Nursing Records/ Documentation – Nursing is a profession within the healthcare sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other healthcare providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialisms with differing levels of prescriber authority.
Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. However, nurses are permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings depending on training level. In the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced and specialized credentials, and many of the traditional regulations and provider roles are changing.
Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, the patient, the patient’s family, and other team members, that focus on treating illness to improve quality of life. Nurses may help coordinate the patient care performed by other members of an interdisciplinary healthcare team such as therapists, medical practitioners, and dietitians. Nurses provide care both interdependently, for example, with physicians, and independently as nursing professionals.
Nursing Records/ Documentation
A record is that which is written to perpetuate knowledge of events. Records are practical and indispensable and to the doctor, nurse and paramedical professional a record is given the best possible service to the individual, family and to the community. All professional person need to be accountable for the performance of their duties to public. Science nursing has been considered as profession, nurse need to record their work on completion.
Nurse should not speak on their work. The record should speak. A record is a permanent written communication that document information relevant to a client’s health care manager. Health records give information about the family members, activities carry out, achievement. General information is mainly about the village, targets and condition of the family individuals.
Definition of Records:
According to Rebecca Samson
Records are formal legal, administrative tools that permanently document information relevant direct or indirect patient care.
According to Potter and Perry
“A record is a permanent written communication that documents information relevant to a client’s health care management, e.g. a client chart is a continuing account of client’s health care status and need.
Or,
Records are administrative tools used to classify and prevent duplication of the information.
Definition of Nursing Record:
A nursing record is a system which is the record of care planned and given to individual clients by qualified nurses or other caregivers under the direction of a qualified nurse.
Definition of Documentation:
Documentation is the written evidence of the care provide by the nurse. It usually includes the client’s clinical history and medical history and chart.
Or
Documentation is defined as anything written or presented that is relied on as record of proof for authorized persons. A medical record should be a comprehensive declaration of the client health status and needs, as well as the service provided for the client care. Good documentation reflects not only quality of care but also evidence of each health care team member accountability in providing care.
Kinds of Records:
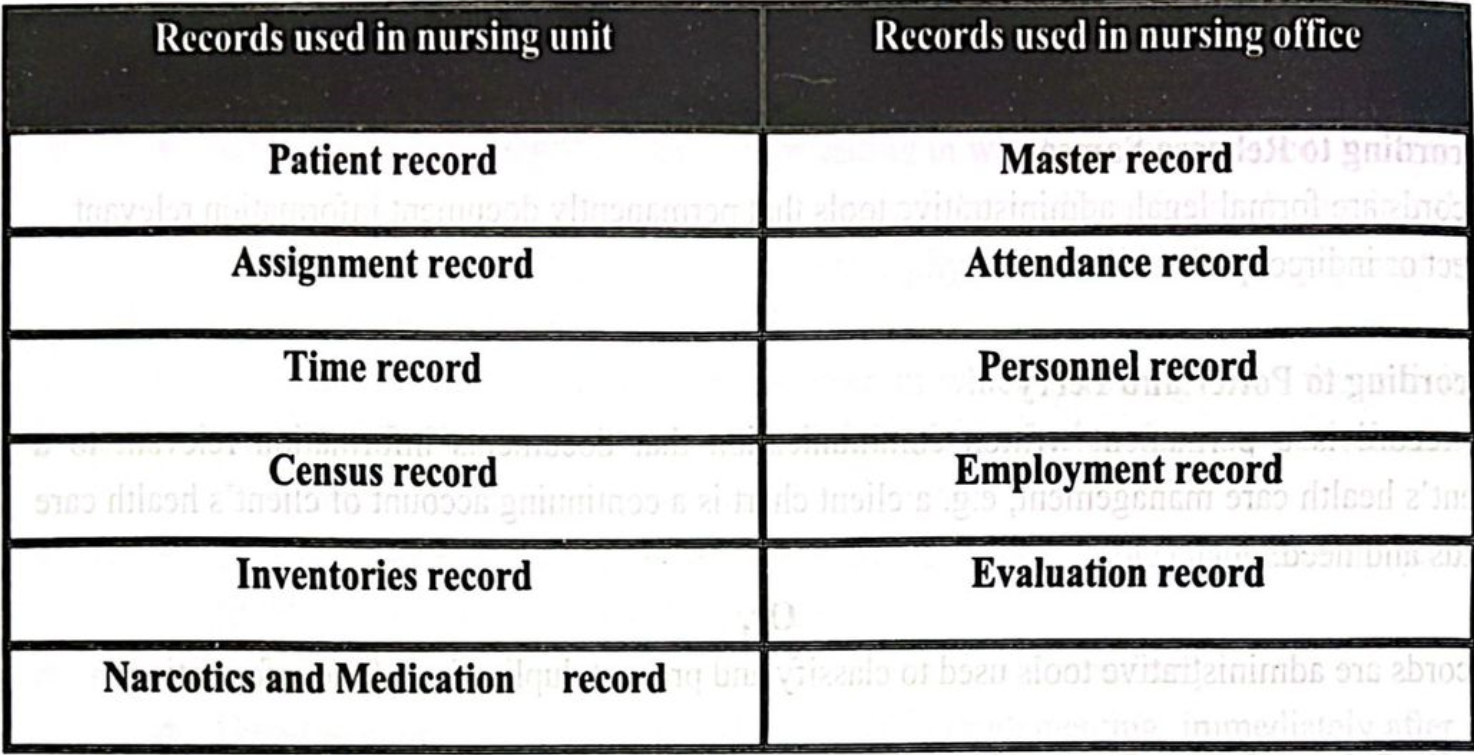
Forms/Types of Records:
There are mainly four forms of records usually used in hospital
1. Kardex
2. Flow Sheets
3. Nurses’ Progress Notes
4. Discharge Summary
A. The Kardex
It is used as a reference throughout the shift and during change-of-shift reports.
- Client data
- Medical diagnoses and nursing diagnoses
- Medical orders
- Activities
B. Flow sheets
- Flow sheets reduce the redundancy of charting in the nurses’ progress notes
- The information on flow sheets can be formatted to meet the specific needs of the client.
C. Nurses’ progress notes
- Nurses’ progress notes are used to document the client’s condition, problems and 2.0 complaints, interventions, responses, achievement of outcomes
- Progress notes can be completely narrative or incorporated into a standardized flow sheet.
D. Discharge Summary
- Client’s status at admission and discharge
- Brief summary of client’s care
- edua Interventions and education outcomes
- Resolved problems and continuing need
- Client instructions
(Another Classification of Records)
1. Concerning nursing staff
2. Concerning other employees and supporting staff
3. General records
A. Record concerning nursing staff:
a. Application forms and other records called for at the time of recruitment selection and appointment.
b. Record of each staff evaluation report,
c. Record of transfer order
d. A progress report showing grades
e. Health record, leave record,
f. Job description for each category nursing personnel.
B. Record concerning others employees:
a. Application form.
b. Copy of appointment.
c. Job description.
d. Periodic evaluation or progress report.
e. Level record.
f. Health record
C. General record:
- Philosophy purposes of the organization
- Written policies of the organization.
- Statement of the budget proposal and allotment.
- Minutes of staff meeting.
- Inventories stock.
Purposes of Maintaining Records/Record Keeping:
- Provide necessary information about the activities within the department.
- Administrator can observe the volume of working increasing, decreasing or remaining the same.
- Observe the progress the work.
- To communicate with health team members.
- To educate nursing students.
- To protects hospital from law suits.
- To evaluate quality patient care.
- It contributes to ward budget preparation.
- Save as the basis for preserving information of historical significance
- Serve as source of legal purpose.
- Records are essential for planning and evaluation.
- Records are work as a tool of communication.
- It indicates plan for the future.
- It provides base line data to estimate the long term changes related to service.
- It provides opportunity for evaluation the nursing personnel.

Importance of Records:
A. For the individual and family:
a) Serve the history of the client.
b) Assist in continuity of care.
c) Evidence to support if legal issues arise.
d) Assess health needs, research and teaching
B. For the Doctor:
a) Serve the guide for diagnosis, treatment, follow-up and evaluation. – Indicate progress and continuity of care.
b) Self-evaluation of medical practice.
c) Protect doctor in legal issues.
d) Used for teaching and research
C. For the nurses:
a) Document nursing service rendered.
b) Shows progress- Planning and evaluation of service for future improvement.
c) Guide for professional growth- Judge the quality and quantity of work done-.
d) Communication tool between nurse and other staff involved in the care.
e) Indicate plan for future e recording system.
The Uses of Medical Records:
- It serves as a means of communication among the professionals sharing in his care.
- The patient’s chart is the basis for planning his care and carrying out the plan.
- It is evidence of the course of his illness and his treatment.
- It is also used as a basis for review. Study and evaluation of the care rendered to the patient.
- As an adjunct in the education of many personnel and often as a reference source.
- As a source of statistical data, such as births, deaths or hospital admissions.
- As a basis for making plans for the future and for anticipating needs.
- As a legal protection for all concerned.
- As subject material for comparative studies and research.
- The medical record system is organized to accord services to many groups; patients, professional staff, administration and the community.
- Nursing department plays a major role in the compiling of high-quality patient records.
- The nursing record greatly contributes to the medical record, providing a historical, documental record that assists the physician in the diagnosis and treatment of the patient.

Principles of Record Writing:
- Nurse should develop their own method of written instead of writing an imposition.
- Record should be written clearly and legibly.
- Record should contain true and false based on observation, conversation and action.
- Printed records always advisable, if not the factors should be printed briefly and clearly.
- Record should be completed and should give accurate information.
- Record should not be kept blank.
- All the records should be filed in serial number and should be properly arranged.
- While record writing, continuity should be maintained.
- Record should be written immediately after our service.
- Record should be brief and neat.
- Record should be kept as confidential.
- Record should provide periodic summary,
- Record should be handled properly, carefully and safely
- Records are used as a basis for research and evaluation. Hence, records should have completeness.
- Record systems are essential for the efficiency and uniformity of service. Hence the 13.0 agency should develop new or revise old forms to meet the need
- Combined checking and narrative record from are useful and save time
Characteristics of a Good Report or Record:
Documentation and reporting are two of the most important functions a nurse performs. The important characteristics must be followed by good documentation which results in a good record and report.
- Timing
- Permanency
- Completeness
- Signature
- Confidentiality
- Accuracy
- Use of standard terminology
Report can be ether oral or written. The purpose of reporting in general is to communicate specific information to a person or a group people. A report should be concise. A good i report includes pertinent information but not extraneous details. Two common types of report are shift reports and the incident reports.
Significant of Nursing Record:
Nursing records / documentation has a significant role in providing effective nursing care and appropriate treatment the important of nursing records and documentation are as follows –
- It acts as a roadmap for the nurses to maintain the continuity of nursing care from one shift to another and from one day to next day.
- It may guide / direct the physician to give appropriate treatment.
- It acts as a future references.
- It acts as a vital part of nursing practice.
- It acts as a legal protection of the person.
- It gives the clear idea about the previous work.
- It evaluates the necessary care and health education.
- Good documentation reflects the quality of care.
- It is an evidence of each health care member’s accountability in given care and appropriate treatment.
- It acts as a management information system (MIS). These are essential for:
✓ Communication.
✓ Assessment of patient health status
✓ Progress of the treatment.
✓ Further care planning.
✓ Education & research purposes
✓ Auditory and legal purposes

Legal Issues Pertaining to Nursing Records:
- The nurse must maintain the confidentiality of documentation.
- The nurse must respect the client right to privacy is reporting.
- Access to records – nurse may be responsible to providing clients with this record and interpreting the information help within them.
Uses of Nursing Record:
- Professional sharing in his care.
- Patient chart basis for planning his care and carrying out the plan.
- Illness and his treatment.
- Study and evaluation of the care.
- Sources of statistical data such as – birth rate, death rate, admission etc.
- As a legal protection for all concerned.
- Material for comparative studies and research.
- Nursing department plays major role of high quality patient record, documental record, assist the physician in the treatment and nursing diagnosis and nursing care plan.
Record Keeping System:
- Sources of record: The information is grouped according to the sources contributed by health care department.
- Nursing carder system: In the carder system, the information needed for the doing care is acceptable from the card it is kept field.
- Problem oriented record: The information is grouped depending on the types of problem.
- Computerized information system: Information can be stored in smaller areas search and analytical tasks can be done and information can be obtained in a faster and efficient manner.
Uses of Computer for Record Keeping in Nursing Profession:
In nursing usage of computer can be divided into 3 categories:
➤ Clinical system: Data collection about patient and identify the patients problem, computer can sort and analyze data and facilitate communication about patients among health care providers.
➤ Management information system:
- Information system used for patient classification.
- Supplies and material management.
- Staff scheduling policy.
- Nursing procedure and budget information and management.
- Personnel record, statistical and administrative reports.
➤ Education system:
- Computers used for instruction to the students.
Way to keep Good Nursing Records:
The patient’s record must provide an accurate, current, objective, comprehensive, but concise, account of his/her stay in hospital. Traditionally, nursing records are hand-written. Do not assume that electronic record keeping is necessary.
- Use a standardized form. This will help to ensure consistency and improve the quality of the written record. There should be a systematic approach to providing nursing care (the nursing process) and this should be documented consistently. The nursing record should include assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation of care.
- Ensure the record begins with an identification sheet. This contains the patient’s personal data: name, age, address, next of kin, career, and so on. All continuation sheets must show the full name of the patient.
- Ensure a supply of continuation sheets is available.
- Date and sign each entry, giving your full name. Give the time, using the 24-hour clock system. For example, write 14:00 instead of 2 pm.
- Write in dark ink (preferably black ink), never in pencil, and keep records out of direct sunlight. This will help to ensure they do not fade and cannot be erased.
- On admission, record the patient’s visual acuity, blood pressure, pulse, temperature, and respiration, as well as the results of any tests.
- State the diagnosis clearly, as well as any other problem the patient is currently
experiencing. - Record all medication given to the patient and sign the prescription sheet.
- Record all relevant observations in the patient’s nursing record, as well as on any charts, e.g., blood pressure charts or intraocular pressure phasing charts. File the charts in the medical notes when the patient is discharged.
- Ensure that the consent form for surgery, signed clearly by the patient, is included in the patient’s records.
- Note all plans made for the patient’s discharge, e.g., whether the patient or career is competent at instilling the prescribed eye drops and whether they understand details of follow-up appointments.
the tips for writing records
1. Ensure the statements are factual and recorded in consecutive order, as they happen. Only record what you, as the nurse, see, hear, or do.
2. Do not use jargon, meaningless phrases, or personal opinions (e.g., “the patient’s vision appears blurred” or “the patient’s vision appears to be improving”). If you want to make a comment about changes in the patient’s vision, check the visual acuity and record it.
3. Do not use an abbreviation unless you are sure that it is commonly understood and in general use. For example, BP and VA are in general use and would be safe to use on records when commenting on blood pressure and visual acuity, respectively.
4. Do not speculate, make offensive statements, or use humour about the patient. Patients have the right to see their records!
5. If you make an error, cross it out with one clear line through it, and sign. Do not use sticky labels or correction fluid.
6. Write legibly and in clear, short sentences.
7. Remember, some information you have been given by the patient may be confidential. Think carefully and decide whether it is necessary to record it in writing where anyone may be able to read it; all members of the eye care team, and also the patient and relatives, have a right to access nursing records.
Reporting
Definition of Reporting:
According to Rebecca Samson
A report is a system of communication aimed at transferring essential information necessary for safe and holistic patient care.
According to Sr. Nancy
“Reports are information about a patient either written or oral”
According to Potter and Perry
A report is a summary of activities or observations seen, performed or heard”
Or,
Report is a document form which include; conclusions or findings based on facts, or recommendations concerning the patient.
Types of Reports:
It can be:-
1. Oral reports
2. Written report.
A. Oral report
- Oral reports are given when information is needed to be reported immediately not for permanency, e.g. oral reports given by head nurse to all personnel, reports about patient condition and needs, onder
B. Written reports:
- Day, evening and night report
- Incident report.
- Report of complain.
- Report including negligence
- Reports for requisition.
Purposes of Reports:
1. To show the kind and amount of service rendered over a specific period.
2. To illustrate progress in teaching goals.
3. It acts as an aid in studying health condition.
4. It acts as an aid in planning
5. To interpret the services to the public and to the other interested agencies.
6. Each agency has specified regulations about reporting services on a daily, monthly, and annual basis. A monthly narrative report provides an opportunity to pursuit problems for administrative considerations. The value of good reports cannot be fully described.
- Good reports are time servers. They prevent duplication of work.
- Direct influence on the progress and even life of the patients.
- Provide a sense of security and confidence to the nurse in doing her work. Giving a good report is an art
Guidelines for Giving Report of Patient:
- Follow a particular order when reporting about a serious of patients, e.g.- follow ward number.
- Identify the patient by name, room number and bed designed, e.g.- Ramu bed no-2. This enables the listeners especially patient / Reliever nurses or those returning from days off or vocation, to relate subsequent information immediately to the patient’s care.
- Depending on the type of unit, provide the reason for admission that is the patient’s medical diagnosis or original complaints. This information may not be necessary in long term patients or newborn nurseries.
- Including diagnostic tests, results and other therapies performed in the past 24 hours. Such as blood transfusions. Surgery initiation of intravenous therapy. Narcotics administered, blood gases level.
- Note any significant changes in the patient’s conditions.
- When reporting about changes, present the pertinent information in this order, assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, intervention and evaluation. e.g. – Temperature 39.3° C, orally at 16.00 hours, 500 mg paracetamol given orally, temperature dropped down to 38.1° C at 18.00 hours. But not temperature was 39 point something during the course of the shift. Given some paracetamol with good effect.
- Include unmark able measurements, e.g. BP, pulse, temperature are within normal limits.
- Report the patient’s emotional responses that need attention before other interventions can be implemented, e.g.- leg is gangrenous, and is now schedule for below knee amputation, needs time to discuss his feeling before the nurse commences preoperative teaching.
Elements of Report:
A. Timings: Most pertinent time. An accident or change in persons conditions are examples of reasons for immediate reporting.
B. Organization: Important points are mentioned in a logical order and stand out from the
explanatory and supporting statements.
C. Clarity: Leaving no doubt of what happened, what was done, or what remains to be done.
D. Brevity: Omit unnecessary words and statements for a clear, complete picture.
E. Correctness: Of all information to prevent serious mistakes in giving continued nursing care.
F. Objectivity: Presentation of facts, not personal feelings, to give a true picture.
Relation of Record and Report
- Record and report are mutually inter-dependent. Report can be prepared on the basis of records.
- Similarly, report can be presented as record.
- Record is always in the written form while report can be oral as well. Report especially oral report, can be forgotten while record can be preserved for a long time.
- Despite being literally different, record and report are synonymous and interrelated, also they are the essential and important component of community health, management and nursing.
NICE TO KNOW
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is the most common scoring system used to describe the level of consciousness in a person following a traumatic brain injury. Basically, it is used to help gauge the severity of an acute brain injury. The test is simple, reliable, and correlates well with outcome following severe brain injury.
The GCS is a reliable and objective way of recording the initial and subsequent level of consciousness in a person after a brain injury. It is used by trained staff at the site of an injury like a car crash or sports injury, for example, and in the emergency department and intensive care units.
Eye Opening (E)
- 4 = Spontaneous
- 3 = To Voice
- 2 = To Pain
- 1 = None
Verbal Response (V)
- 5 = Normal Conversation
- 4 = Disoriented Conversation
- 3 = Words, But Not Coherent
- 2= No Words, Only Sounds
- 1 = None
Motor Response (M)
- 6 = Normal
- 5 = Localized To Pain
- 4= Withdraws To Pain
- 3 = Decorticate Posture (An Abnormal Posture That Can Include Rigidity, Clenched Fists, Legs Held Straight Out, And Arms Bent Inward Toward The Body With The Wrists And Fingers Bend And Held On The Chest)
- 2 = Decerebrate (An Abnormal Posture That Can Include Rigidity, Arms And Legs Held Straight Out, Toes Pointed Downward, Head And Neck Arched Backwards)
- 1 = None
Clinicians use this scale to rate the best eye opening response, the best verbal response, and the best motor response an individual makes. The final GCS score or grade is the sum of these numbers.
Using the Glasgow Coma Scale
Every brain injury is different, but generally, brain injury is classified as:
- Severe: GCS 3-8 (You cannot score lower than a 3.)
- Moderate: GCS 9-12
- Mild: GCS 13-15
Mild brain injuries can result in temporary or permanent neurological symptoms and a neuro- imaging tests such as CT scan or MRI may or may not show evidence of any damage.
Moderate and severe brain injuries often result in long-term impairments in cognition (thinking skills), physical skills, and/or emotional/behavioral functioning.
Limitations of the Glasgow Coma Scale
Factors like drug use, alcohol intoxication, shock, or low blood oxygen can alter a patient’s level of consciousness. These factors could lead to an inaccurate score on the GCS.
Children and the Glasgow Coma Scale
The GCS is usually not used with younger children, especially those too young to have reliable language skills. The Pediatric Glasgow Coma Scale, or PGCS, a modification of the scale used on adults, is used instead. The PGCS still uses the three tests-eye, verbal, and motor responses – and the three values are considered separately as well as together.
Here is the slightly altered grading scale for the PGCS:
Eye Opening (E)
- 4 = Spontaneous
- 3 = To Voice
- 2= To Pain
- 1 = None
Verbal Response (V)
- 5= Smiles, Oriented To Sounds, Follows Objects, Interacts
- 4 = Cries But Consolable, Inappropriate Interactions
- 3 = Inconsistently Inconsolable, Moaning
- 2= Inconsolable, Agitated
- 1 = None
Motor Response (M)
- 6 = Moves Spontaneously Or Purposefully
- 5 = Withdraws From Touch
- 4 = Withdraws To Pain
- 3 = Decorticate Posture (An Abnormal Posture That Can Include Rigidity, Clenched Fists, Legs Held Straight Out, And Arms Bent Inward Toward The Body With The Wrists And Fingers Bend And Held On The Chest)
- 2 = Decerebrate (An Abnormal Posture That Can Include Rigidity, Arms And Legs Held Straight Out, Toes Pointed Downward, Head And Neck Arched Backwards)
- 1 = None
Pediatric brain injuries are classified by severity using the same scoring levels as adults, i.e. 3-8 reflecting the most severe, 9-12 being a moderate injury and 13-15 indicating a mild TBI. As in adults, moderate and severe injuries often result in significant long-term impairments.
NOTE
✓ While score 15: a patient whom level of consciousness is normal (maximum).
✓ While score 3: a patient who is in deep coma (minimum)
Stage-1: fully conscious and oriented:
- Conscious & oriented in place and person but not time.
- Conscious & oriented in person but disoriented in time and place.
- Conscious but disoriented in time, place and person
Stage-2: Maximum motor response to minimum sensory stimuli.
Stage-3: Minimum motor response to maximum sensory stimuliai
Stage-4: No response
