ABO blood group & Rh blood group-The course is designed for the basic understanding of anatomical structures and physiological functions of human body, musculoskeletal system, digestive system, respiratory system; cardiovascular system; urinary system, endocrine system, reproductive system, nervous system, hematologic system, sensory organs, integumentary system, and immune system.The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and skills regarding anatomy and physiology.
ABO blood group & Rh blood group
ABO Blood Group
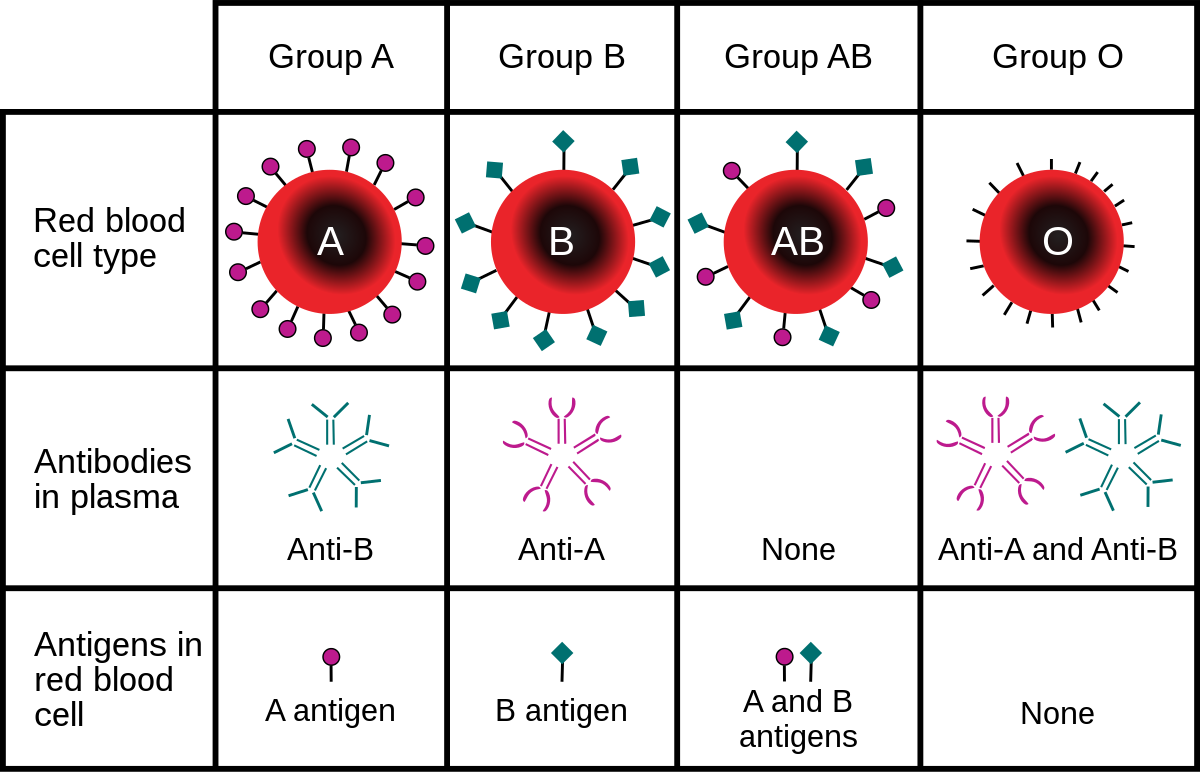
The ABO blood group is based on two antigens called A and B.
- People whose RBCs display only antigen A have type A blood
- Those who have only antigen B are type B
- Individuals who have both A and B antigens are type AB, and
- those who have neither antigen A nor B are type O
In about 80% of the population, soluble antigens of the ABO type appear in saliva and other body fluids, in which case blood type can be identified from a sample of saliva. The incidence of ABO blood types varies among different population groups.
In addition to antigens on RBCs, blood plasma usually contains antibodies or agglutinins that react with the A or B antigens if the two are mixed. These are the anti-A antibody, which reacts with antigen A, and the anti-B antibody, which reacts with antigen B.
The antibodies present in each of the four ABO blood types are also shown in. You do not have antibodies that react with your own antigens, but you do have antibodies for any antigens that your RBCs lack.
For example, if you have type A blood, it means that you have A antigens on the surfaces ofyour RBCs, but anti-B antibodies in your blood plasma. If you had anti-A antibodies in your blood plasma, they would attack your RBCs.

Rh Blood Group
The Rh blood group is so named because the Rh antigen, called Rh factor, was first found in the blood of the rhesus monkey. People whose RBCs have the Rh antigen are designated Rh (Rh positive); those who lack the Rh antigen are designated Rh (Rh negative).
The percentages of Rh “and Rh individuals in various populations. Under normal circumstances, plasma does not contain anti-Rh antibodies. If an Rh person receives an Rh blood transfusion, however, the immune system starts to make anti- Rh antibodies that do remain in the blood.
Following is a summary of ABO blood group interactions:
| Blood type | A | B | AB | O |
| Compatible donor blood types (no hemolysis) | A, O | B, O | A, B, AB, O | O |
| Incompatible donor blood types (hemolysis) | B. AB | A, AB | – | A, B, AB |
Agglutination
Agglutination (clumping) of red blood cells occurs when cells with A-type antigens are mixed with anti-A antibodies and when cells with B-type antigens are mixed with anti-B antibodies. No agglutination would occur with type O blood (not shown).
(Ref:-J. TORTORA, The essentials of anatomy and physiology, 8″ edition-P-369, 370)
Read more:
