All About Candidiasis (Thrush) – Basic microbiology, parasitology, and immunology; nature, reproduction, growth, and transmission of common microorganisms and parasites in Bangladesh; prevention including universal precaution and immunization, control, sterilization, and disinfection; and specimen collections and examination. Students will have an understanding of common organisms and parasites caused human diseases and acquire knowledge about the prevention and control of those organisms.
All About Candidiasis (Thrush)
Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by a yeast (a type of fungus) called Candida. Some species of Candida can cause infection in people; the most common is Candida albicans
Clinical Features:
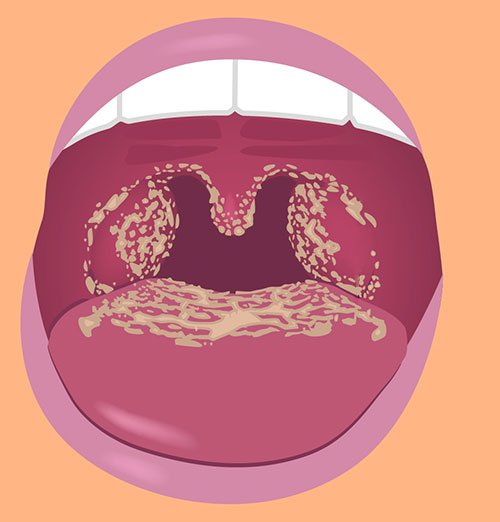
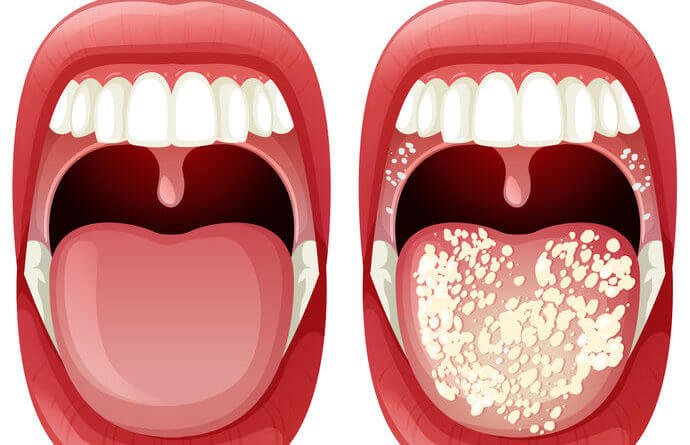
A. Oral Candidiasis (Thrush): a yeast infection of the mouth or throat area is called thrush. Healthy adults do not usually get thrush. It is most often seen in:
➤ Creamy white (curd – like) patches in the mouth or on the throat
➤ Redness or discomfort in the mouth area
➤ Sore throat and difficulty swallowing
➤ Cracking at corners of the mouth where lips meet
➤ Painful cracks at the corners of the mouth
B. Yeast Infection of the Genitals: Vaginal yeast infections are common in women. Common symptoms include:
➤ Extreme itching in the vaginal area
➤ Soreness and redness in the vaginal area
➤ White, clumpy vaginal discharge that look like cottage cheese
➤ Painful intercourse. But men can get a yeast infection, too. This is more likely in men who are not circumcised.
➤ Red rash on penis
➤ Itching or burning on the tip of the penis
C. Skin Infection: skin rashes, patches, and blisters found most commonly in the groin, between fingers and toes, and under the breasts. Diffuse papulae erythematous rash with pin point satellite lesion around edges of affected area.
Nursing Interventions/Management of Candidiasis:
➤ Observe standard precautions.
➤ Provide a non-irritating mouthwash to loosen tenacious secretions and a soft toothbrush to avoid irritation.
➤ Relieve mouth discomfort with a topical anesthetic, such as lidocaine at least 1 hour before meals.
➤ Apply cornstarch, nystatin powder, or dry padding in intertriginous areas of obese patients to prevent irritation and candidal growth.
➤ Record dates of I.V. catheter insertion and replace the catheter according to hospital policy to prevent phlebitis.
➤ Provide appropriate supportive care for patient’s with systemic infections.
➤ Prepare to give blood transfusions if ordered and if the patient has low platelet count.
➤ Frequently check the vital signs of a patient with systemic infection,
➤ If you note a vaginal discharge, document the color and amount.
➤ Carefully monitor intake and output and potassium levels while the patient is receiving medications.
➤ If the patient has renal involvement, carefully monitor blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, and urine
➤ Assess the patient with candidiasis for underlying systemic causes, such as diabetes BOTA SOT mellitus, infection, or immune dysfunction.
➤ Demonstrate comprehensive oral hygiene practices, and have the patient perform a return demonstration.
➤ Recommend that the patient use alkaline mouth care products because increased acidity promotes candidal growth.
➤ Tell the patient who’s using nystatin solution to swish it around in his mouth for several nomn minutes before swallowing.
➤ Suggest a soft diet for the patient with severe dysphagia
Predisposing Factors of Candidiasis:
Any condition which causes immunosuppression is a predisposing factor for candidiasis, e.g.-
- Immunodeficiency diseases: AIDS, malignancy.
- Drug; Broad-spectrum antibiotics, steroid, anticancer drugs, prolonged use of contraceptive pill. Endocrine: Diabetes mellitus
- Physiologic: Pregnancy, extreme age (old age & infancy):
- Traumatic: Bum, maceration.
- Others: Indwelling catheters
Lab. Diagnosis of Candidiasis:
Principle: Diagnosis is based on demonstration of causative agent by microscopic examination, and isolation & identification by culture. Germ- tube test is also helpful.
Steps:
➤ Specimen: Depends upon the site of infection.
- Swabs from surface lesion
- Scrapping from surface lesion
- Sputum
- Exudate
- Vaginal swab (in vaginal candidiasis / moniliasis)
➤ Microscopic examination:
- In case of skin scrapping – Preparation of film by dissolving with 20% КОН.
- In case of other specimens – Wet film preparation with normal saline.
- Findings: Unstained: Yeast and pseudo-hyphae
Gram stain: Gram-positive
➤ Isolation & identification from culture,
- Culture is done in Sabouraud’s dextrose agar media at 37°C for 24-48 hours.
- It can be also cultured in blood agar media
- Findings: Naked eye – cream coloured colony within 48 hours.
✔ Microscopic – Yeast with or without pseudohyphae