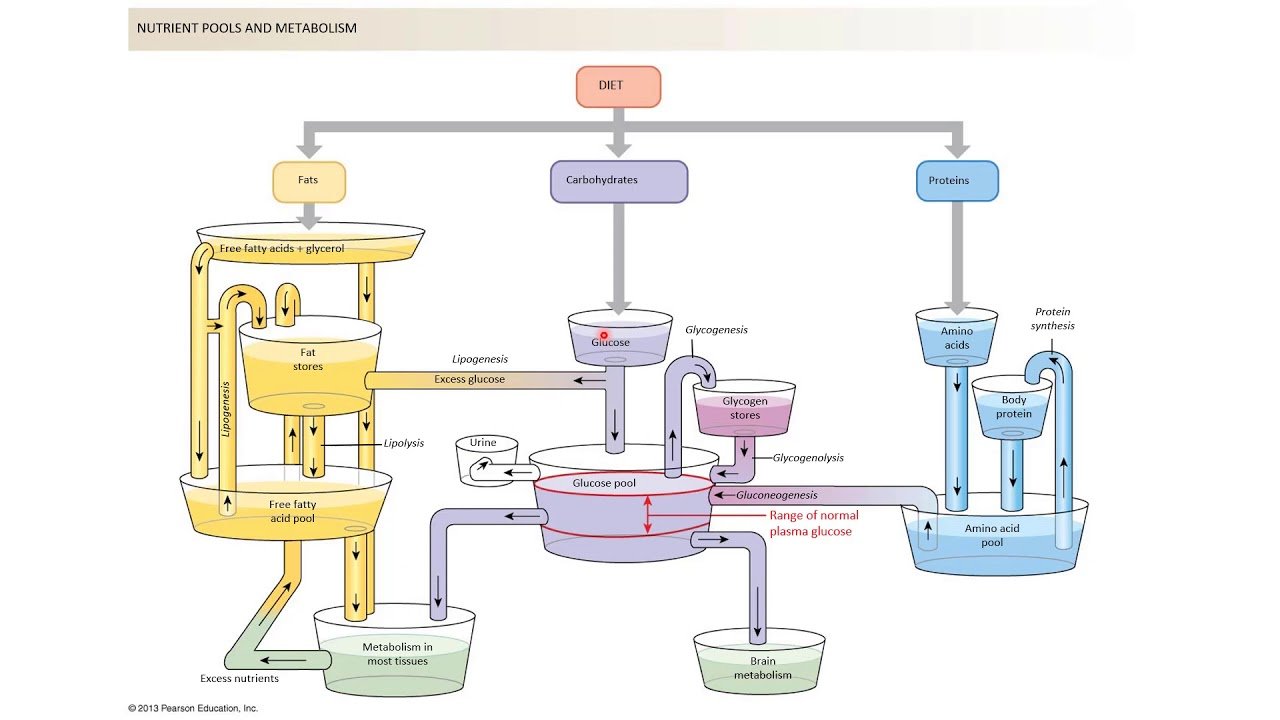
Metabolism and Energy Balance
Metabolism encompasses the chemical processes that occur within a living organism to maintain life, and diet is a principal factor that influences these processes.
Basal Metabolic Rate
BMR is the amount of energy expended at rest. Factors such as age, gender, muscle mass, and hormonal balance can affect BMR.
Energy Expenditure
Total energy expenditure includes BMR, physical activity, and the thermic effect of food. An individual’s diet can significantly influence energy balance and metabolic rate.
The Role of Diet in Weight Management
Weight management is a common concern, with diet playing a central role in influencing body weight.
Caloric Intake vs. Expenditure
Understanding and managing the balance between caloric intake and energy expenditure is fundamental to weight loss, gain, or maintenance.
Macronutrient Ratios
The proportion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins can affect satiety, energy levels, and body composition.

Nutrition in Disease Prevention
Nutrition has a profound effect on the risk and progression of diseases, particularly chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Heart Health
Dietary components like fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and plant sterols have been shown to influence cardiovascular health positively.
Diabetes Management
A diet with a controlled glycemic load is crucial in managing blood sugar levels in diabetes.
Diet and Gut Health
The gastrointestinal tract is not only the site of digestion and absorption but also an ecosystem teeming with microorganisms that influence overall health.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Dietary components that influence the gut microbiome can have systemic effects, including on immune function and mental health.
Fiber Intake
Fiber plays a vital role in maintaining gut health, with benefits extending to cardiovascular health and weight management.

Nutrition Through the Lifespan
Nutritional needs change throughout life, and diet must adapt to these evolving requirements.
Childhood and Adolescence
These stages are critical for growth and development, requiring increased amounts of certain nutrients like calcium and iron.
Aging Population
Older adults have different nutritional needs, often requiring more protein and certain micronutrients to maintain muscle mass and bone health.
Global Nutrition Challenges
Nutrition is a global issue, with both undernutrition and overnutrition posing significant public health challenges.
Food Security
Access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, nutritious food is a basic human right, yet remains a challenge for many.
The Double Burden of Malnutrition
Many populations face the double burden of undernutrition along with overweight and obesity, complicating public health interventions.

Conclusion
The relationship between nutrition, diet, and metabolism is complex and dynamic. A deeper understanding of this interplay is essential for crafting dietary patterns that promote health and prevent disease. As we unravel the intricacies of how the body processes and responds to different nutrients, personalized nutrition becomes more of a reality, providing individualized pathways to health through diet.
Read more:
