Definition of Insect bites – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Definition of Insect Bites
When the insect pierces its sting into the tissue and release venom (toxic, foreign protein, antigen), it is known as insect bite. The venom contains chemical compounds which produce allergy.
Insect bites and stings can cause an immediate skin reaction. The bite from fire ants and the sting from bees, wasps, and hornets are most often painful. Bites caused by mosquitoes, fleas, and mites are more likely to cause itching than pain.
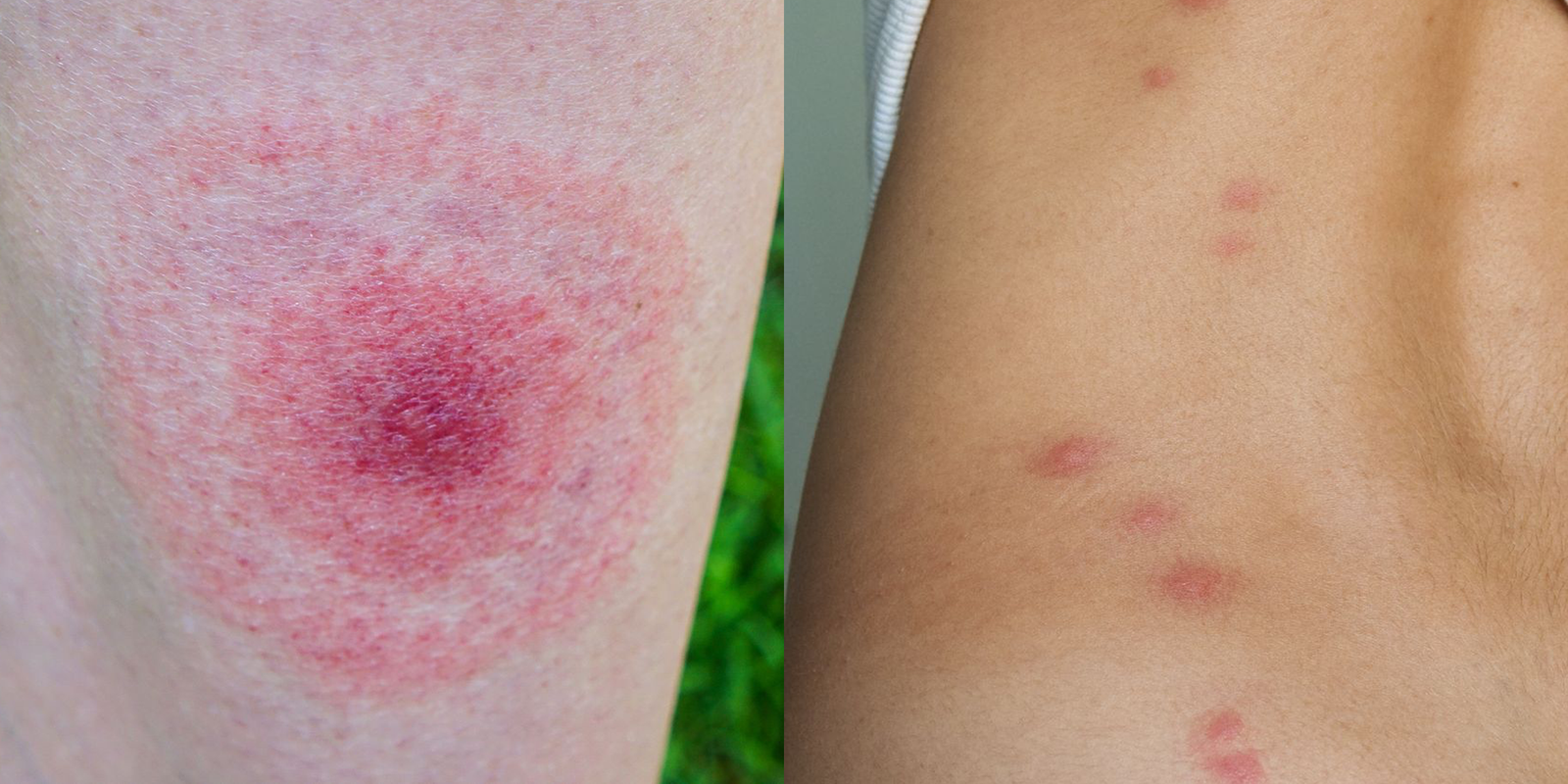
Sign and symptoms of Insect Bite:
Most common symptoms include:
1. Pain
2. Redness
3. Swelling
4. Itching
5. Burning
6. Numbness
7. Tingling
Some people have severe, life-threatening reactions to bee stings or insect bites. This is called anaphylactic shock. This condition can occur very quickly and lead to rapid death if not treated quickly. Symptoms of anaphylaxis can occur quickly and affect the whole body. They include:
1. Chest pain
2. Face or mouth swelling
3. Difficulty swallowing
4. Difficulty breathing
5. Fainting or lightheadedness
6. Abdominal pain or vomiting
7. Rash or flushing
First Aid Treatment of Insects Bite:
1. Removing of the stings if the sting has been left embedded in the skin hold tweezers as near to the skin as possible grasp the sting and remove it.
2. Local treatment:
- Bee venom is acid and it should be neutrilized by application of ammonia, soda or methylene blue.
- Wasp venom is alkaline and it should be neutralized by application of vinegar or lemon juice.
- To relieve pain and swelling by applying cold compress and surgical spirit.
- For jelly fish stings apply calamine lotion.
3. Treatment of insect stings inside the mouth or throat:
- To reduce swelling by giving ice to suck, rinse the mouth with cold water or solution of water and bicarbonate of soda (Sod bicarbonate)
- If breathing becomes difficult, place the casualty in recovery position.
4. If required, shift the casualty to hospital.

