Theories Contributing To Modern Biology – Introduction to fundamental concepts of Biological Science including the organization and common characteristics of living matters, cell structures and functions, food production by photosynthesis, harvesting energy, mechanism of cells reproduction, genetics, evolutions, and Human Biology. Introduction to general chemistry including basic concepts about matter, atomic structure, chemical bonds, gases, liquid, and solids, solutions, chemical reactions, acid, bases, and salt;
organic and biochemistry including hydrocarbons and their derivatives, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, nucleic acids; principles of physics and applications to nursing including gravity and mechanics, pressure, heat and electricity; nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, effects of radiation on human beings, and protection and disposal. The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills in general biological science, general chemistry and physics.
Theories Contributing To Modern Biology
Modern biology is based on several great ideas, or theories:
1. The Cell Theory
2. Gene Theory
3. Homeostasis
4. The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection

The Cell Theory
The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of all organisms. The Cell Theory states that all living things are made of one or more cells, or the secretions of those cells. For example, shell and bone are built by cells from substances that they secrete into their surroundings. Cells come from cells that already exist, that is, they do not suddenly appear from nowhere. In organisms that are made of many cells (called multicellular organisms), every cell in the organism’s body derives from the single cell that results from a fertilized egg.

Gene Theory
An organism’s traits are encoded in their DNA, the large molecule, or macromolecule that holds the instructions needed to build cells and organisms. DNA makes up the genes of an organism. Traits are passed on from one generation to the next by way of these genes. Information for how the organism appears and how its cells work come from the organism’s genes.
Although the appearance and cell function of the organism may change due to the organism’s environment, the environment does not change its genes. The only way that genes can change in response to a particular environment is through the process of evolution in populations of organisms.

Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the ability of an organism to control its body functions in order to uphold a stable internal environment even when it’s external environment changes. All living organisms perform homeostasis. For example, cells maintain a stable internal acidity (pH); and warm- blooded animals maintain a constant body temperature.
Homeostasis is a term that is also used when talking about the environment. For example, the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide on Earth has been regulated by the concentration of plant life on Earth, because plants remove more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during the daylight hours than they emit to the atmosphere at night.
Evolution
Evolution by natural selection, is the theory that maintains that a population’s inherited traits change over time, and that all known organisms have a common origin. This theory, initially described by Charles Darwin, describes why organisms must adapt to their environments
Factors of Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution
The factors that contribute to the change in allele frequency of a population are as follows:
Genetic Recombination
Recombination is a process where new combinations of alleles are formed. The genetic recombination occurs during sexual reproduction at the time of gamete formation. There occurs an exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids during meiosis that is called crossing over. It leads to recombination and is one of the causes of genetic variability present within a population.
Mutation
Mutations are the sudden inheritable changes that occur in the gene and have a certain phenotypic effect. Chromosomal mutations may be due to change in the genes or chromosome structure or number, e.g. deletion, inversion, duplication, translocation, aneuploidy, polyploidy, etc.
Mutation produces a variety of changes that may be harmful. Many of the mutant forms of genes are recessive and are expressed only in the homozygous condition. Advantageous mutations may be selected by natural selection and gradual small changes get accumulated over time. These mutations cause variation in a population.
Genetic Drift and Gene Flow
Any change in the gene/allele frequency of a population due to sudden, random changes, is referred to as genetic drift. It occurs due to chance events. Genetic drift is more prominent in a small population. Gene flow is due to the immigration or emigration of individuals from one population to another. If the migration occurs multiple times it leads to gene flow and changes the allele/gene frequency of the populations.
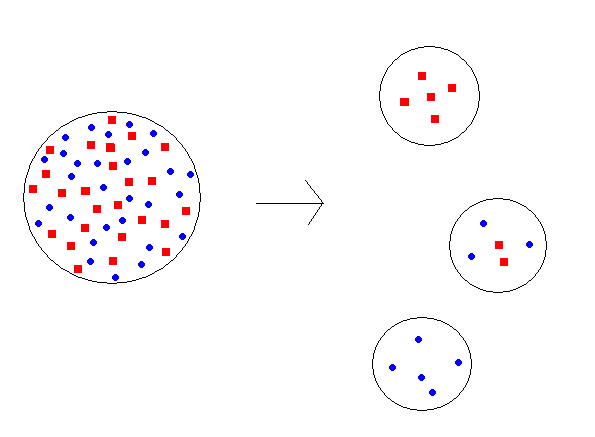
Natural selection
Organisms that are better adapted to the environment are selected by nature. Natural selection produces a change in the frequency of the genes from one generation to the other favouring the differential form of reproduction.

Isolation
It is one of the significant factors responsible for the synthetic theory of evolution. The isolation helps in preventing the interbreeding of related organisms which is a reproductive form of isolation. In addition to these factors, other factors such as hybridization between two species increases the genetic variability of the population.
Read More….