Concept about Delegation – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Concept about Delegation
Delegation is the assignment of any responsibility or authority to another person (normally from a manager to a subordinate) to carry out specific activities, such as starting on proper tires during a wet race. It is one of the core concepts of management leadership. However, the person who delegated the work remains accountable for the outcome of the delegated work. Delegation empowers a subordinate to make decisions, i.e. it is a shift of decision-making authority from one organizational level to a lower one.
Delegation, if properly done, is not abdication. The opposite of effective delegation is micromanagement, where a manager provides too much input, direction, and review of delegated work. In general, delegation is good and can save money and time, help in building skills, and motivate people. On the other hand, poor delegation might cause frustration and confusion to all the involved parties.

Definition of Delegation:
According to Louis Allen: “Delegation is the dynamics of management, it is the process a manager follows in dividing the work assigned to him so that he performs that part which only he, because of his unique organizational placement, can perform effectively, and so that he can get others to help him with what remains.”
Or,
According to F.C. Moore: “Delegation means assigning work to the others and giving them authority to do so.”
Or,
Delegation is the assignment of any responsibility or authority to another person (normally from a manager to a subordinate) to carry out specific activities, such as starting on proper tires during a wet rасе.
Or,
Delegation is the use of personal to accomplish a desired objectives through allocation of authority & responsibility.
Or,
“Delegation can simply be defined as “getting work done through other or directing the performance of one or more people to accomplish organizational goals”
Importance/ Benefits of Effective Delegation:
Effective delegation benefits the delegator, delegate, patient’s and organization.
A. Benefits to the Delegator-
- Allows to devote more time to those task that cannot be delegated.
- Provides chance to develop new knowledge and abilities, facilitating the opportunity for carrier advancement and
- Having individuals with advanced skills provides continuity in the delegators absence
B. Benefits to the delegate-
- Allows delegate to gain new skills and abilities that can facilitate upward mobility.
- Provides the scope to bring trust and support, build self-esteem and confidence.
- Improves morale.
- Develops a sense of pride and belonging as well as greater awareness of responsibility
- Allow for learning to appreciate the roles and responsibilities of others and Increases cooperation and enhances teamwork.
C. Benefits to the organization
- As teamwork improves, the organization benefits by achieving its goals more efficiently.
- Overtime and absence decreases, subsequently, productivity increases, and the organizations financial position may improve.
D. Benefits to the patient-
- As delegation increases efficiency, the quality of care improves.
- As quality improves, patient satisfaction increases.
Purposes of Delegation:
1. It helps to assigning work
2. Promotes internalized motivation.
3. Helps to build interpersonal relationships among the working team.
4. Cost savings.
5. To ensure best outcome within the short possible period of time,
6. Prevents any biasness activity in professional work
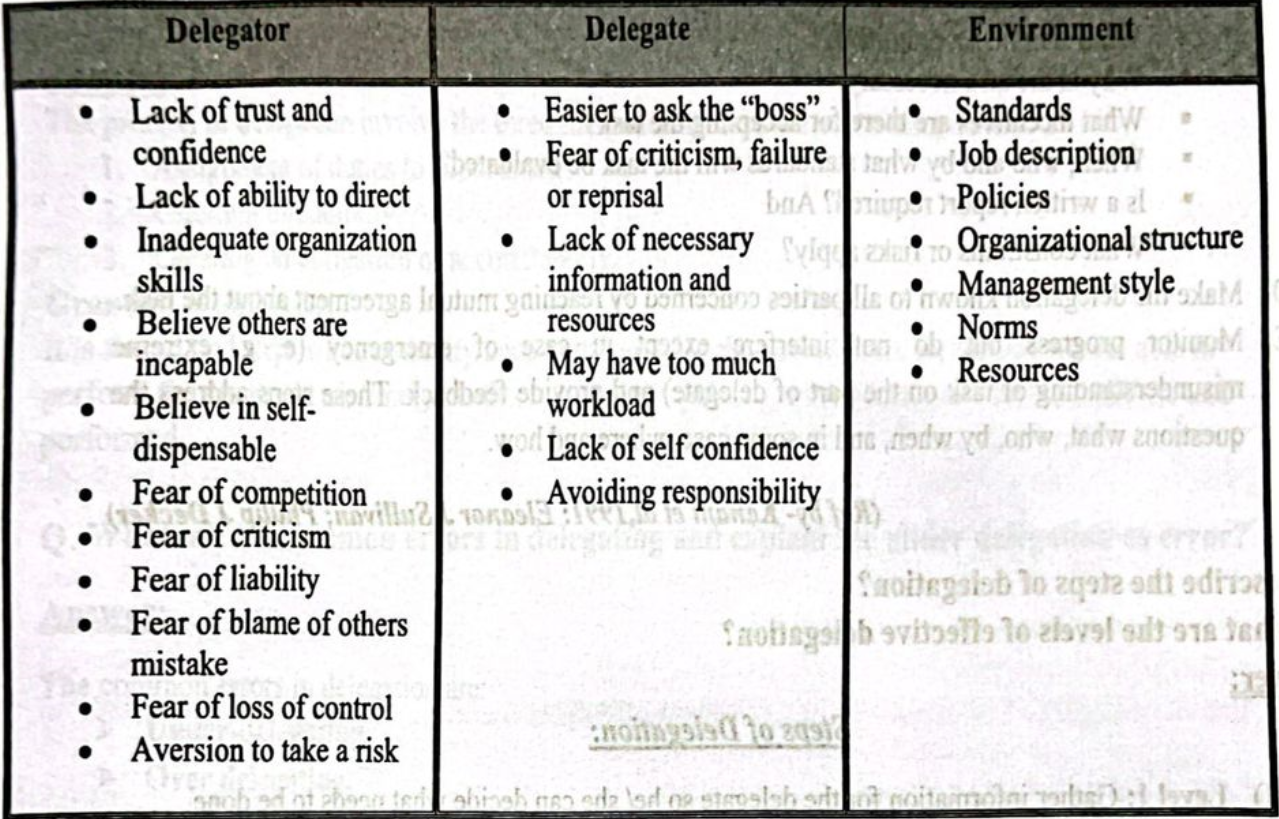
Barriers to Effective Delegation
Often managers are reluctant to delegate. Here is listed some of the barriers which may hinder effective delegation.
Process of Delegation:
Delegation is a complex undertaking and perfection cannot be achieved. However, the following steps should always be carefully observed by the delegator in order to avoid failure,
A. Define clearly in your mind the task and the related authority and responsibility to be delegated. Check carefully
- What can you delegate?
- What are the complexities of the task?
- What areas of authority must the person control?
- What resources are needed?
- Are there any limitations to the amount of authority or resources?
- What level of delegation should be used?
B. Choose a person willing and capable of accepting responsibility and carrying out the task.. In doing this check carefully-
- What skills or abilities are necessary?
- Are there any limitation imposed by scope of practice law?
- Who is available? And
- Who is willing?
C. Provide clear instructions with sufficient authority as well as time to obtain the results. In doing this, check carefully the follows-
- What is to be accomplished?
- Why is the task necessary?
- What incentives are there for accepting the task?
- When, who and by what standards will the task be evaluated?
- Is a written report required? And
- What constrains or risks apply?
D. Make the delegation known to all parties concerned by reaching mutual agreement about the task.
E. Monitor progress but do not interfere except in case of emergency (e. g. extreme misunderstanding of task on the part of delegate) and provide feedback. These steps address the questions what, who, by when, and in some case, where and how.
Steps of Delegation:
1) Level 1: Gather information for the delegate so he/she can decide what needs to be done.
2) Level 2: Determine alternative courses of action from which the delegate may choose.
3) Level 3: Have the delegate perform one part of the task at a time and obtain approval for each new step.
4) Level 4: Have the delegate outline an entire course of action for accomplishing the whole task
and have it approval before proceeding.
5) Level 5: Allow the delegate to perform the whole task using any preferred method and report only the result
Principles of Delegation:
A. Clarity of delegation.
B. Delegation to be consistent with result expected.
C. Responsibility cannot be delegated.
D. Parity of authority and responsibility.
E. The exception principal.
F. Other principals of delegation are-
a) Interference should be minimum
b) Tolerance of mistake
c) Adequate should be established.
d) Goals should be predetermined.
e) Policies, rules and procedures should be establish to guide decisions
f) Upward delegation should be allowed.
The process of delegation involve the three fundamental steps/elements/component-
1. Assignment of duties to subordinate.
2. Granting of authority.
3. Creating on obligation or accountability.
Granting of authority:
It is the second steps when authority need to delegated to the subordinates for making his/her able to perform the assigned task timely. Authority is right to power granted to an individual to make the task performed.
The common errors in delegation are:
➤ Under-delegating.
➤ Over delegating.
➤ Improper delegating.
Under delegating:
It occurs frequently due to-
- The false assumption of manager that delegation of manager that delegation may be interpreted as a lack of ability to the job correctly or completely.
- The desire of manager about the accomplishment of whole job by himself having the lack of trust to the subordinates.
- The lack of experience in the job or in delegation itself.
The reason for delegation are as bellows-
1. Transforming authority and responsibility to his subordinates.
2. Nobody can work all the time.
3. It save time and eliminates long delay.
4. Placing confidence and trust among subordinate,
5. Bring the personality issue.
6. Creation of leadership and creation of skill.
7. Division of labor and decentralization.
8. It helps in expansion of an organization
The common errors in delegation are:
1. Under-delegating.
2. Over delegating.
3. Improper delegating
Over delegating:
Some managers over delegate burdening their subordinates, because they are very poor in time management, they spend most of their time on just trying to gate organized. Others over delegate because they feel insecure in their ability to perform a task.
