Definition of Helminthes – Basic microbiology, parasitology, and immunology; nature, reproduction, growth, and transmission of common microorganisms and parasites in Bangladesh; prevention including universal precaution and immunization, control, sterilization, and disinfection; and specimen collections and examination. Students will have an understanding of common organisms and parasites caused human diseases and acquire knowledge about the prevention and control of those organisms.
Definition of Helminthes
The helminthes are multicellular, bilaterally symmetrical animals having three germ, layers (triploblastic metazoa).
Common Helminthes in Our Country:
1. Ascaris lumbricoides (round worm)
2. Ankylostoma duodenale (hook worm)
3. Enterobius vermicularis (pin worm)
4. Trichuris trichuria (whip worm)
5. Taenia saginata (tape worm)
Soil Transmitted Helminthes:
A. Ascariasis (round worm disease)
a) Mode of transmission:
1. By faecal oral route by ingestion of food and drinks contaminated with eggs such as salad, vegetables, polluted water readily convey the infection.
2. Other methods are: Contaminated fingers, eating contaminated soil, contaminated dust.
b) Complications:
1. Breathlessness
2. Intestinal obstruction
3. Cholestasis, extra hepatic
4. Acute Pancreatitis
5. Short stature
c) Prevention:
1. Primary prevention
- Sanitary disposal of faeces
- Provision of safe drinking water
- Food hygiene habits
- Health education of community regarding: Use of sanitary latrines, personal hygiene, and changing behavioural patterns.
2. Secondary prevention:
- Albendazole: 400mg all ages above 2 years, Single dose
- Mebendazole: 500 mg single dose or 100 mg twice daily for 3 days.
B. Ankylostomiasis (hook worm disease)
1. Mode of transmission: Penetration of skin (usually feet) by infective larvae and direct ingestion of infective larvae through contaminated fruits and vegetables,
2. Complication
- Anemia
- Severe protein loss with fluid up in the tissues.
- Other nutritional deficiency
3. Prevention and control:
- Sanitary disposal of faeces – Installing sewage disposal system in urban areas and low cost sanitary latrine in rural areas.
- Anti-helminthic therapy: Periodic case finding and treatment, periodic campaigning of
anti-helminthic prophylaxis. - Anemia correction
- Awareness through health education and improvement of socioeconomic condition.
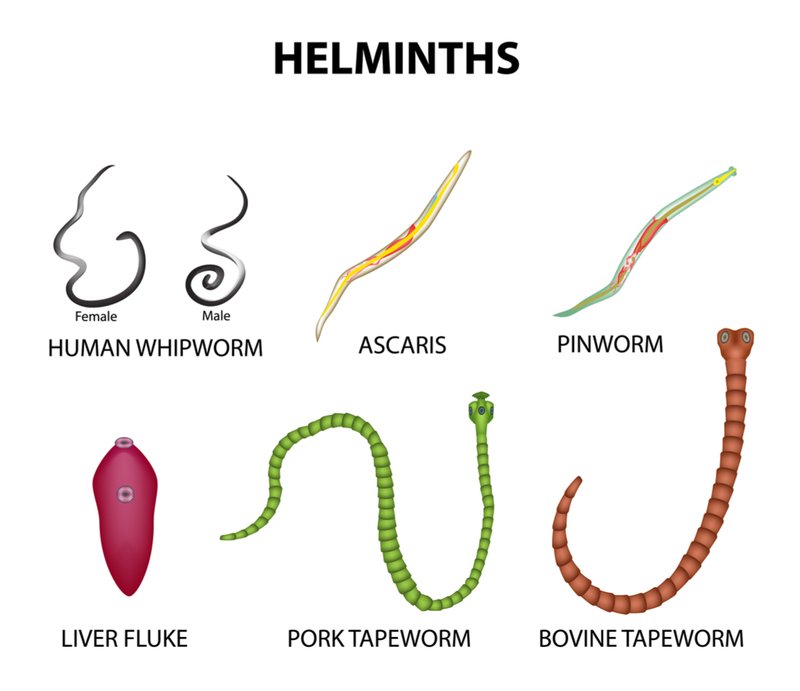
Common Helminthes Found in Intestine:
➤ Cestodes:
- Taenia saginta
- Hymenolepis nana
- T. solium
➤ Nematode:
- A. lumbricoides
- A. duodenale
- E. vermicularis
- T. trichiura
➤ Trematodes:
- Fasciolopsis buski
- Gastrodiscoids hominis
Types of Helminths:
Outline of Diagnosis of Helminthic Diseases:
Principle: Diagnosis of helminthic diseases is based on demonstration of ova cor larva by microscopic examination. Nonspecific serological test is also helpful.
Steps:
➤ Specimen:
- Stool
- Rectal contents
- Perianal swab
➤ Microscopic examination:
- Ova: of Ascaris lumbricoides, Ankylostoma duodenale, Necator americana
- Larva: of S. stercoralis.
➤ Physical examination:
- Adult worm-is. E. vermicular and A. lumbricoides
- Proglotides– T. saginata
- Larva-S. stercoralis
➤ Others
- Occult blood test
- Examination of blood – Hb%, TC, DC of blood.