Acute and chronic illness – Health of the children has been considered as the vital importance to all societies because children are the basic resource for the future of humankind. Nursing care of children is concerned for both the health of the children and for the illnesses that affect their growth and development. The increasing complexity of medical and nursing science has created a need for special area of child care, i.e. pediatric nursing.
Pediatric nursing is the specialized area of nursing practice concerning the care of children during wellness and illness. It includes preventive, promotive, curative and rehabilitative care of children. It emphasizes on all round development of body, mind and spirit of the growing individual. Thus, pediatric nursing involves in giving assistance, care and support to the growing and developing children to achieve their individual potential for functioning with fullest capacity.
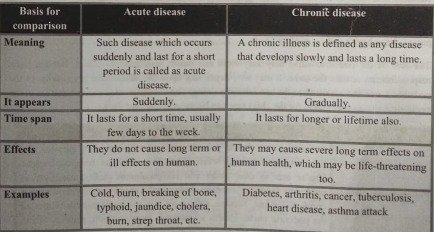
Acute and chronic illness

Definition of Acute Illness:de
A disease or disorder that lasts a short time, comes on rapidly, and is accompanied by distinct sy mptoms.
Or
Disease which occurs suddenly and last for a short period is called as acute disease/ illness. Two common examples are colds and the flu.
Characteristics /Nature of Acute Illness:
An acute illness has the following characteristics:
- Onset is usually abrupt and from a single cause
- Develops quickly and worsens rapidly, such as an infection, trauma or injury
- Usually isolated to one bodily area
- Can be diagnosed and responds to treatment
- Acute pain stops when the illness is healed
- May heal by itself or can be treated and returned to normal within a few days or up to three months
- If it lasts longer than three months, it may be the start of a chronic illness
Examples/Types of Acute Illnesses
1. Common short-term infections such as-
- Colds,
- Flu,
- Strep throat,
- Acute sinusitis,
- Ear infection and
- Bladder infection
2. More severe diseases such as-
- Pneumonia (severe lung infection),
- Acute bronchitis (infection of airways to the lungs),
- Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (viral infection resulting in inflammation of the brain or spinal column),
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (severe condition of lung failure), and
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia (a rapid-growing cancer that starts in the bone marrow)
3. Physical injury such as-
- A cut injury, broken bone, burn or trauma
4. Organ failures such as-
- A heart attack or acute kidney failure
Definition of Chronic Illness:
A chronic illness is defined as any disease that develops slowly and lasts a long time. Examples of common chronic illnesses are diabetes, arthritis, congestive heart failure, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke.
Or
A chronic condition is a human health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long- lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term chronic is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months.

Characteristics/Nature of Chronic Illness:
The following are generally descriptive of chronic illnesses:
- Onset is commonly gradual
- Duration is lengthy and indefinite
- Cause is usually multiple and can be a combination of genetic and environmental factors
- Diagnosis is often uncertain; getting an accurate diagnosis can be a long, difficult process
- There is no cure and requires management over time
Examples of Chronic Illnesses
The following are some common chronic diseases:
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Arthritis
- Cancer
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Cerebrovascular disease
- Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
- Cystic fibrosis
- Diabetes
- Epilepsy
- Heart disease
- Hereditary Hemochromatosis
- Hypertension
- Kidney disease
- Liver disease
- Osteoporosis
- Renal disease
- Sickle-cell disease
Difference between Acute Illness & Chronic Illness