Types of Education – Behavioral sciences explore the cognitive processes within organisms and the behavioral interactions between organisms in the natural world. It involves the systematic analysis and investigation of human and animal behavior through the study of the past, controlled and naturalistic observation of the present and disciplined scientific experimentation and modeling.
It attempts to accomplish legitimate, objective conclusions through rigorous formulations and observation. Generally, behavior science deals primarily with human action and often seeks to generalize about human behavior as it relates to society.
Types of Education
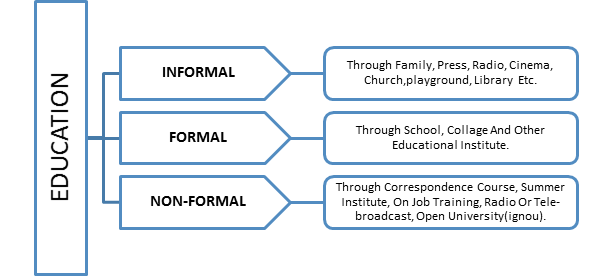
There are mainly three types of education
1. Formal education
2. Non-formal education and
3. Informal education
A. Formal Education
Formal education typically provided by an education or training institution, structured (in terms of objectives, learning time or learning support) and leading to certification. Formal learning is intentional from the learners’ perspective.
Formal education occurs when a teacher has the authority to determine that people designated as requiring knowledge effectively learn a curriculum taken from a pre-established body of knowledge…whether in the form of age-graded and bureaucratic modern school systems or elders initiating youths into traditional bodies of knowledge.

B. Informal education
Informal Education is a general term for education outside of a standard school setting. Informal Education is the wise, respectful and spontaneous process of cultivating learning. It works through conversation, and the exploration and enlargement of experience. For Example, Informal education has activities with children, young people and adults. Sometimes there is a clear objective link to some broader plan – example around the development of reading. It can refer to various forms of alternative education, such as:
- Un-schooling or homeschooling
- Auto-didacticism (Self-teaching)
- Youth work
Informal education consists of accidental, unclear, quantitative information. It usually has a quantitative aspect then a qualitative one. Informal education exceeds formal education in content and knowledge
It is the truly lifelong process whereby every individual acquires attitudes, values, skills and knowledge from daily experience and the educative influences and resources in his or her environment – from family and neighbors, from work and play, from the market place, the library and the mass media.

C. Non formal education
Non-formal education is a loosely defined term that refers to schooling that takes place outside the formal education system. Non-formal education includes programs that do not have or provide formal certification or curriculum, but have more structure than informal learning, which refers to learning absorbed from daily experience. Four characteristics came be associated with non-formal education:
- Relevance to the needs of disadvantaged groups.
- Concern with specific categories of person.
- A focus on clearly defined purposes.
- Flexibility in organization and methods.
Difference between Formal & Non Formal Education
| Features | Formal education | Non formal education |
| 1. Type of education | General | Specific |
| 2. Duration | Long term | Short term |
| 3. Based on | Academic | Practical |
| 4. Knowledge delivered by | Institutions | Environment or community |
| 5. Certificate system | yes | no |
| 6. Controlled by | External or other one | Governed by self |
| 7. Delivery system | Teacher Centre training | Student Centre training |
| 8. Example | B.sc nursing course, MBBS, | Training on breast feeding |
Purposes/Importance of Education:
- To gain knowledge and skills.
- To develop the quality of a person
- Develop of individual self-confidence.
- Develop of desirable behavior
- Develop of individual intellectually
- Development of desirable behaviors.
- Proper socialization of people.
- Help the people to a responsible citizen.
- It ensures people contribution in civilization.
- Helps person to become economically self-sufficient.
- Raise awareness among people about their rights.
- Preserve culture and house born
- To develop the innate qualities of person to make him/her holistic person who is emotionally, socially and spiritually balanced and can live in harmony with the total existence.
- To live better, serve better, better adjustment of the society in adequate the hanging in the situation.
Characteristics of Education
- Education is a fundamental process of life.
- It is a continuous process it effects all modes of behavior.
- Education is change in response or behavior, may be favorable or unfavorable.
- It is a process of change not a product in the form of changed behaviour.
- Education takes place when an organism reacts in a situation.
- Education is universal
- Education is total reaction of the individual to the total situation.
- Education is transferable.
- Education is a process and not a product.
- The process of education is determined by conscious as well as unconscious experiences.
Process of Education
The education process is systematic, sequential, logical, scientifically based, planned course of action consisting of two major interdependent operations, teaching and learning. The education process consists of the basic elements of assessment, planning, implementation and evaluation.
A. Assessment: Ascertain learning needs, readiness to learn, and learning styles.
B. Planning: Develop teaching plan based on mutually predetermined behavioral outcomes to meet individual needs.
C. Implementation: Perform the act of teaching using specific instructional methods and tools.
D. Evaluation: Determine behavior changes (outcomes) in knowledge, attitudes and skills.