All About Measles – Basic microbiology, parasitology, and immunology; nature, reproduction, growth, and transmission of common microorganisms and parasites in Bangladesh; prevention including universal precaution and immunization, control, sterilization, and disinfection; and specimen collections and examination. Students will have an understanding of common organisms and parasites caused human diseases and acquire knowledge about the prevention and control of those organisms.
All About Measles
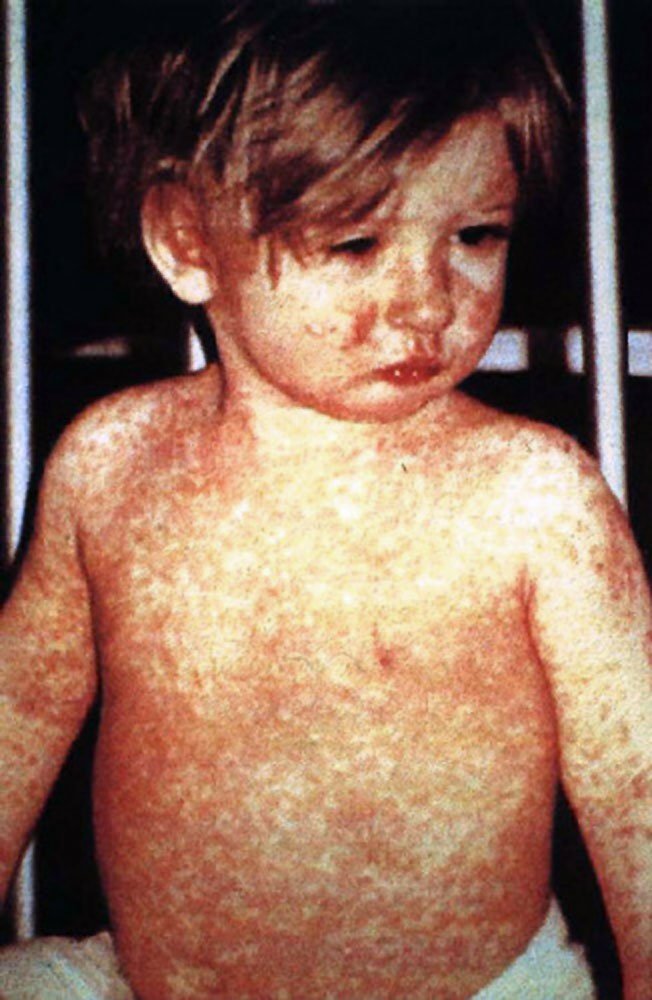
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by the measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10-12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7-10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than 40 °C (104 °F), cough, runny nose, and inflamed eyes. Small white spots known as Koplik’s spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms.
- Disease: This virus causes measles
Clinical Feature of Measles:
- Prodromal phase is characterized by – Fever, conjunctivitis, running nose and coughing.
- Koplik’s spot.
- Maculopapular rash appears on the face and proceeds gradually down the body to lower extremities, including the palms and soles
Pathogenesis of Measles:
➤ Measles virus acquired by inhalation
➤ Primary viraemia: Viruses multiply in lymphoid tissue of respiratory tract and invades blood stream and localize in the reticulo-endothelial system
➤ Secondary viraemia: causes flu like symptoms; high fever, cough and conjunctivitis.
➤ From blood virus localize epithelial surface of skin, respiratory tract, and conjunctiva.
➤ Rash result from interaction of immune T-cells with virus infected cells in the blood vessel.
Complications of Measles:
- Encephalitis
- Primary measles pneumonia
- Secondary bacterial pneumonia
- Secondary bacterial otitis media
- Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE)
- In pregnant woman there is increased risk of still birth
- Fetal death