First aider – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
First aider
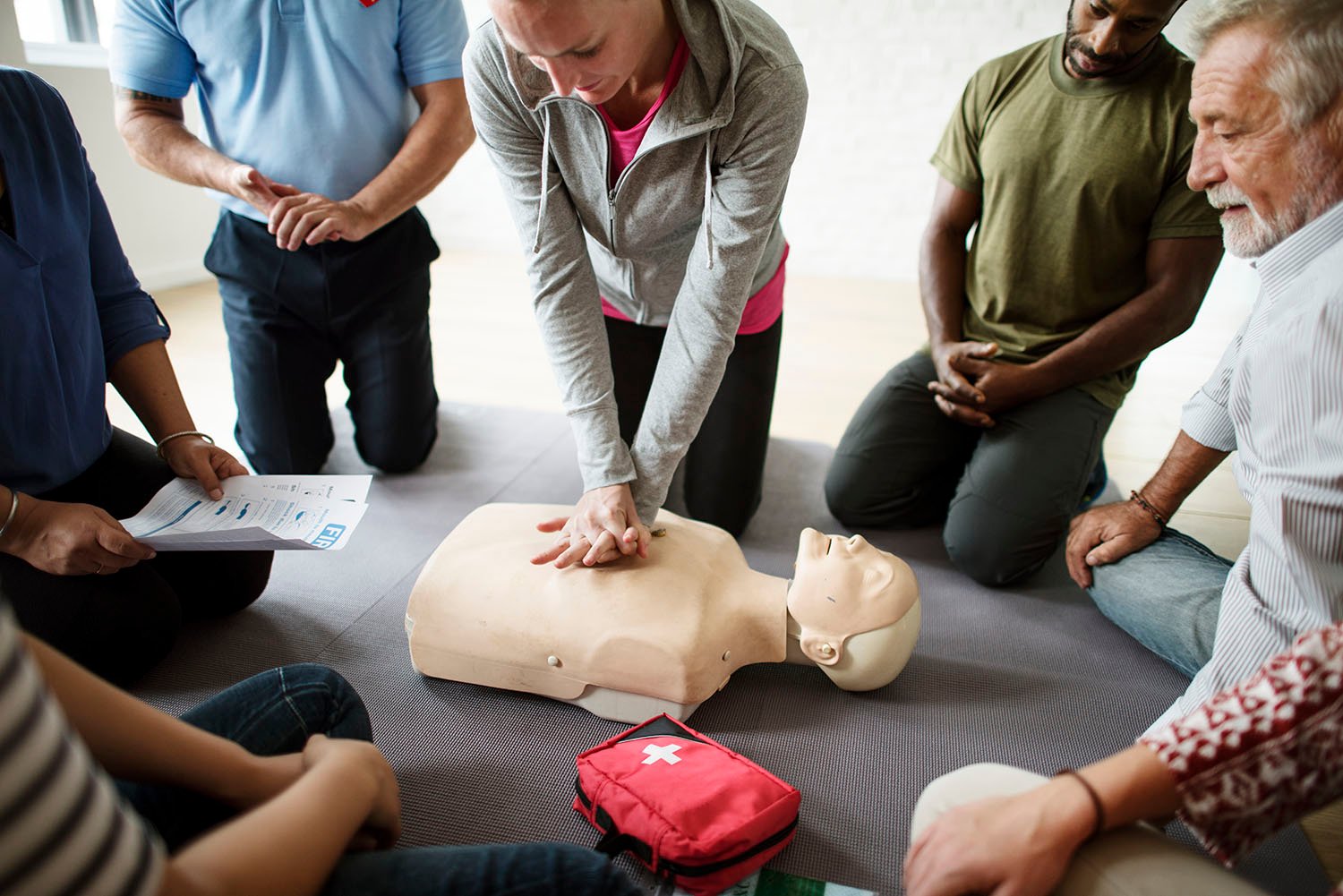
Definition of First Aider
A first-aider is someone who has undertaken training appropriate to the circumstances. They must hold a valid certificate of competence in either:
- first aid at work
- emergency first aid at work
- any other level of training or qualification that is appropriate to the circumstances
Or
A first aider is just a person who may have learned a standard method at application of first aid suited to his skill. He is trained to reach patients, identify the problem, and provide emergency care and when necessary move patients without causing further injury.
Responsibilities of First Aider:
1. Assess the condition of casualty.
2. Gain access to the patient in easiest and safest way.
3. Arrange for doctor/hospitalization.
4. Keep family/relatives inform.
5. Keep record of casualty and incidence.
6. To find out whether casualty is unconscious, conscious, alive or dead.
7. Identify the disease or condition from which the casualty is suffering.
8. Determine priority of first aid measure.
9. Give immediate, appropriate and adequate treatment considering priority of first aid measures.
10. Should bear in mind that a casualty may have more than one injury and that some casualties will require more urgent attention than others.

(Ref by-Dr. L.C. Gupta’s/TB-Lecture
Qualification of A First Aider:
1. Have the necessary knowledge.
2. Have sympathy and understanding
3. Have common sense.
4. Have initiative and sense of leadership.
5. Have the ability to act quickly, make decision and improvise
6. Should be a good observer.
7. Should not get panicky or excited.
8. Should have self-confidence and ability to judge injuries to be tracked first
9. Should be sympathy patients and relatives and providing good counseling.
10. Should be reassured the patient and his or her relative.
(Ref by-Lecture)
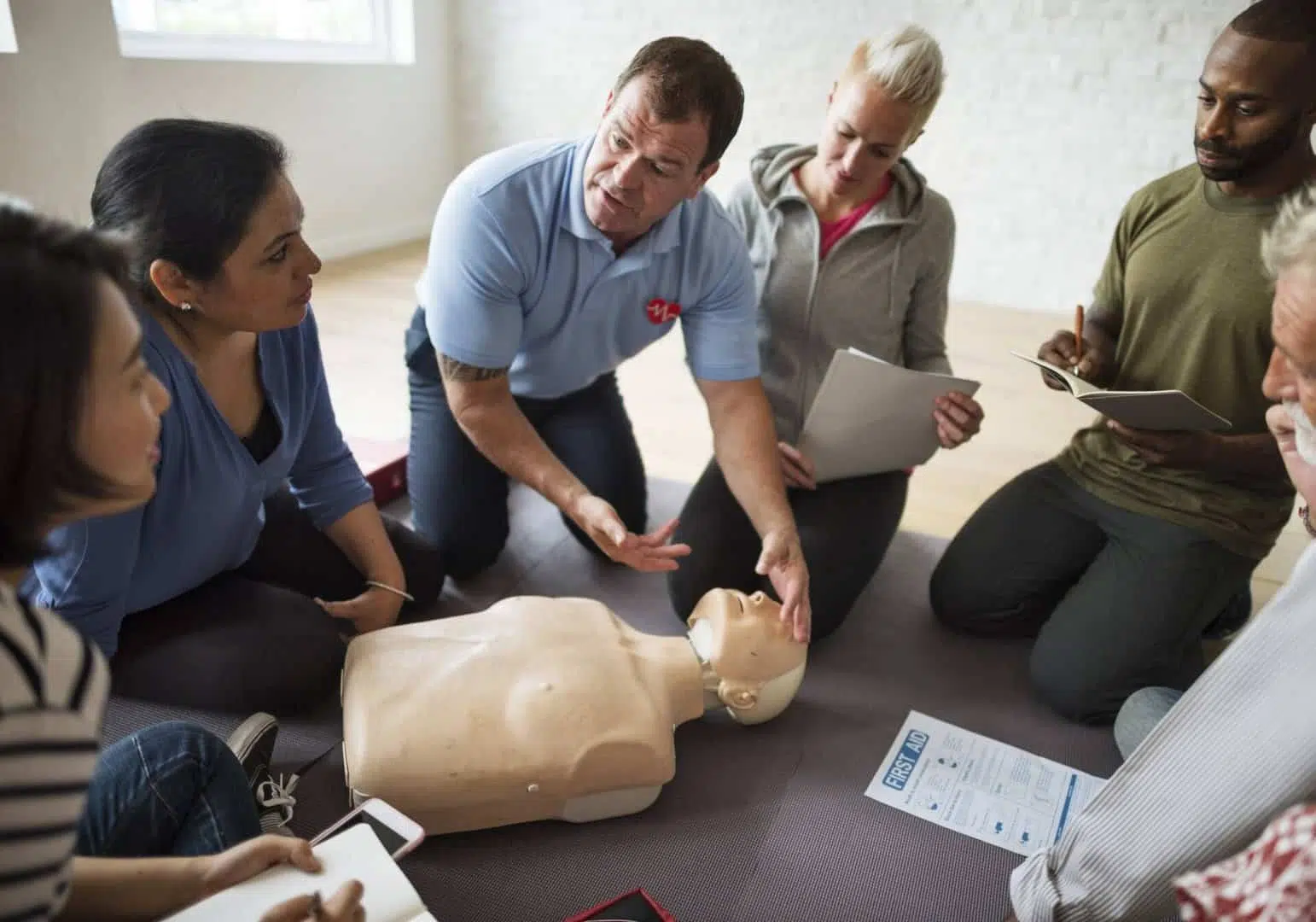
Summary of First Aider Skill:
1. Control the scene of accident.
2. Gain access to the patient.
3. Evaluate the scene in terms of safety and possible cause of accident.
4. Gather information from patient and bystanders.
5. Determine diagnostic signs and relate those to possible injuries or sudden illness that require emergency care
6. Determine vital signs. (Pulse, breathing, skin, temperature).
7. Perform the necessary ABCS of emergency care
- Open airway.
- Breathing (pulse lossness-provide one and two rescuer, cadio pulmonary resuscitation.)
- Bleeding control (Heamorrhage controlled by direct pressure and elevation, pressure points and tourniquets)
8. Diagnosis and care for shock.
9. Diagnosis and care for soft tissue and internal injuries including basic dressing and bandaging techniques.
10. Diagnosis and care for open and closed fractures, sprains, strains and dislocations including cold treatment and basic splinting techniques.
11. Detect and care for heart attack, stroke, diabetic come, insulin shock and epileptic or other seizures.
12. Diagnosis and care for facial injuries, head injuries, neck and spinal injuries and chest injuries including fractured ribs, flail chest and penetrating wounds.
13. Detect and care for poisoning including alcohol and drug abuse.
14. Diagnosis and care for burns and smoke inhalation.
15. Diagnosis and care for exposure to heat and cold which includes heat cramps, heat exhaustion, hypothermia and frost bite.
16. Assist in child birth and care of the new born.
17. Psychological and proper emergency care to victims of crises and diseases.
18. Perform proper transformation techniques.
