Assertive & Responsible Communication – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Assertive & Responsible Communication
Assertiveness
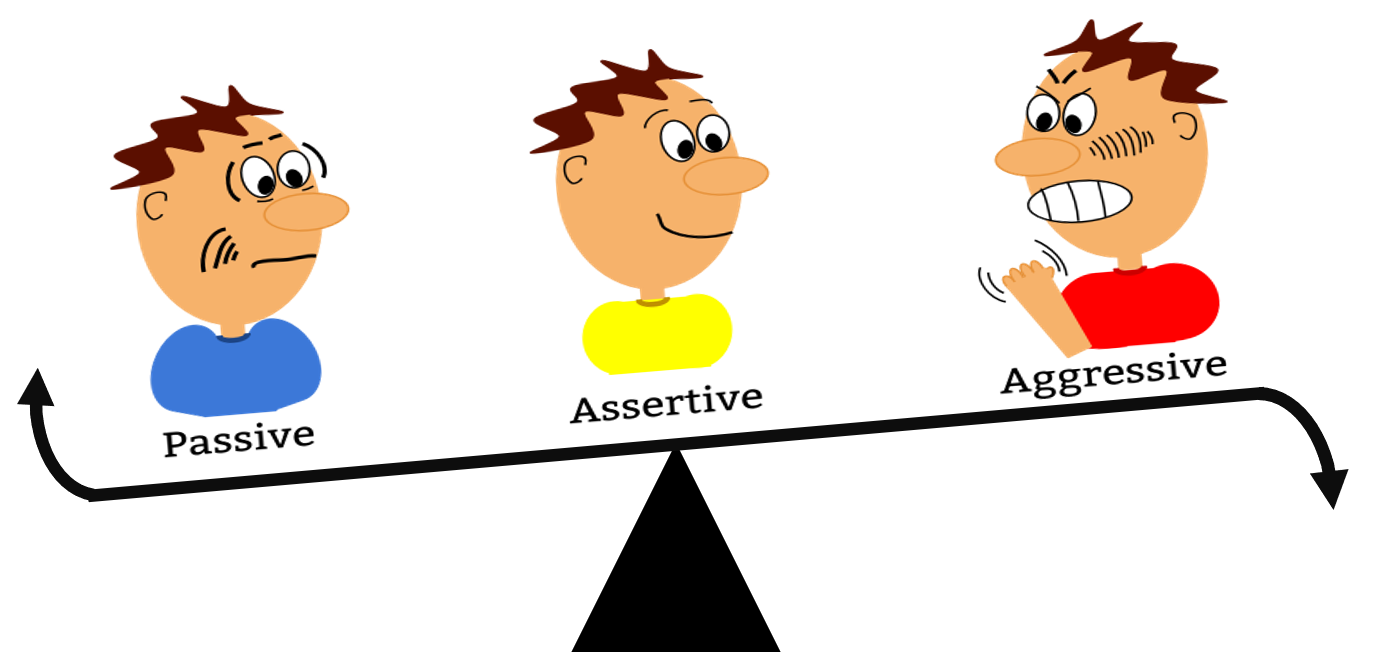
Assertiveness is the ability to express one’s feelings, opinions, beliefs, and needs directly, openly and honestly, while not violating the personal rights of others. Assertive staff nurses are able to present suggestions in a direct, comfortable way, give and take criticism, assess the rights and responsibilities in a nursing situation, and act on assessments in a thoughtful problem-solving way. Lack of assertiveness results in diminished communication efficacy, thus compromising patient care. (Poroch and McIntosh, 1995).
or
Assertiveness is a proactive problem solving and coping behavior is a verbal communication skill that states one’s own right positively without hampering the others write. Effective use of assertiveness prevents interpersonal misunderstanding and solves inevitable conflict that can be arise.
Dorland’s Medical Dictionary defines assertiveness as: “A form of behavior characterized by a confident declaration or affirmation of a statement without need of proof; this affirms the person’s rights or point of view without either aggressively threatening the rights of another (assuming a position of dominance) or submissively permitting another to ignore or deny one’s rights or point of view”

Assertive Communication:
Assertive means expressing opinions or desires strongly and with confidence. “To be assertive is to assert one self, positive, forthright to which it can be communicated in particular way. Assertive behavior consists of imparting feelings, emotions, and opinions. In health care settings, assertive behavior is a key element in ensuring that patient care is delivered appropriately.
Components of Assertive Behavior/Communication:
The following components of assertive communication are given below
1. Respect to others
2. Respect to oneself
3. Self-awareness
4. Effective clear & consistence communication
A. Respect to others: We respect their right to make demands. Ask for favors and express their feelings. When we respect others they are more likely to use appropriate behavior in responding to our demands, feelings, and needs.
B. Respect to oneself: Respect to oneself make us less likely to be dependent on others for approval and self-worth and less likely to act against our will. This can prevent us from following a cause of action that we know to be wrong.
C. Self-awareness: Enables us to approach every circumstance with some idea of what might happen and how we might feel about it. This way we can take responsibility for our emotions and are less likely to blame others.
D. Effective clear and consistence communication: Ensure that others understand what we say and what we mean. It also ensures that they know that we understand what they want from us. Also if we communicate clearly and consistently, we are less likely to mislead, mystify and maltreat others
and even ourselves.
Barriers of Assertive Communication:
1. Fear of rejection
2. Previous bad experience
3. Fear of failing
4. Fear of upsetting people
5. Others people’s perception
6. Self-perception
7. Lack of knowledge and skill
8. Emotional problems
9. Psychological problem
10. Fear of losing control
11. Lack of self esteem
12. Lack of self-confidence.
13. Lack of support
14. Lack of role models.
15. Fear of other peoples response.
16. Fear of change
17. Unwillingness of change
18. Incomplete understanding of the term assertiveness
19. Lack of role models
20. Feeling of powerlessness
21. Gender and cultural issues.
Responsible Communication:
“To be responsible” means: “Likely to be called upon the answer, able to respond or answer for one’s conduct and obligations.” This accountability may be described as being personally responsible for the outcome of our professional actions. To act this responsibility means that our nursing care is based on knowledge, not tradition or myth.
“To communicate responsibly” means to communicate logical, systemic way based on facts presented in the situation and your nursing knowledge. Responsible Communication demonstrates accurate problem solving behavior for the particular situation.
Ways to Establish Responsible Communication
According to Smith, the steps of the nursing process are followed to ensure responsible communication.
1. Collection of Data
2. Assessment of the data
3. Establishing expected outcome
4. Planning the communication strategy
5. Implementing the plan
6. Evaluation
A. Collection of Data: Collect essential verbal and nonverbal data about the client’s thoughts and feelings.
B. Assessment of the data: After ensuring the secured data are obtained, one must be analyzed the information to identify what request the client may request. Assessment is essential to effective communication. Assessment should look for factors that alter a client’s ability to receive, process, transmit information such as:
- Language barrier
- Cognitive skills (Developmental delay s involving the central nervous system affect language skill)
- Sensory perception alterations (assess for hearing deficit)
- Physiological barrier( Difficulty speaking may be respiratory problem
C. Establishing expected outcomes: Deciding whether it is reasonable to meet the client’s request. One must indicate what one hopes to achieve by communication. Individual client’s outcomes and goals depend on the nursing diagnosis you identify. For example for impaired verbal communication, you might write the following desired outcome
- Uses alternative method of communication (writing picture board)
- Communicates effectively using a translator
D. Planning the communication strategy: Decide what one will say or behave to transmit the message. The plan should be congruent with the expected outcomes. The overall goal for persons with impaired verbal communication is to reduce or resolve the impaired communication
- Developing listening skill
- Becoming aware of how people respond
- Developing a helping relationship
E. Implementing the plan: Responds to the client or colleague assertively and responsively
F. Evaluation : Check whether one’s response was assertive or responsible, and whether the objectives were achieved.
