Abruptio placenta – This course is designed to understand the care of pregnant women and newborn: antenatal, intra-natal and postnatal; breast feeding, family planning, newborn care and ethical issues, The aim of the course is to acquire knowledge and develop competencies regarding midwifery, complicated labour and newborn care including family planning.
Abruptio placenta
Definition of Abruptio Placenta
It is one form of APH where the bleeding occurs due to premature separation of normally situated placenta.
Or
Placental abruption (also known as abruptio placenta) is a complication of pregnancy, wherein the placental lining has separated from the uterus of the mother prior to delivery. It is the most common pathological cause of late pregnancy bleeding.
Types of Abruptio Placenta
A. It is most commonly classified depending on the nature of bleeding into two types:
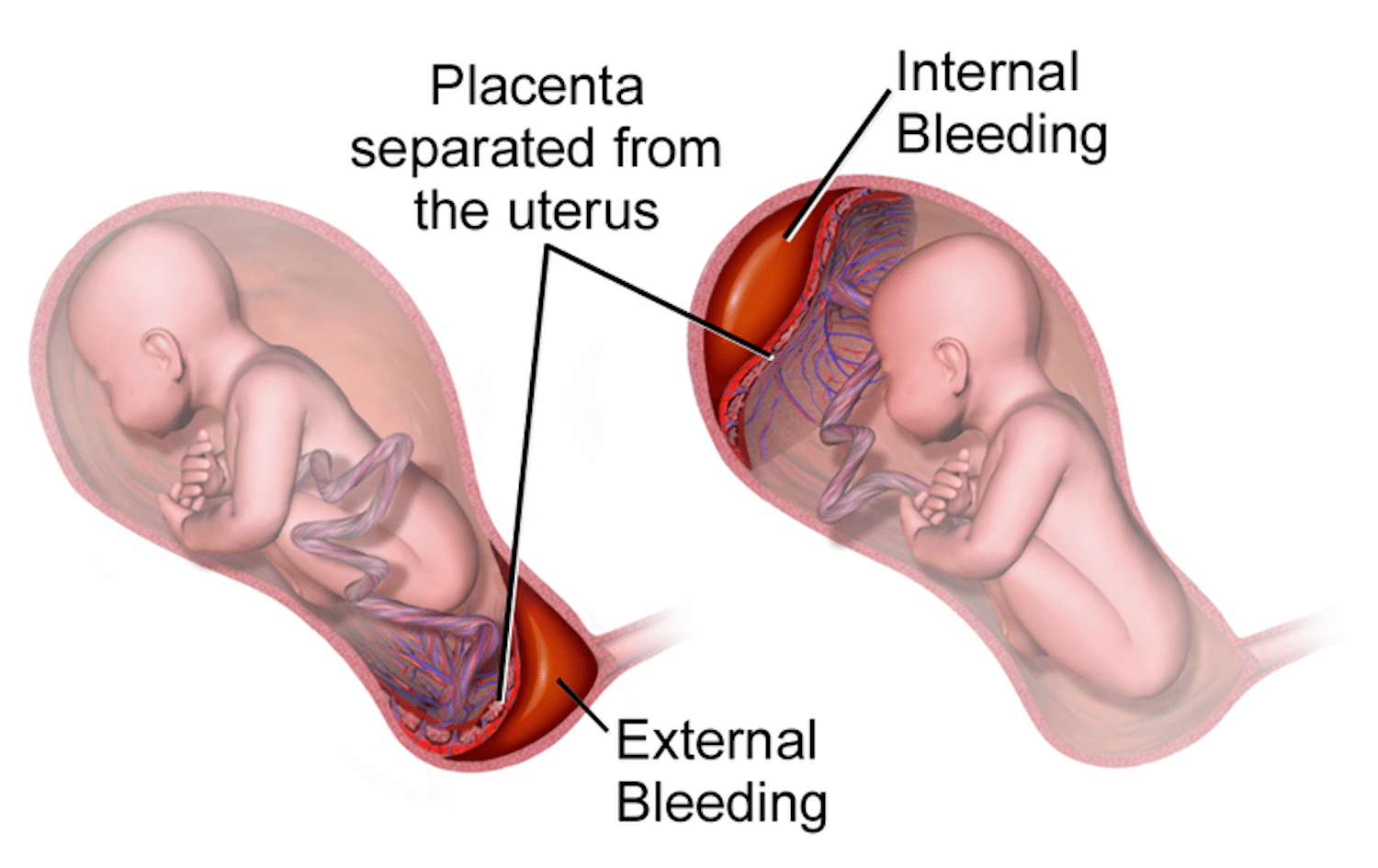
2. Revealed/Visible Placental Abruptio: Causes vaginal bleeding (external or overt bleeding) that helps with early detection of the complication. Around 80% of the total cases lead to external bleeding.
3. Concealed Placental Abruptio (Internal Placental Abruption): Sometimes, there is no vaginal bleeding as the blood gets trapped, pooling behind the placenta. It can only be be detected only through an ultrasound.
B. Classification according to severity:
1. Grade 0: Asymptomatic in nature, usually diagnosed by examining the placenta after delivery
2. Grade 1: Characterized by vaginal bleeding, accompanied by mild uterine tenderness and tetany in the mother; however, there is no maternal or fetal distress.
3. Grade 2: Characterized by various symptoms in the mother; however, does not cause maternal shock. Some evidence of fetal distress may be found by fetal heart rate assessment.
4. Grade 3: Causes severe bleeding (concealed or revealed), which may lead to fatal complications of maternal shock and even fetal death.
Causes/Etiology of Abruptio Placenta
The etiology is unknown, but there are some factors –
1. Preeclampsia
2. Multiparity, advancing maternal age, poor socioeconomic condition, malnutrition, anemia
3. Multiple pregnancies
4. IUGR
5. Abruption on previous pregnancy
6. Trauma from external cephalic version or direct blow
7. Sudden uterine decompression
8. Uterine over distention
9. Fibroid uterus
10. Folic acid deficiency
11. Smoking
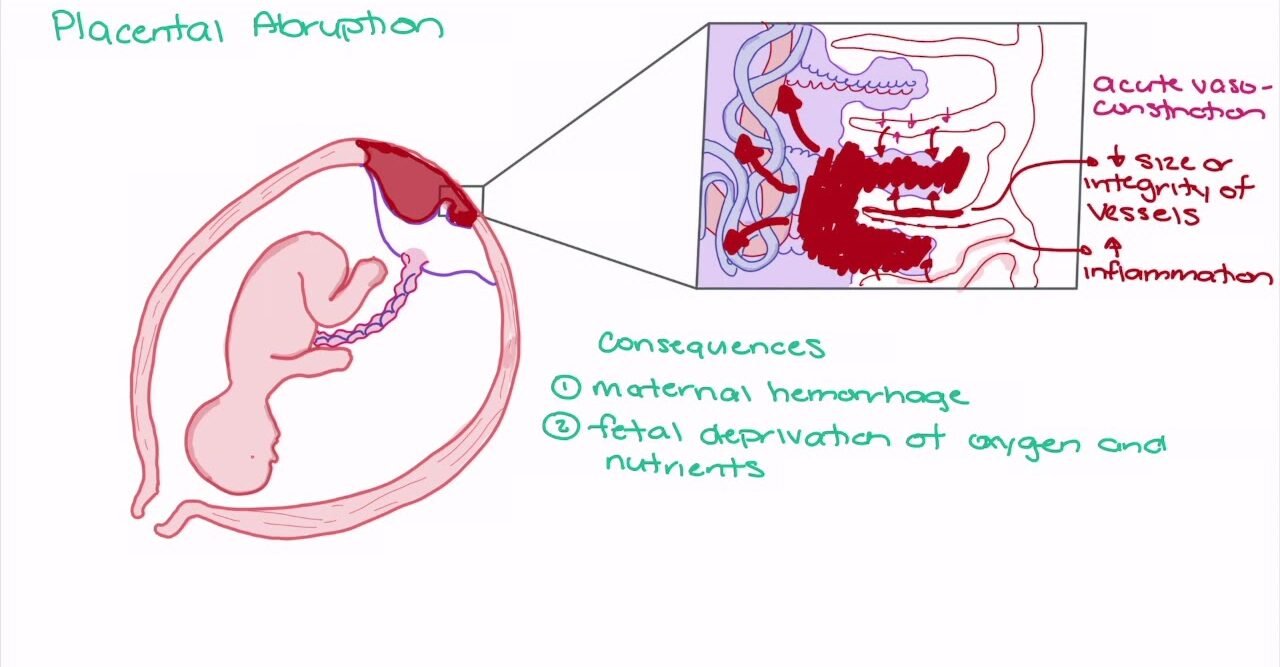
Management of Abruptio Placenta
Clinical features:
A. Symptoms:
1. Bleeding per-vagina (revealed or mixed type)
2. Abdominal pain
3. There may be nausea and vomiting
4. There may be history of preeclampsia
B. Signs:
1. Pallor, features of shock and general condition is proportional to the visible blood loss or out of proportion.
2. Vaginal bleeding in revealed type
3. Height of uterus:
- More than gestational period
- Normal in revealed type
4. Fetal parts cannot be demonstrated
5. Fetal heart sound usually absent in concealed type
6. Per vaginal inspection reveals –
- Continuous dark colored bleeding (revealed type)
- No bleeding (concealed type)
Investigation
1. USG of the uterus
2. Blood for Bb%, blood grouping and Rh typing
3. Urine for RME
4. To exclude DIC: Clotting time, Fibrinogen level, Fibrin degradation product
Management
A. General Rx:
1. Hospitalization
2. Wide bore IV channel is opened
3. Blood is sent for grouping and cross matching
4. IV fluid Hartman solution
5. If available blood transfusion
6. Analgesics
7. Catheterization
8. Careful monitoring
B. Obstetrical Rx: Termination of pregnancy
1. If point are favorable termination of pregnancy by ARM sometimes followed by oxitocin drip
If point are not favorable – Termination of pregnancy by C/S and
- No response to conservative Rx
- Oliguria
- Falling of fibrinogen level
2. 5 point is:
- Presentation Normal
- Baby size Average
- Liquor Adequate
- Cervix-Dilated
- Pelvis Adequate
Difference between Placenta Praevia and Abruptio Placenta
| Points | Placenta praevia | Abruptio placenta |
| Clinical features | ||
| 1. Nature of bleeding | Painless, apparently causeless and E recurrent Bleeding is always revealed | Painful, continuous bleeding Reveled, concealed or usually mixed |
| 2. Character of blood | Bright red | Dark colored |
| 3. General condition and anemia | Proportionate to visible blood loss C | Out of proportion to the visible blood loss in concealed or mixed variety |
| 4. Features of preeclampsia | Not relevant | Present in one third cases |
| Abdominal examination | ||
| 5. Height of uterus | Proportionate height | May be disproportionately enlarged in concealed type |
| 6. Feel of uterus | Soft and relaxed | May be tense, tender and rigid |
| 7. Mal- presentation | Mal-presentation is common. The head is height floating | Unrelated, the head may be engaged |
| 8. Fetal hart sound | Usually present | Upper segment |
| Placentography | ||
| 9. Placenta | Lower segment | Upper segment |
| Vaginal examination | ||
| 10. Placenta is felt | On the lower segment | Not felt on the lower segment |
